This is an automatically translated article.
In the human body there are about 70 trillion cells, among them there is a special type of cells called epithelial cells. So what are epithelial cells and are epithelial tumors dangerous?
1. What are epithelial cells?
Epithelium is composed of many different layers of cells, lining the outer surface of the body, the inner surface of organs and natural cavities. Epithelial cells are located close to each other, in the middle there are very narrow spaces containing the intercellular fluid. The barrier between the epithelium and the underlying connective tissue is the basement membrane.
The origin of epithelial cells can be from the ectoderm (such as the skin, mucous membranes of the oral cavity, nose, anus ...) or the endoderm (such as the larynx, trachea, bronchi, and alimentary canal mucosa). metabolism, hepatobiliary bladder, etc.). Besides organs, glands in the body are also lined with epithelial cells.
2. Characteristics of epithelial cells
Epithelial cells have the following characteristics:
Diversified origin from ectoderm, endoderm or mesoderm; The epithelium has a very tight structure, consisting of many layers and very little intercellular substance; Inside the cell contains many keratin fibers; Epithelial cells receive nutrients through osmosis from the basement membrane, without blood vessels; Epithelial cells are tissues with the ability to regenerate rapidly and strongly; The epithelial layer has tasks such as protecting the underlying connective tissue, absorbing, secreting, transporting substances ...
3. Types of epithelial cells in the human body
3.1. Covering epithelium
Epithelial lining inside natural organs or cavities in the body, including many different types:
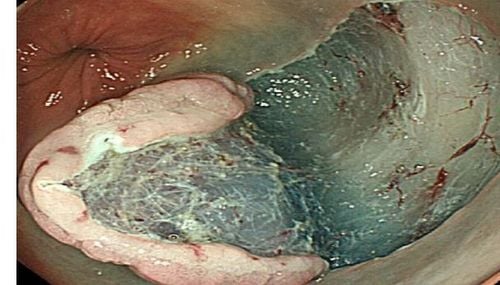
Simple squamous epithelium: The structure is a layer of epithelial cells of many shapes arranged in thin flattened layers. Simple squamous epithelial cells line structures such as the outer leaf of the Bowman capsule of the glomerulus, the ascending loop of Henle of the renal tubule, body membranes such as the peritoneum, lungs, heart, or the inner lining of blood vessels (endothelial layer); Simple square epithelium: Composed of a single layer of square epithelial cells lining the surface of small ducts, terminal bronchioles, thyroid follicles...; Simple columnar epithelium: Consists of columnar epithelial cells, arranged in a single layer. At the peak, these cells can change to contain the mucus of secretory cells or appear microvilli, pseudo-hairs, cilia...; Pseudostratified columnar epithelium with cilia: This type of epithelium lines the respiratory tract. In fact, there is only a single layer of columnar epithelial cells, but the cell nuclei are located at different heights and have reserve cells, so it creates a feeling of layering; Keratinized squamous epithelium: Especially found in the skin. The structure consists of 5 layers from the outside to the inside: the stratum corneum, the ball layer, the granulosa cell layer, the squamous cell layer, and the basement membrane. Non-keratinized squamous epithelium: Consists of many squamous cells arranged in many layers, lining the inner surface of the oral cavity, gastrointestinal tract and vagina; Square stratified epithelium: Consists of many square-shaped epithelial cells arranged in many layers, found in salivary or sweat glands; Urinary epithelium: A particularly recognizable type of epithelium because of its racket-shaped appearance. This type of epithelial cell is found only in the urinary tract. Epithelial neoplasms arising from squamous cells include two types, benign papilloma and squamous cell carcinoma.

Giải đáp tế bào biểu mô là gì?
3.2. glandular epithelium
These are essentially superficial epithelial cells but progress deep into the underlying stroma and transform into glandular epithelium with the function of secreting substances. The structure of the glandular epithelium depends on whether the gland is exocrine or endocrine:
Exocrine gland: Epithelial cells divide into ductal and secretory parts. The ductal epithelium is structurally and functionally intermediate between the mantle and glandular epithelium, so it coats the inside of the ducts but has no secretory capacity. The secretory epithelial cells are essentially cylindrical, pyramidal or polyhedral cells, within the cytoplasm containing secretory granules. Endocrine glands: Endocrine epithelial cells are responsible for secreting hormones with physiological functions into the blood. The glandular epithelium is usually arranged in a reticular, cystic and diffuse pattern; Epithelial tumors arising from adenocarcinomas include benign adenomas and adenocarcinomas.
4. What is an epithelial tumor?
Epithelioma has a different structure from connective tissue tumors, the abnormal cells are close together and arranged in clusters, foci or bands. Epithelial tumor cells are not linked to each other, but between clusters or clusters of cells, there are connective organizations.
Because the epithelial layer has no blood vessels, the nourishment, secretion and transport of substances take place only through basement membrane permeability. After that, most of them are reabsorbed into the blood vessels, a few are reabsorbed through the lymphatic route, so most types of malignant epithelial tumors metastasize through the lymphatic route.
4.1. Benign epithelial tumor
4.1.1. Papilloma
Papilloma is one of the types of benign epithelial tumors of the covering epithelial cells, commonly found in locations such as skin, tongue mucosa, vagina, renal pelvis, ureter, bladder...
U papillae occurs due to excessive hyperplasia of epithelial cells, overgrowth of connective tissue and high protrusion (papillary). There are two types of papillomas, squamous papillomas and mucosal papillomas.

U nhú là một trong các loại u biểu mô lành tính của các tế bào biểu mô phủ
4.1.2. Adenomas
Adenoma is a common, benign epithelial tumor and is similar in structure to normal glands. In fact, there are many masses that are considered adenomas but are in fact foci of compensatory hyperplasia. For example, when a part of liver tissue is damaged, it will stimulate the remaining liver tissue to hyperplasia, creating a new tissue, protruding above the liver surface and being misunderstood as an adenoma.
The structure of an adenoma varies greatly depending on the gland that produces it. The adenoma must have a clear envelope; the microscopic appearance may be similar to that of normal glands. Structures can be tubular adenomas (such as breast, stomach, small intestine, pancreas...) or trabecular, banded (such as liver, adrenal...). The inside is lined with many layers of abnormal epithelial cells, but the glandular shape is completely normal, without destroying the basement membrane or invading the underlying connective tissue.
Gastric and intestinal adenocarcinoma cells often have an elongated stem shape due to the influence of contractile peristalsis. Therefore, this type of epithelial tumor often protrudes inside the gastrointestinal tract like a polyp, so it is also called polypoid adenoma or adenoma.
In particular, despite being benign epithelial tumors, gastrointestinal adenomas still have the ability to become malignant with a rate of about 5-20% in the stomach and 10% in the colon.
A special form of adenocarcinoma is when the cells lining the surface of the ducts enlarge due to secretions and form cysts. Therefore, it is also called a cystadenoma and is most common in the ovaries.
4.2. Malignant carcinoma (carcinoma or epithelioma)
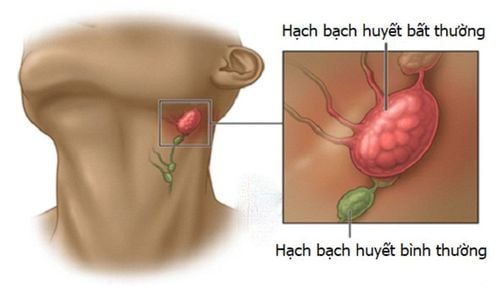
Malignant carcinoma, also known as carcinoma, is characterized by invasion of the lymphatic system and metastasis to the surrounding connective tissues. Malignant carcinoma is more common than sarcoma.
Malignant cells are arranged in an epithelial arrangement, bound in groups or into tubular or vesicle walls. The association is only between groups of cells, not between cells. Malignant carcinoma or carcinoma can spread in the following ways:
Invasion into surrounding connective tissue; Invasion into the lymphatic system; Invasion of nearby lymph nodes or possible metastasis to distant lymph nodes; Metastasis to distant organs via vascular route. The epithelium is composed of many different layers of cells. Epithelial cells are located close to each other, in the middle there are very narrow slits containing intercellular fluid. The barrier between the epithelium and the underlying connective tissue is the basement membrane.
Follow Vinmec International General Hospital website to get more health, nutrition and beauty information to protect the health of yourself and your loved ones in your family.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.