This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Doctor Dam Thi Quynh - Pediatrician - Pediatric Center - Vinmec Times City International Hospital
Phototherapy is considered as one of the effective, easy to implement and cost effective treatment for neonatal jaundice. However, the treatment effectiveness of this method also depends a lot on: Intensity - wavelength of light emitted by the lamp, the distance from the jaundice lamp to the newborn, how to choose the right projector for jaundice. fit...
1.Characteristics of jaundice in newborns
Jaundice is a yellow tint to the skin and mucous membranes when bilirubin is increased in the blood. Neonatal jaundice is a physiological phenomenon caused by increased destruction of fetal red blood cells, decreased function of metabolic enzymes produced by the liver, and increased enterohepatic cycle. In some cases, when the level of indirect bilirubin is too high in the blood, it can progress to severe jaundice. This complication also depends on many factors such as: preterm or full term gestational age, blood group incompatibility, healthy baby or disease.Physiological jaundice: Approximately 60% of full-term infants and 85 preterm infants have clinically apparent jaundice on the 3rd day of life. Jaundice increases highest from 5-7 days after birth, but not higher than 7-7.5 mg%, then gradually decreases and can last up to 14 days.

Pathological jaundice : Jaundice appears as early as 24 hours after birth, severe jaundice with risk factors, bilirubin level exceeds the threshold for intervention. Early jaundice in the first 48 hours is abnormal, possibly due to hemolysis (Rh incompatibility, ABO blood group, subtype), premature delivery <37 weeks
Jaundice from 3-10 days is more common than other causes may be due to premature delivery (<35-37 weeks), baby with bruising on the skin, serous goiter, polycythemia vera, delayed meconium, dehydration, breastfeeding, Asians, mother's child have a history of diabetes, especially a large fetus
Jaundice lasts > 14 days: If it is due to indirect hyperbilirubinemia, the cause is usually breast milk jaundice, sepsis, hypothyroidism, congenital glucurronyl transferase deficiency born. If jaundice due to direct hyperbilirubinemia is common due to congenital biliary atresia, hepatitis,... Therefore, other investigations related to hepatobiliary disease are needed.
2. Why do babies need to be illuminated?
When the bilirubin level rises too high in the blood (> 22mg%) the child is at risk of nuclei of the brain jaundice. In children at risk such as premature birth, asphyxia, hypoglycemia, brain cell damage, brain edema, this number may be lower.
Bilirubin indirectly causes toxicity to brain cells and destroys neurons by inhibiting intracellular enzymes in some specific regions such as striatum, supraoptic body, hippocampus. In addition, both the brainstem and cerebellum were yellowed without loss and left severe sequelae even though the symptoms of jaundice gradually subsided with or without treatment.
The aim of jaundice treatment is to reduce the concentration of free bilirubin in the blood as quickly as possible, avoiding brain damage caused by too high levels of free bilirubin. So what are the main measures to treat indirect hyperbilirubinemia? There are two basic measures to treat jaundice, which are: Light therapy and blood exchange.
Phototherapy is used for the treatment and prevention of all babies with jaundice. Blood exchange is applied to children with elevated bilirubin levels depending on age and risk factors. Before and after the blood change, still light the child in the most positive way.
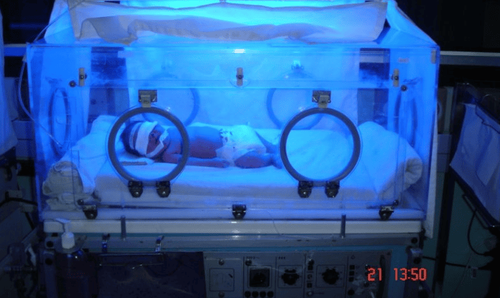
Light therapy (phototherapy) is an inexpensive, effective, safe method that is indicated for all cases of elevated free bilirubin regardless of the cause of the jaundice.
There are 2 types of light used to treat jaundice in children: Blue light and Halogen light. Both types of light have wavelengths of 400 – 480 nm. Under the effect of light of the same wavelength as on the free bilirubin molecules (insoluble in water, soluble in fats and oils, easy to penetrate the skin, mucous membranes and brain, toxic to nerve cells) are converted into Photobilirubin Soluble in water, excreted in bile and urine, non-toxic to nerve cells.
3. What can happen during lighting?
The child is placed in an incubator with a temperature of 28oC, bare, only covering the eyes and genitals, the lamp is 50-60cm away from the child, so that the light shines directly on the child's skin, change position 2-4h / time, continuous exposure for 24 - 48 hours only stop showing when breastfeeding, until the bilirubin is below the indicated depending on the bilirubin level.
When children are exposed to light, their stools are green and their urine is darker, and they often lose water under the light. Therefore, it is necessary to increase the amount of fluid 10-20% compared to the needs of the child.
During irradiation, the child is still continuously monitored Bilirubin index, depending on the child's response to light therapy, the doctor decides to stop the child, continue irradiation or need a blood change.
4. What can happen after the child is exposed to light?
Some of the side effects of phototherapy that may occur to children are darkening of the child's skin, bronzed skin syndrome, diarrhea, burns, dehydration, skin rashes... These side effects will disappear after children stop lighting.
Light irradiation reduces the concentration of free bilirubin in the blood. So, after stopping the lamp, the child's skin is still yellow. Parents need to continue to monitor the child, if the child's jaundice is found, re-examination immediately at the nearest medical facility.

Jaundice due to increased free bilirubin is a common phenomenon in newborns, especially premature babies. Treating jaundice with light therapy is simple, inexpensive, safe, and effective. However, phototherapy must be performed early when no complications of nuclear jaundice have occurred. Therefore, when detecting signs of jaundice in the baby (in the first 6 days after birth), it is necessary to take the baby to a medical facility with neonatal specialists for the most appropriate examination, consultation and treatment.
Pediatrics Department - Vinmec International General Hospital is the address for receiving and examining newborn diseases, including jaundice. At Vinmec, it is equipped with a safe and easy-to-implement lighting system, babies can still breastfeed while under lights, can be combined with 10% Glucose infusion. There are many types of illuminator suitable for each jaundiced object that needs to be illuminated: crib light (child lying directly on top, double lamp with upper and lower projection (used in cases where positive light is required), lamp form blankets, bags wrapped around the young (very convenient for mothers to take care of the baby: just pick it up to breastfeed, light up the light).
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Distinguish between physiological neonatal jaundice and pathological jaundice
MORE:
Neonatal Jaundice What is nuclei of the brain? Distinguish between physiological neonatal jaundice and pathological jaundice