This is an automatically translated article.
Cerebral vascular malformation AVM is a dangerous disease with symptoms such as severe headache, sudden seizures, generalized convulsions... causing a high risk of death for patients.
1. Overview of cerebrovascular malformations
Cerebrovascular malformations account for about 2% of hemorrhagic strokes each year. Cerebral vascular malformation when rupture is very fatal and is common only after cerebral aneurysm disease.
1.1. Classification Cerebral vascular malformations include many forms, mainly abnormalities of blood vessel structures in the brain: Abnormalities of arteries or veins such as:
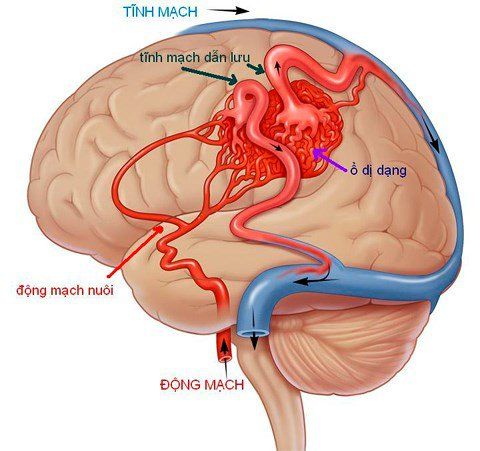
Arteries communicate with veins. Arteries communicate with arteries. Veins communicate with veins. AVMs can occur anywhere, but are most common in the brain, spinal cord, and lungs.
1.2. How it forms Normally, oxygen-rich blood is transported in the body through the arteries (large arteries divide into small arteries) and pushed into the capillaries, where the cells take in oxygen and expel CO2. veins and carry deoxygenated blood out of the tissues.
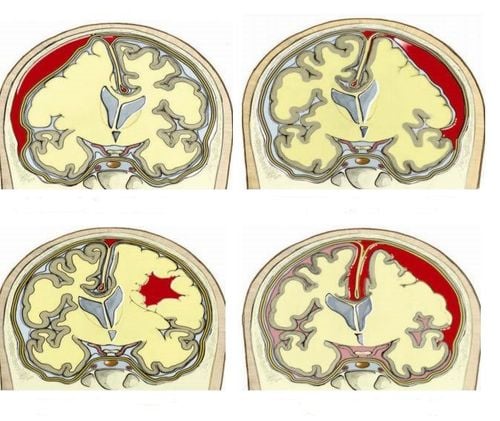
In the normal state, the blood in the arteries belongs to the high pressure system, and when it reaches the vessels, it becomes smaller and smaller, when it reaches the capillaries and veins, the pressure has become significantly lower. For the AVM, the capillary network is absent and instead a group of arteries is directly connected to a group of veins. The vessels of the AVM can become bundled or malformed and cause high systolic pressure. In addition, when brain blood vessels are malformed, they can press on adjacent structures, causing effects on other brain functions. Depending on the location of the malformation, brain function will be affected differently:
Cerebral vascular malformation in the hippocampus: Affects memory. Cerebral vascular malformation in the basal ganglia: Affects mobility. Nerve fiber malformations: Sensory disturbances, causing muscle weakness, paralysis of body parts.
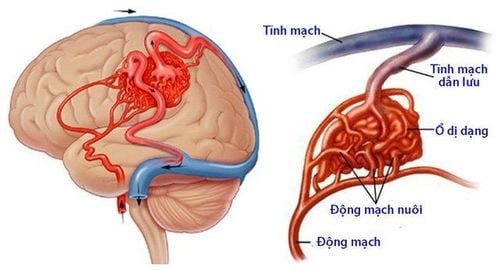
Một nhóm các động mạch được nối trực tiếp với một nhóm tĩnh mạch
1.3. Causes Some opinions suggest that the causes of cerebrovascular malformations include:
Congenital factors. Patients with connective tissue disease. Patients with long-term high blood pressure In which, congenital causes account for the highest rate and usually occurs at 4-8 weeks of pregnancy. Congenital cerebrovascular malformations usually do not present clinical symptoms in early life. The disease is usually only discovered when there is a rupture of the malformation, before the patient may present with severe headache or epileptic seizures.
2. Symptoms to recognize cerebrovascular malformations
Typical signs of cerebrovascular malformation include:
Headache, dizziness (mild symptoms) Blurred vision Severe headache High blood pressure Seizures, convulsions Brain hemorrhage (up to 50%) patients with cerebrovascular malformations will bleed) Stroke Hemiplegia Diarrhea, inability to speak Drowsy consciousness or coma

Các dấu hiệu điển hình của dị dạng mạch máu não là tăng huyết áp và các triệu chứng khác kèm theo
3. Diagnostic measures
Cerebral vascular malformation AVM can be diagnosed and identified through the following steps:
Step 1: Brain magnetic resonance imaging (brain MRI) to detect vascular malformations. Step 2: After detecting signs, further evaluation by taking images of cerebral vascular malformations (Angiogram). Angiogram helps the doctor to have accurate information about the position, shape, and size of the malformed vessel to chart the blood vessel where the malformed blood vessels arise. Cerebral vascular malformation AVM, if not detected and treated, can develop and rupture causing cerebral hemorrhage or subarachnoid hemorrhage, leading to permanent brain damage. In some cases, patients with headaches buy self-medication through speakers, which can be too late, causing unfortunate death. Therefore, early screening for early detection and intervention of AMV cerebrovascular malformation is urgent.
4. Treatment measures
Because of the high risk of complications, AVM is often indicated even when there are no signs. Treatment measures may include:
Use of medication to treat mild symptoms (headache, nausea). Traditional open surgery. Radiosurgery: Using a beam of radiation to target AVM malformations that cause blood vessels to scar or close. Minimally invasive vascular ligation surgery locks the malformed vessel with a variety of materials to block blood flow.

Sử dụng thuốc để điều trị các triệu chứng nhẹ của dị dạng mạch máu não AVM
Overall, the most important goal of AVM treatment is to prevent bleeding from rupture and re-rupture. Because the location of AVM malformation is very diverse, the treatment is also surgical or non-surgical depending on each case.
Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in medical examination and treatment, patients can rest assured to visit. examination and treatment at the Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.