This is an automatically translated article.
Unlike vitamin A or vitamin B, vitamin K2 is not really popular and not too many people know about it. Vitamin K2 rarely appears in the Western diet and does not receive much attention. However, it is a nutrient that plays an important role in many aspects of human health.
1. Overview of vitamin K
In 1929, vitamin K was first discovered and considered as a nutrient that plays an important role in the blood clotting cascade in the body. The first report was recorded in the German scientific journal as "Koagulationvitamin", which is also the origin of the name vitamin K.
Vitamin K was also discovered by dentist Weston Price, who traveled around the world during the early part of the 20th century to study and research the link between diet and disease in different territories. He realized that in less industrialized countries, people's diets contain an unknown nutrient in relatively high levels, which helps prevent the formation of plaque on teeth and diseases. chronic cause. He calls this mysterious nutrient activating factor X (originally “activator X”), which is what vitamin K2 is today.
Vitamin K is divided into 2 main groups including:
Vitamin K1: Also known as phylloquinone found in plant-based foods such as green leafy vegetables. Vitamin K2: Also known as menaquinone, is common in animal-based foods and fermented foods. Vitamin K2 can be divided into several different groups, the most important of which are MK-4 and MK-7.

Vitamin K có vai trò quan trọng trong dòng thác đông máu trong cơ thể
2. What effect does vitamin K have?
In general, vitamin K is responsible for activating proteins that play a role in blood clotting, calcium metabolism and regulation of the cardiovascular system.
One of the most important functions of vitamin K is to regulate the deposition of calcium ions. In other words, it promotes bone mineralization and prevents calcification in the walls of blood vessels and kidneys.
Some scientists think that the roles of vitamin K1 and vitamin K2 are not the same, and that they should be classified into different nutrients in the body. This view is supported by animal studies showing that vitamin K2 reduces calcification inside blood vessels while vitamin K1 does not. Controlled studies in humans have also observed that vitamin K2 supplements have the potential to improve heart and bone health while vitamin K1 does not. However, more human studies are needed to understand the difference in the effects of vitamin K1 and vitamin K2.
3. Vitamin K's ability to prevent cardiovascular disease
Calcification and calcium deposition in the vessel walls are leading risk factors for many dangerous cardiovascular diseases. Therefore, any agent that can reduce calcium deposition has a role in the prevention of many cardiovascular diseases. Vitamin K works to prevent calcium from being deposited inside the lumen of the arteries. In a study that lasted 7 to 10 years, people who took the highest levels of vitamin K2 had a 52% greater risk of developing calcified arteries and a reduced risk of dying from cardiovascular disease. go 57%. Another study conducted in 16057 women also showed that those whose diets were high in vitamin K2 had a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease. With a daily intake of vitamin K2 at 10 micrograms, the risk of cardiovascular diseases decreased by 9%.
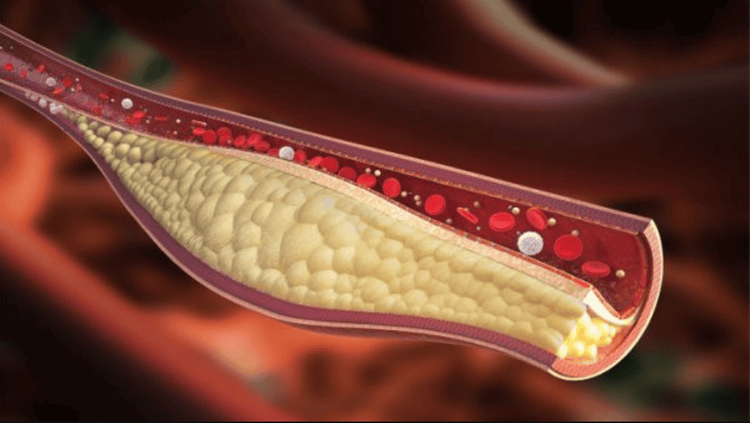
Vitamin K có tác dụng ngăn cản canxi lắng đọng bên trong lòng của động mạch
On the other hand, vitamin K1 had no effect in these studies. However, it should be kept in mind that all of the above studies are observational studies and they cannot prove a cause-and-effect relationship. A small number of controlled studies have been done that have used vitamin K1 but have been largely ineffective. More controlled trials on vitamin K2 and long-term cardiovascular diseases should be done. However, there are currently several highly plausible biological mechanisms for the effectiveness of vitamin K2 and its association with cardiovascular health in observational studies.
4. Vitamin K's ability to improve bone health and reduce the risk of osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a common health problem in many countries around the world, especially in the elderly population. Older women are the most susceptible to osteoporosis and are at increased risk of fractures and other disease burdens.
As mentioned above, vitamin K2 has a central role in the metabolism of calcium, the main micronutrient in human bones and teeth. Vitamin K2 activates the calcium-binding proteins osteocalcin and GLA, which help build bones and maintain strength. In addition, strong evidence from controlled studies also suggests that vitamin K2 provides many benefits for bone health in the body. A three-year study of 244 postmenopausal women found that taking vitamin K2 supplements slowed the aging process of bone mineral density loss. Many long-term studies in Japanese women have found similar benefits to high doses of vitamin K2. Of the 13 studies, only one failed to show an improvement in bone health.
Seven clinical trials observing fractures found that vitamin K2 reduced spine fractures by 60%, hip fractures by 77% and other fractures by 81%.
Besides, vitamin K supplements are also officially recommended for the purpose of preventing and treating osteoporosis in Japan. However, some researchers are not really convinced, as two large observational studies concluded that the evidence for vitamin K supplementation for this purpose is insufficient.

Người dùng bổ sung vitamin K bằng đường uống cần tham khảo ý kiến bác sĩ trước khi dùng
5. The oral health improvement effect of vitamin K
Researchers suggest that vitamin K2 may have an effect on oral health. However, there are no human studies to prove this. Based on numerous animal studies and the role of vitamin K2 in bone metabolism, there is reason to conclude its effect on oral health.
One of the main proteins that regulate oral health is osteocalcin, which is also a protein that plays an important role in bone metabolism and vitamin K2 activation. Osteocalcin activates the mechanism of growth and production of dentin, the calcified tissue layer under the enamel. Vitamin A and vitamin D also play an important role here, working together with vitamin K2.
6. The anti-cancer effect of vitamin K
Cancer is an increasingly common disease in many regions of the world with a high mortality rate. Many new drugs have been discovered to treat cancer, yet the number of new cases continues to increase. Therefore, the discovery of effective cancer prevention measures is of paramount importance.
Many studies have been done to find an association between vitamin K2 and certain types of cancer. Two clinical studies suggest that vitamin K2 reduces the recurrence of liver cancer and prolongs survival. Furthermore, an observational study of 11,000 men found that taking a high vitamin K2 supplement was associated with a reduced risk of prostate cancer while vitamin K1 had no such effect. However, more quality studies are still needed before making conclusions about this effect of vitamin K in general and vitamin K2 in particular.
7. Methods of supplementing vitamin K2 for the body
A variety of foods are rich in vitamin K1 but low in vitamin K2. The human body can partially convert vitamin K1 into vitamin K2. This really helps because the vitamin k1 content in conventional diets is 10 times higher than vitamin K2. However, more recent evidence indicates that this conversion is not really efficient and that the human body needs to get more vitamin K2 directly from its diet. Vitamin K2 is also produced from the intestinal flora in the colon. Some evidence suggests that the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics causes vitamin K2 deficiency.

Người dùng có thể bổ sung vitamin K2 qua chế độ ăn uống hằng ngày
The average content of vitamin K2 is quite low in today's modern diet. Vitamin K2 is mainly found in some meats and fermented foods, which are not selected for regular use. Animal food sources rich in vitamin K2 include high-fat dairy products from cows, egg yolks, and animal liver.
Vitamin K is a fat-soluble compound, which means lean meat or low-fat animal foods don't contain much vitamin K2. Animal foods contain many MK-4 subtypes of vitamin K2 while fermented foods contain many MK-5 to MK-14 subtypes.
If foods rich in vitamin K2 are not readily available, the use of vitamin K2 supplements may be an alternative. The effectiveness of vitamin K2 supplements can be enhanced when combined with vitamin D supplements. Meeting the daily needs of vitamin K2 promises to improve health status for many people, although More research is still needed in the future.
Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in medical examination and treatment, patients can rest assured to visit. examination and treatment at the Hospital.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.
SEE MORE
Prevention of vitamin K deficiency and brain hemorrhage in children Vitamin K deficiency can cause brain hemorrhage in young children Vitamin K3 (Menadione): All you need to know