This is an automatically translated article.
Inguinal hernia is now a very common disease. The Valsalva test of inguinal hernia ultrasound is an effective method to detect the disease, from which the doctor will come up with an effective treatment plan.
1. What is an inguinal hernia?
Inguinal hernia is a condition in which a part of abdominal organs such as intestines and omentum enter the inguinal hole to form a hernia sac. Inguinal hernia is common in men because the structure of the inguinal region in men has the spermatic cord running through, so the abdominal wall here is quite weak. Inguinal hernia is rare in women and usually occurs only when there is a medical condition that increases intra-abdominal pressure or after surgery.
In other words, the inguinal region has natural openings during fetal development that some anatomical structures pass to descend, such as the testicles that descend into the scrotum in men. When these anatomical holes are wide, it is possible that it is the source of inguinal hernia, femoral hernia, from which part of the abdominal viscera passes through this enlarged natural opening.
Inguinal hernia is manifested by swelling in the groin area, mostly in standing position or with exertion. Hernias can occur at any age, and inguinal hernias are more common in men, and femoral hernias are more common in women. Hernias in children are the result of congenital abnormalities.
2. Complications of inguinal hernia
When the hernia has formed, the patient will feel the hernia growing up, fast or slow depending on the individual, the disease will not be able to go away on its own if not treated with intervention.
Over time, the natural progression of the disease increases discomfort for the patient. A strangulated hernia is the leading risk factor for intestinal entrapment in the hernia, at this time, the hernia mass cannot be pushed up and is very painful. The patient must be examined and treated urgently.

Thoát vị bẹn gây cảm giác đau đớn cho người bệnh
The risk of strangulated hernias varies depending on the anatomic type of hernia: less common with direct inguinal hernias, more common with femoral hernias. To understand the risk of strangulation, the patient should discuss with the surgeon during the examination. There are patients with hernia with local pain but not strangulation. This pain may be associated with other conditions that are not necessarily due to the hernia and so they may persist after hernia surgery.
3. Signs of inguinal hernia
Inguinal hernia can occur without any other symptoms. Sometimes, the patient feels pain or tightness in the groin area. Usually, the patient can push the hernia sac back on its own or the hernia sac can disappear when the patient lies down. Babies may have hernia sacs that appear in waves each time they push, cry, cough, or stand.
Complications include incarcerated and strangulated hernia:
Incarcerated hernia is part of the intestine, fatty tissue or ovary trapped in the hernia sac. Incarcerated hernias can form a firm, painful mass that causes vomiting, constipation, and irritation. The most dangerous condition is a strangulated hernia. A strangulated hernia occurs when the tissues in the hernia sac become twisted. This condition can lead to necrosis, which means that the tissues in the hernia sac die because there is not enough blood supply. A strangulated hernia can cause symptoms of fever and the hernia area is swollen, red, inflamed, and very painful.

Thoát vị nghẹt có thể gây ra triệu chứng sốt cho người bệnh
4. Causes and factors that increase the risk of inguinal hernia
The disease can occur at any age, but is common in the elderly when the abdominal wall is weakened. Inguinal hernias are usually divided into two groups, congenital and pathological.
In congenital cases : Due to a structure in the inguinal canal, it was supposed to close after birth but for some reason the canal did not close. Therefore, intra-abdominal contents pass through this tube causing hernia. However, not everyone with this tube is sure to have the disease.
Due to pathology: Acquired inguinal hernia is common cause is weakening of abdominal wall due to old age. Malnutrition, obesity, trauma or surgery to the groin can also cause hernias.
In addition, favorable factors increase abdominal pressure continuously or intermittently for a long time, increasing the risk of disease:
Persistent cough; Perennial constipation ; Pregnancy can weaken your abdominal muscles and cause increased pressure inside your abdomen; Large tumor in the abdomen.
There are many factors that can increase the risk of an inguinal hernia, including:
Gender: men are at higher risk than women; Family history: the risk of an inguinal hernia is increased if you have a close relative, like a parent or sibling, with the condition; Certain medical conditions: people with cystic fibrosis, a condition that causes severe lung damage, often have a chronic cough and are more likely to develop an inguinal hernia; Chronic cough: such as in smokers, may increase the risk of inguinal hernia; Chronic constipation: straining to have a bowel movement is a common risk factor for inguinal hernia; Being overweight: puts extra pressure on the patient's abdomen; Pregnancy: this can weaken both the abdominal muscles and cause increased intra-abdominal pressure; Certain occupations: there are some jobs that require standing for long periods of time or heavy manual labor that increase the risk of inguinal hernia; Premature birth.

Mang thai là một trong nhiều yếu tố làm tăng nguy cơ thoát vị bẹn
5. Ultrasound Valsalva test of inguinal hernia
Currently, there are many methods to diagnose and examine inguinal hernia, but the most used method is the Valsalva maneuver, which is used in ultrasound examination of inguinal hernias.
5.1 What is the Valsalva maneuver? The Valsalva maneuver is a breathing technique that can be used to help diagnose problems with the autonomic nervous system (autonomic nervous system). The test is named after the seventeenth-century Italian physician, Antonio Maria Valsalva. The general principle when performing the procedure is that the patient must inhale as much as possible and try to exhale while the airway is blocked (glottis closed).
This movement is described as pushing when defecating, has the effect of increasing pressure in the chest. The sudden expulsion of air when breathing through the nose will change the heart rate and blood pressure rapidly, so the patient needs to be done very gently. For the first time, the patient will perform this technique under the supervision of a doctor to ensure the correct procedure in a safe yet effective period of time.
5.2 Ultrasound process of inguinal hernia using the Valsalva maneuver Patient position: the patient takes off his pants, exposing the groin, thighs, and genitals. In adults and older children, examine in the standing position. If the patient is unable to stand, the patient can lie on his or her back. Order of ultrasound: look, touch, hear. The doctor will look at the groin area to determine which side of the hernia. After that, the patient needs to cough or bulge the abdomen, if the bulge appears, then diagnose the patient has an inguinal hernia After that, the doctor can make a few other diagnoses such as: touching the finger and blocking the inguinal hole. deep.
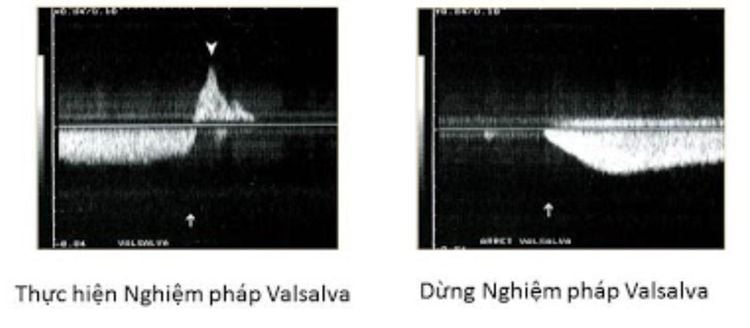
Hình ảnh kết quả siêu âm bằng nghiệm pháp Valsalva
Vinmec International General Hospital, currently equipped with leading equipment system and a team of high-class doctors and technicians to serve laparoscopic inguinal hernia surgery and robotic surgery:
Robotic systems, such as the Da Vinci robot at Vinmec International General Hospital, help convert the surgeon's movements into machine movements through computer communication between the system working directly on the patient and the patient. remote and doctor's console. Hand-held robots have more flexibility than conventional endoscopes. The robot is attached with a motor and control unit to the endoscopic handle, which helps the surgical head function as a flexible wrist joint that can be angled. In addition, the instrument also includes an endoscope that automates through voice, laser, eye tracking and other methods, allowing the surgeon to control the laparoscope without an assistant holding the lamp when surgery. In addition, with the Hybrid clean operating room system, the risk of postoperative complications due to infection and infection is minimized. To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact the nationwide Vinmec Health System Hotline, or register online HERE.