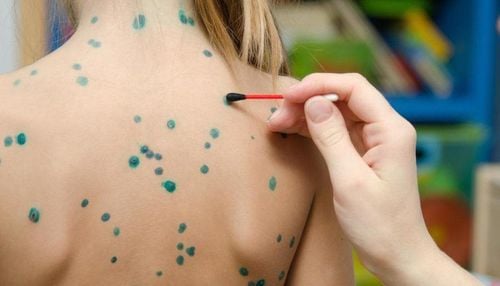
This is an automatically translated article.
Varizig (Varicella Zoster Immune Globulin) is indicated for the post-exposure prophylaxis of varicella in high-risk populations including children, neonates and pregnant women with immunodeficiency.
1. What is Varizig?
Varizig is used to help provide protection (antibodies) against a certain viral infection (varicella zoster) commonly known as chickenpox.
The drug is given to people who have not been vaccinated or previously infected and have recently been in contact with someone infected with chickenpox. This medicine is made from healthy human blood that has high levels of the varicella zoster antibody that helps fight infection.
2. Indications of the drug Varizig
Varizig is Varicella Zoster (human) Immunoglobulin indicated for post-exposure prophylaxis in high-risk individuals. High-risk groups include:
Immunocompromised people, Newborns of mothers who had chickenpox just before or after birth, Premature babies, infants under 1 year of age Adults with no evidence of chickenpox immunity, Pregnant women. Use Varizig to reduce the severity of chickenpox. Use Varizig as soon as possible after exposure to varicella zoster virus (VZV), ideally within 96 hours for maximum effectiveness.
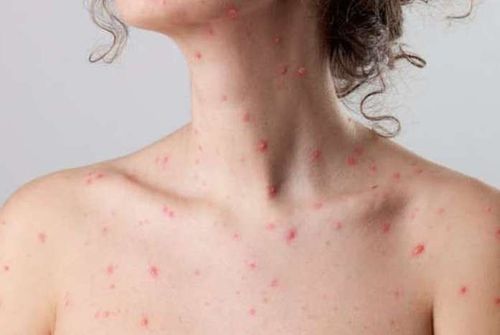
Sử dụng Varizig nhằm giảm mức độ nghiêm trọng của bệnh thủy đậu
3. How to use Varizig
Varizig is usually injected into a muscle by a healthcare professional. Adults and children are usually given the shot in the upper arm, and infants in the upper thigh. Large doses (more than 3ml) should be divided into 2 or more injections and injected at separate injection sites. The dose and schedule of injections depend on your medical condition, weight, and response to treatment. This medicine is given as soon as possible after you come into contact with someone who has chickenpox. If you wait too long after exposure, the medicine may not be as effective. Not all people exposed to this infection should receive varicella zoster immune globulin. Discuss the risks and benefits of taking the medication with your doctor.
4. Side effects of the drug Varizig
The most serious adverse drug reactions observed in clinical trials for all subjects and patients included fever, nausea, chills, and vomiting. The most common adverse drug reactions observed in clinical trials for all subjects and patients were injection site pain, headache, chills, fatigue, rash, and nausea.

Một số phản ứng có hại của thuốc Varizig là đau tại chỗ tiêm, nhức đầu, ớn lạnh, mệt mỏi, phát ban và buồn nôn
5. Be careful when using Varizig
People with IgA deficiency have the potential to develop IgA antibodies and have severe, possibly life-threatening allergic reactions. In patients with severe thrombocytopenia or any coagulopathy, intramuscular injection is contraindicated. Thrombotic events may occur following treatment with Varizig and other immunoglobulin products. Products made from human plasma may carry a risk of transmitting infectious agents, e.g. viruses and theoretically the causative agent of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Tell your doctor about any recent or planned vaccinations. This medicine can prevent the body's good response to certain live virus vaccines (such as measles, mumps, rubella, varicella). If you have recently been given any of these vaccines, your doctor may ask you to test for a reaction or you will get the vaccine again later. If you're planning on getting any of these vaccines, your doctor will tell you the best time to get them so you get a good response. The drug may falsify test results (including certain blood sugar tests, Coomb's test). So make sure laboratory staff and all your doctors know you use this medicine. Keep a list of all the products you use (including prescription/nonprescription drugs and herbal products). Do not stop or change the dose of any medicine without consulting your doctor/pharmacist.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: Webmd.com