This is an automatically translated article.
Egudin medicine has the main ingredient Solifenacin succinate. So what is the use of Egudin and how is it used? Check out the article below for more useful information.
1. Uses of Egudin
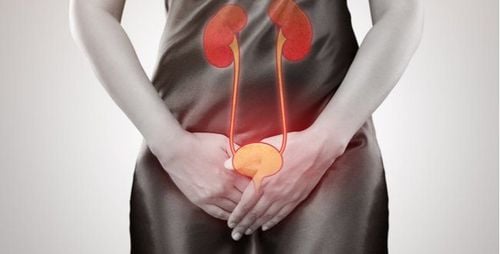
Egudin medicine has 2 different strengths such as Egudin 5mg and Egudin 10mg. It is indicated for the symptomatic treatment of urinary incontinence due to urge (urinary incontinence) and/or urinary urgency and frequency in patients with overactive bladder syndrome.
Solifenacin is a competitive muscarinic receptor antagonist. Muscarinic receptors play important roles in the function of the parasympathetic nervous system, including inducing contraction of bladder smooth muscle and stimulation of salivary secretion. Solifenacin doses of 5 mg/day and 10 mg/day have been studied in several randomized, controlled clinical trials in patients with overactive bladder. Results showed that both the 5 mg and 10 mg doses significantly improved the primary and secondary endpoints compared with placebo. The drug effect was observed within a week of starting treatment and stabilized within 12 weeks. Treating symptoms of overactive bladder also benefits patients' quality of life, sleep, and vitality.
2. Dosage of Egudin
Egudin 5mg is taken orally and can be taken with or without meals. The specific dosage of solifenacin succinate is as follows:
Adults: The recommended dose of Egudin is 5 mg, once daily. If the patient tolerates the 5 mg dose well, the dose can be increased to 10 mg once daily. Children: The safety and effectiveness of solifenacin in children have not been established. Therefore, this medicine should not be used in children. Patients with renal impairment: Patients with mild to moderate renal impairment (ClCr > 30 ml/min) do not require dose adjustment of Egudin. In patients with severe renal impairment (ClCr ≤ 30 ml/min) the daily dose of Egudin should not exceed 5 mg. Patients with hepatic impairment: For mild cases, no dose adjustment of Egudin is required. In patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh B), the daily dose of Egudin should not exceed 5 mg. People who are taking strong inhibitors of CYP3A4 (eg, Ketoconazole, nelfinavir itraconazole, ritonavir,), the daily dose of Egidine should not exceed 5 mg.
3. What to do in case of an overdose of Egudin?
Overdosage of solifenacin can lead to serious anticholinergic effects such as dilated pupils, blurred vision, tremors, constipation, and dry skin. The above symptoms occurred on day 3 in healthy volunteers taking 50 mg/day (5 times the recommended dose) and disappeared within 7 days after drug discontinuation. In case of overdose of solifenacin, appropriate treatment measures such as induction of vomiting, gastric lavage and symptomatic therapy should be instituted.
4. Contraindications of Egudin
Egudin is contraindicated in the following cases:
Patients with urinary retention. The patient has gastric retention. Patient with uncontrolled narrow-angle glaucoma. Patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C). Patients with hypersensitivity to any component of the drug.
5. What are the side effects when using Egudin?
During the course of taking the drug, the patient may experience some side effects such as:
Common: Constipation, digestive disorders Uncommon: hypertension, lower extremity edema; abdominal pain, dyspepsia, nausea, upper abdominal pain, vomiting, flu, depression, somnolence, fatigue Rare: Abnormal liver function tests, anaphylaxis, angioedema, atrial fibrillation, confusion, decreased appetite, delirium, dizziness, dry nose, digestive disorders, erythema multiforme, exfoliative dermatitis, ..
6. What is the note when using solifenacin?
Angioedema: Angioedema of the face, lips, tongue and/or larynx has been reported; Some cases have occurred after the first dose. Drug-induced angioedema can be life-threatening. Patients should stop taking the drug immediately and seek supportive care if edema is involved in the tongue, hypopharynx, or larynx. Central Nervous System Effects: CNS effects have been reported (eg, headache, confusion, hallucinations, somnolence). Attention should be paid to monitoring for CNS effects, especially when starting or increasing the dose, reducing the dose or stopping if necessary. In addition, the drug may cause drowsiness and/or blurred vision, which may impair physical or mental abilities. Patients should therefore be warned against performing tasks that require mental alertness (eg, operating machinery, driving a vehicle). Hypersensitivity Reactions: Anaphylactic reactions have been reported rarely but can be life-threatening. Patients should immediately discontinue treatment if an anaphylactic reaction occurs. Alzheimer's disease: Preliminary data suggest that long-term use of anticholinergics may adversely affect the clinical course of Alzheimer's disease in patients receiving cholinesterase inhibitors. Further monitoring of cognitive and functional impairment as well as increased problem behavior should be considered in dementia patients receiving dual therapy with acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and anticholinergics of the bladder. such as solifenacin. Gastrointestinal disorders: Use with caution in patients with decreased gastrointestinal motility (severe constipation, ulcerative colitis) or obstructive disorders of the gastrointestinal tract (pyloric stenosis) because it may increase the risk of bleeding. stomach medicine. Contact a doctor or pharmacist if severe abdominal pain or constipation persists for more than 3 days Glaucoma : Use with caution in patients with treated narrow-angle glaucoma. Contraindicated for use in uncontrolled narrow-angle glaucoma. Hepatic impairment: Use with caution in patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh B, not recommended in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C). QT prolongation: Use with caution in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C). Patients with a history of QT prolongation or other risk factors for QT prolongation (eg, concomitant use of drugs known to prolong the QT interval, electrolyte abnormalities). Anticholinergic effects that have been reported with the use of solifenacin include headache, hallucinations, confusion, and somnolence.Patients should be monitored for these symptoms, especially after initiation of therapy. Treatment or dose increase Pregnancy: There are no adequate studies on the effects of solifenacin in pregnant women.Therefore, solifenacin should not be used in pregnant women unless the potential benefit to the mother outweighs the risk. Breast-feeding: It has not been established whether solifenacin is present in breast milk.According to the manufacturer, the decision to breastfeed during treatment should take into account the risk of exposure to the infant, the benefits of breastfeeding, and the benefit of the drug to the mother. In short, to use the drug effectively, patients need to use Egudin exactly as directed by their doctor or pharmacist.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.