This is an automatically translated article.
Vacocholic drugs are prescribed by doctors to effectively treat digestive problems such as cholesterol-rich gallstones, primary biliary cirrhosis,... Patients need to adhere to the treatment schedule with Vacocholic drugs strictly. the doctor's regimen for early improvement of the disease.1. What is Vacocholic?
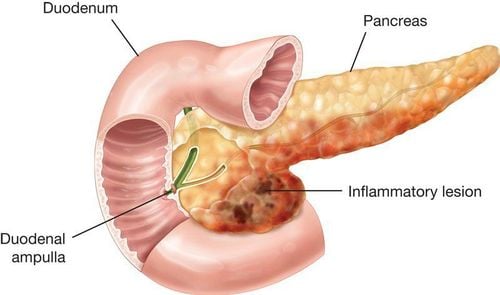
Vacocholic belongs to the group of gastrointestinal drugs, used to effectively reverse conditions such as primary biliary cirrhosis, cholesterol stones in the gallbladder or cystic fibrosis in children. Currently, Vacocholic drugs are manufactured by Vacopharm Pharmaceutical Joint Stock Company - Vietnam in the form of film-coated tablets and packaged in boxes of 3 blisters, 5 blisters, 10 blisters or 100 blisters x 10 tablets. The main active ingredient of Vacocholic is ursodeoxycholic acid 150mg. In addition, each Vacocholic tablet contains other auxiliary excipients, added by the manufacturer to enhance the pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties of the main active ingredient.2. Uses of Vacocholic 150
2.1. What does ursodeoxycholic acid do?
According to research, the component ursodeoxycholic acid in Vacocholic medicine is a natural bile salt and is present in the human body in a negligible amount. Compared with other endogenous bile salts, ursodeoxycholic acid is very hydrophilic but does not carry a detergent effect.In general, ursodeoxycholic acid has an effect on the liver-enteric cycle of endogenous bile acids, helping to promote bile secretion, and at the same time reduce their reabsorption. This effect of ursodeoxycholic acid stems from its ability to inhibit active reabsorption in the intestine, thereby helping to significantly reduce the concentration of endogenous bile acids in the blood.
For cases of cholesterol stones in the gallbladder, ursodeoxycholic acid can be used as an effective treatment. Thanks to its ability to reduce cholesterol reabsorption and help enhance the conversion of cholesterol in the liver into bile acids by increasing the activity of cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxyase enzyme in the liver, ursodeoxycholic acid can promote the effect of reducing blood levels. cholesterol in bile is very effective. Normally, ursodeoxycholic acid is absorbed passively in the small intestine. About 50-60% of ursodeoxycholic acid is first metabolized in the liver and conjugated with taurine and glycine occurs. When taking a dose of 10-15mg/kg body weight/day, ursodeoxycholic acid accounts for about 50-70% of the bile acids circulating inside the body.
Currently, ursodeoxycholic acid salt is mainly used to treat liver disorders, cirrhosis, gallstones, liver abnormalities, liver disease or some other conditions.
2.2. Indications - Contraindications to the use of Vacocholic
Vacocholic is commonly prescribed by doctors to treat the following conditions:Primary biliary cirrhosis. Treatment is aimed at dissolving cholesterol-rich gallstones less than 15mm in diameter, without contrast, and with a functioning gallbladder. Treatment of cystic fibrosis in children from 6 years old - under 18 years old. However, the use of Vacocholic is contraindicated in the following patients:
Patients with a history of allergy or hypersensitivity reaction to ursodeoxycholic acid or any other ingredient in the drug. Do not use Vacocholic for people with liver - intestinal disorders that interfere with the circulation of bile salts in the liver. Vacocholic should not be used in patients with calcified gallstones. Vacocholic is contraindicated in patients with acute cholecystitis/cholangitis. Vacocholic is not recommended for people with bile duct obstruction. Relative contraindications Vacocholic for women who are pregnant or planning to become pregnant.
3. Dosage and effective use of Vacocholic drugs
3.1. The recommended dose of Vacocholic
Vacocholic drug is used according to the doctor's prescription with the following specific dosage:Treatment of cholesterol stones in the gallbladder: Use a dose of 6-12mg/kg body weight/day. Obese patients can take Vacocholic up to a dose of 15mg/kg body weight/day. Patients should take a single dose of Vacocholic at bedtime or divide the dose into 2-3 times/day. In general, the daily dose of Vacocholic for cholesterol-rich gallstones may be unevenly distributed; however, larger doses of the drug should be taken in the evening to help neutralize the overnight rise in bile cholesterol levels. . Duration of treatment should last from 6-24 months, depending on the size of the stone. After the stone has disappeared, the patient should also continue to take the drug for another 3-4 months. Treatment of primary biliary cirrhosis: Use a dose of 13-15mg/kg body weight/day, divided into oral doses 2-4 times/day. Vacocholic should be taken immediately after a meal. Treatment of cystic fibrosis in children from 6 to under 18 years old: 10 - 15 mg/kg body weight/day, total daily dose should be divided into 3 times.
3.2. How should Vacocholic be used?
Because it is prepared in the form of film-coated tablets, Vacocholic is taken orally with filtered water (about 180-240ml). Patients should swallow the tablet whole, avoiding chewing or crushing it, which can affect the effectiveness of the active ingredient in the drug.Before starting treatment with Vacocholic, patients should also carefully read the instructions for use listed on the application form or printed on the product packaging. In addition, the use of Vacocholic medicine also needs to follow the dose recommended by the doctor, avoid self-medicating or change the dose without approval.
4. What side effects does Vacocholic cause to users?
Here are some of the side effects that patients are at risk of experiencing during treatment with Vacocholic:Common side effects such as diarrhea or loose stools. Rare side effects such as rash or calcification of gallstones. Very rare side effects such as increased liver enzymes, nausea or vomiting. If any of the symptoms mentioned above occurs, the patient should immediately notify the doctor so that there can be a remedy soon.
5. What should be noted when using Vacocholic?
During long-term treatment with Vacocholic, rectal monitoring of the patient should be performed even though ursodeoxycholic acid does not pose a carcinogenic risk. In addition, patients also need to be careful with some other things as follows:
It is necessary to check the effectiveness of cholesterol gallstone treatment for patients by imaging after about 6 months of taking the drug. Caution and close monitoring are required when administering Vacocholic to patients with cirrhosis with impaired hepatocellular function or with cholestasis (bilirubinemia > 200 micromol/L). The starting dose of ursodeoxycholic acid should be gradually increased to 200 mg/day in patients with cholestasis leading to pruritus. In this case, the patient can take more Cholestyramine, but must take it about 5 hours from ursodeoxycholic acid to avoid drug interactions. There isn't enough research to know if Vacocholic will affect pregnancy, so pregnant women should avoid taking it or take it only when absolutely necessary and as directed by their doctor. Breastfeeding women should consult their doctor about the benefits and risks of Vacocholic before deciding to use it. Check the expiry date and quality of Vacocholic before use. When there are signs that the tablet is moldy, watery, discolored, or has expired, the patient should stop treatment and discard the medicine according to the doctor's instructions. Vacocholic should be stored in a dry place, away from light and high humidity. In addition, keep Vacocholic medicine in a place out of reach of children to avoid the risk of children taking the medicine without knowing it.
6. Vacocholic drug interacts with other drugs?
According to the doctor's recommendation, patients should avoid using Vacocholic with the following other drugs to avoid interactions:Aluminum-containing antacids, Colestipol, Cholestyramine or activated charcoal when taking copper. Concomitant administration of ursodeoxycholic acid may reduce drug absorption. Anti-hyperlipidemic drugs (typically Clofibrate), Neomycin, Estrogens, Progestins when used together with ursodeoxycholic acid can reduce the effect of the drug due to increased cholesterol saturation in the bile.