This is an automatically translated article.
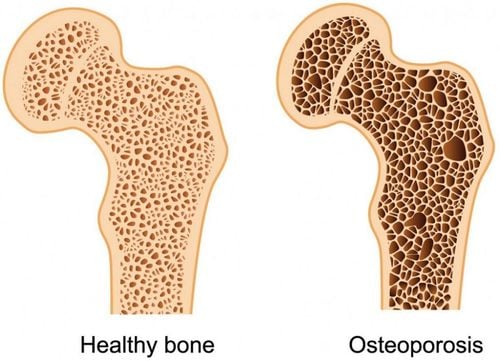
Raloxifene belongs to a group of drugs that affect bone metabolism and is commonly used in women to prevent and treat osteoporosis after menopause, slow bone loss, and help keep bones strong. Raloxifene extra may also reduce the risk of certain types of breast cancer after menopause.
1. Uses of the drug Raloxifene
Raloxifene is a selective estrogen receptor modulator that has very estrogen-like effects in some tissues such as bone, with no effect in other tissues such as breast and uterus. Raloxifene has many uses, which can be listed as follows:Maintains bone density may have other benefits for postmenopausal women Effective in shrinking uterine fibroids Prevents treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis Menstruation Slows bone loss and helps keep bones strong, less likely to break Reduces the risk of certain types of breast cancer after menopause though. Raloxifene is not an estrogen hormone but acts like estrogen in certain parts of the body such as bones. In contrast to other parts of the body (womb and breasts), Raloxifene acts as an estrogen inhibitor. Raloxifene belongs to a class of drugs called selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs), but does not relieve menopausal symptoms. Note Raloxifene is not used before menopause and is not used to prevent heart disease.
Raloxifene is usually indicated in the following cases:
Treatment and prevention of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women Prevention and treatment of osteoporosis-related vertebral fractures in postmenopausal women, but is usually indicated Indicated for patients who cannot take bisphosphonates or who have been treated with bisphosphonates for 1 year and still have fractures or who have decreased bone mineral density (BMD) compared with pre-bisphosphonate treatment. Reduced risk of invasive breast cancer in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis Prevention and treatment of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis
2. Dosage of Raloxifene
Raloxifene is usually taken by mouth, is quickly absorbed and does not involve food. Reference dosage for each specific subject is as follows:
Adults with osteoporosis: 60mg orally per day Adults to prevent osteoporosis: 60mg orally per day Adults to prevent breast cancer: 60mg orally if used Long-term medicine should pay attention to calcium and vitamin D supplementation in women with a diet low in these two substances. The optimal duration of use has not yet been determined, may extend to the end of life, and there are no special recommendations for patients with geriatric, renal and hepatic impairment.
3. Raloxifene side effects
In some patients when using Raloxifene, common side effects may occur such as:
Hot flashes Leg cramps Peripheral edema Flu-like syndrome Joint pain Sweating Headache, migraine syndrome Floating rash, mild breast tenderness, increased blood pressure Nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dyspepsia Less commonly symptoms of stroke, deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism or superficial thrombophlebitis may be present. In addition, the drug Raloxifene also has some contraindications such as:
Patients with hypersensitivity to any ingredient of the drug. Women are capable of giving birth. History of venous thromboembolic events, including deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, and retinal vein thrombosis. Liver failure, cholestasis. Severe kidney failure. Unexplained uterine bleeding. There are signs of endometrial cancer.
4. Precautions while using Raloxifene
When using Raloxifene, the following precautions should be observed:
Stop Raloxifene >72 hours before and during prolonged immobilization (eg, after surgery, prolonged bed rest), continue treatment after the patient Fully ambulatory to avoid the risk of venous thromboembolic events Postmenopausal women with coronary heart disease are at increased risk of major coronary events when using raloxifene, the benefits and risks should be weighed when using raloxifene. Indications Women with a history of significant hypertriglyceridemia during oral estrogen therapy should have their serum triglycerides monitored while receiving raloxifene because of the potential for increased levels. Raloxifene hydrochloride is not effective in vasodilating. (reduced hot flashes), or other symptoms of menopause related to a lack of estrogen. Possible drug interactions with Raloxifene include:
Patients should be monitored for prothrombin time when taking warfarin, coumarin Concomitant use of cholestyramine is not recommended unless there is experience with systemic estrogens. Raloxifene is a drug that affects bone metabolism and is commonly used in women to prevent and treat postmenopausal osteoporosis, slow bone loss, and help keep bones strong. To ensure the effectiveness of treatment and avoid unwanted side effects, patients need to strictly follow the instructions of the doctor, professional pharmacist.
Follow Vinmec International General Hospital website to get more health, nutrition and beauty information to protect the health of yourself and your loved ones in your family.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.