This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by BSCK II Le Nghiem Bao - Deputy Head of General Surgery Department - General Surgery Department, Vinmec International General Hospital Da Nang.Traumatic brain injury is a leading cause of death, especially in industrialized and developing countries. Treatment of traumatic brain injury is quite complicated, requiring expertise, modern equipment and long rehabilitation time.
1. Symptoms of traumatic brain injury
The symptoms of traumatic brain injury in each case are different, depending on the location of the injury, the speed of the impact, the cause of the injury, and the severity. People with mild traumatic brain injury may experience headaches, dizziness, lightheadedness, ringing in the ears, fatigue, mental and emotional disturbances, and memory and concentration problems. In case of more severe traumatic brain injury, the patient may experience severe headache, vomiting, convulsions, loss of consciousness, dilated pupils, coma...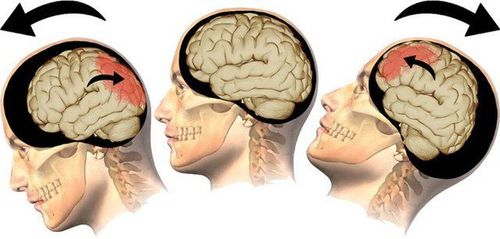
Chấn thương sọ não có thể dẫn đến nhiều di chứng sau này, thậm chí nguy hiểm đến tính mạng
1.1. Primary Injury Primary injury is the symptoms of traumatic brain injury that appear immediately after an impact or accident. These are head and skull injuries at the impact site and inertia-related injuries caused by excessive shaking of the skull.
Symptoms of traumatic brain injury at the site of impact include:
Scalp injury: Scalp tear, bleeding head Injury to skull: Cranial fracture, skull fracture, skull concave, cranial osteomyelitis Injury Injury to the meninges: The broken skull presses into the meninges, causing damage to the meninges, meningeal tears, cerebrospinal fluid, and brain tissue escaping. Damage to blood vessels: Epidural hematoma, lower hematoma dura mater, cerebral hemorrhage, cerebral blood vessel rupture, cerebral infarction Inertia-related damage: brain damage, brain contusion, causing the patient to be in a coma for a long time. 1.2. Secondary injuries Secondary injuries are lesions that do not appear immediately after the head impact but are formed later, including:
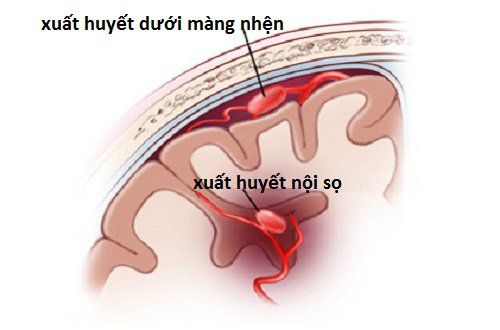
Cerebral edema: In many cases of severe traumatic brain injury, there will be cerebral edema. Cerebral edema is caused by damage to the blood-brain barrier and cell membranes, resulting in abnormal fluid retention in the interstitial and intracellular spaces. The increased brain volume increases intracranial pressure, the blood supply to the brain decreases, causing brain ischemia, brain edema becomes more serious. Intracranial hematoma: Intracranial hematoma is caused by damaged blood vessels when being bumped, causing bleeding in the skull, blood accumulates and occupies a place in the skull, causing increased intracranial pressure, cell damage. Brain. Intracranial hematoma is divided into epidural hematoma and subdural hematoma
Epidural hematoma: bleeding from the fracture line of the skull bone or damaged meningeal blood vessel causing the blood mass to gather between the dura and the bone Blood Subdural hematoma: usually caused by veins in the cerebral cortex, combined with brain tissue contusion to form a hematoma. Subdural hematomas are divided into two types: acute subdural hematoma and chronic subdural hematoma. This condition is very dangerous, threatening the life of the patient. Ventricular dilatation: is a bleeding phenomenon that obstructs the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid. In addition, symptoms of traumatic brain injury also have a few lesions occurring later such as purulent meningitis, intracranial pressure...
1.3. Symptoms of traumatic brain injury in children Traumatic brain injury in children is very dangerous, because the baby's scalp and skull are in the process of developing softer, the effects of traumatic brain injury are also severe. much heavier.
Symptoms of traumatic brain injury in children include:
The child loses consciousness after a fall. The time of unconsciousness lasts more than 1 minute The child is still awake after falling, but after some time there are abnormal manifestations such as: agitation, intense crying, lethargy, sleeping a lot, lethargy, inability to concentrate ... Children vomiting continuously (vomiting more than 5 times) or vomiting for a long time (more than 6 hours) The fontanel is swollen, the fontanel is swollen, the child is pale, weak The child is bleeding at the impact area When the child falls If the child is bumped or has one of the above symptoms, it is necessary to take the child to the hospital immediately so that the doctor can conduct an examination, diagnosis and timely treatment plan.
2. How is traumatic brain injury treated?
Chẩn đoán và điều trị chấn thương sọ não với các thiết bị tiên tiến, máy móc hiện đại tại Vinmec
In case of moderate and severe traumatic brain injury, the following principles of treatment for traumatic brain injury should be applied:
Take the patient to the emergency room as soon as possible so that the doctors can conduct first aid and initial examination. , if the condition is severe, the patient can perform surgery immediately. Control the patient's respiratory status and circulation ability. In case a patient has a hematoma that compresses the brain with symptoms such as pupil dilation, paralysis... it is necessary to conduct surgery immediately, otherwise it will affect the patient's life Exercise and rehabilitation after injury. This process requires a lot of hard work, combined with rest for a long time. Vinmec Da Nang International General Hospital is one of the leading medical facilities for diagnosing and treating traumatic brain injury today:
The hospital is fully equipped with modern medical machines and equipment. The most advanced imaging equipment to support diagnosis and treatment such as: G.E 3.0 MRI (MRI) scanner, Toshiba 640 slices CT SCAN, cerebral angiogram, MRA and CTA... for image quality Clear, easy diagnosis and treatment of brain and spine diseases of both medical and surgical pathology (brain tumor, brain degeneration, white matter degeneration, congenital pathology of brain structure, trauma) brain injury, spinal cord injury, cerebrovascular diseases: aneurysms and cerebrovascular malformations...) Being examined and treated by a team of qualified and experienced medical doctors, especially Dr. II Le Nghiem Bao - Deputy Head of General Surgery Department, Vinmec Da Nang International Hospital. With 30 years of experience in neurosurgery, Dr. Bao used to teach. dumbbell Da Nang Hospital will help the treatment of traumatic brain injury effectively, minimizing the sequelae. Patients are treated and recovered in modern wards, fully equipped with international standards, helping patients feel comfortable, providing maximum support for the treatment process.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.