This is an automatically translated article.
Laparoscopic surgery for inguinal hernia treatment is performed to shield and strengthen the posterior wall of the inguinal canal. This method has many advantages such as low recurrence rate, less pain for patients, quick recovery,...
1. Treatment methods for inguinal hernia
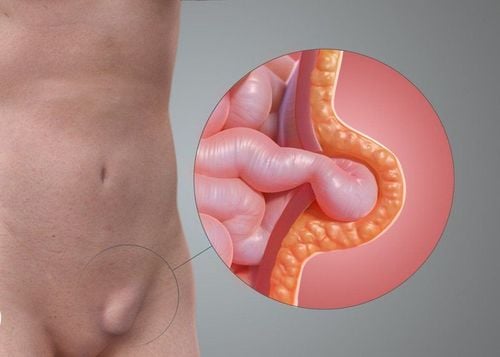
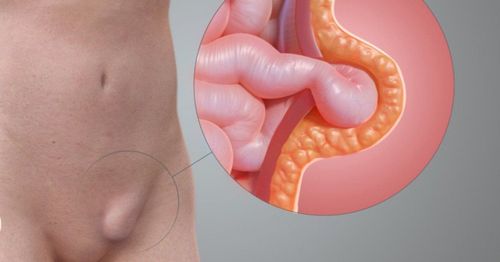
Inguinal hernia is a condition in which an abdominal viscera (such as intestine, great omentum) leaves its place and enters through the inguinal hole to form a hernia sac. The pathogenesis of inguinal hernia is due to an imbalance between the intra-abdominal pressure and the abdominal wall sealing mechanism, causing the peritoneum through the weak area of the abdominal wall to push out, pulling the internal organs. The main causes of inguinal hernia are:
Existence of the peritoneal canal: The peritoneal tube is an extension of the peritoneum during the passage from the abdomen to the scrotum of the testicles in boys. Normally, at the end of fetal life, the peritoneal tube will atrophy itself into a fibrous fiber. If the peritoneal tube is not closed, the intestines and abdominal organs may descend into the inguinal-scrotal region in the duct, causing a congenital inguinal hernia. This is the cause of inguinal hernia in children, rarely seen in adults. Inguinal hernias caused by viscera passing through the testicular canal are called direct inguinal hernias. Inguinal hernia due to increased intraperitoneal pressure, weak abdominal wall due to reasons such as ascites, pregnancy, intra-abdominal tumor, chronic cough, frequent constipation, straining to urinate, doing heavy work, depression nutrition, thin, aging tissue... This type of inguinal hernia is called indirect inguinal hernia. When suffering from inguinal hernia, the patient feels heaviness, increased pressure on the pelvis. The most characteristic symptom is the appearance of a bulge in the groin area. This bulge enlarges, causing sharp pain, discomfort when doing heavy work, pushing, running, jumping, ... and disappearing when lying down, resting. Inguinal hernia, if not detected and treated promptly, will cause many life-threatening complications. In which, the most dangerous and common complication is strangulated hernia, causing necrosis of the intestine and mesentery.
Treatment of inguinal hernia is mainly surgery. The classic inguinal hernia surgery used in the treatment of inguinal hernia was formerly using autologous tissue to regenerate and suture to cover the weakness of the abdominal wall. The disadvantage of this method is that the fascia from two distant locations is sewn together, causing tension in the sutures, causing a lot of pain for the patient, a long postoperative time, and slow recovery of personal activities after surgery. In addition, the suture layers are stretched, there is lack of blood to nourish, the scar is difficult to heal, and the risk of hernia recurrence is high.
In order to reduce the recurrence rate and avoid the disadvantages caused by autologous tissue reconstruction of the abdominal wall, surgical placement of an artificial mesh for the treatment of inguinal hernia is performed to shield and strengthen the posterior wall of the inguinal canal. This is a non-radical abdominal wall reconstruction surgery, so it is less painful and does not change the structures that make up the inguinal canal. There are two types of surgery to place an artificial mesh to treat inguinal hernia: open surgery and laparoscopic surgery. In which laparoscopic surgery has many advantages such as:
Small incision, less pain after surgery, quick recovery Safe, effective, few complications Small incisions so less scarring, high aesthetics Due to Because of many advantages, laparoscopic surgery with artificial mesh to treat inguinal hernia is increasingly commonly performed in clinical practice.
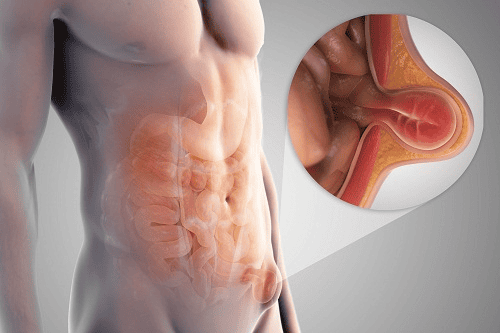
Thoái vị bẹn gây suy nhược cơ thể, ốm yếu
2. Laparoscopic surgery to place an artificial mesh to treat inguinal hernia
2.1. Preparation before laparoscopic surgery to place an artificial mesh to treat inguinal hernia
Laparoscopic surgery to place an artificial mesh to treat inguinal hernia can be performed in patients with indirect, direct inguinal hernia, unilateral or bilateral inguinal hernia. Before surgery, the medical staff will explain to the patient and family the purpose of surgery and possible risks during and after surgery. Surgery can only be performed when the patient or family member signs an undertaking to consent to the surgery. Basic laboratory tests are performed to ensure that the patient is in good health for surgery.
2.2. Steps to perform laparoscopic surgery to place artificial mesh to treat inguinal hernia
Position
The patient is instructed to lie supine on the operating table, legs closed, arms closed. The monitor is placed at the patient's feet. The main surgeon will stand opposite the hernia to be operated on, the assistant will hold the camera next to, above the main surgeon. The person in charge of the instrument stands opposite the main operator. The surgical team conducts urethral catheterization for the patient, may not need a urethral catheter if the patient urinates before surgery. Anesthesia
Anesthesiologists administer general anesthesia or spinal anesthesia in combination with epidural anesthesia. Steps to perform surgery
The surgeon places the first 10mm trocar below the navel and inflates air. Then, two more trocars of 5 were placed on the lateral border of the rectus abdominis muscle on both sides, across the navel, under the microscope. Based on the image on the screen captured from the camera, the doctor conducted a pelvic and inguinal exploration with anatomical landmarks: middle navel, lateral umbilicus, inner inguinal triangle, posterior inguinal ring, outer navel fold. After locating the hernia and herniated viscera, the doctor used scissors to open the peritoneum in a horizontal line from the anterior iliac spine to the middle navel fold, 2-3cm from the upper border of the hernia hole. Dissecting the peritoneum downwards. Next, dissection follows the pubic bone to the side of the hernia to the internal iliac vein. Dissect laterally, to the level of the anterior superior iliac spine, and posteriorly until the iliac lumbosacral or supraclavicular iliac spines are visible. Perform dissection, pull the hernia sac directly or indirectly inward. If the indirect hernia sac is large, it is not recommended to dissect all of the hernia sac, but tie the proximal end and then cut across the hernia sac, leaving the distal end open to avoid the accumulation of fluid later. In women, the round ligament can be removed when dissecting the hernia sac. Dissect the peritoneum from the pelvic wall, about 5-7cm below the pubic band. Place a 10x15cm or 12x15cm artificial mesh to cover the entire commissure, including the deep inguinal ring, the inner inguinal triangle, and the femoral foramen. The mesh covers the large hernia holes 5-7cm, do not cut the mesh to bypass the spermatic cord, the lower edge of the mesh rests on the dissected peritoneal fold. If the hernia is small, there is no need to fix the mesh center. If the hernia hole is >3cm, the mesh can be fixed with glue or a fixing needle. Fixation by needle is fast but expensive. If the hernia is bilateral, it is possible to place 2 artificial mesh panels on both sides, overlapping in the midline about 2cm or put an artificial mesh with a large size of 10x30cm. Then, use a needle, clip to fix the peritoneum to the abdominal wall or suture the peritoneum with slow-dissolving sutures. Exhaust gas, stitch scales and skin.
Mổ nội soi đặt lưới nhân tạo điều trị thoát vị bẹn an toàn, ít biến chứng
3. Complications can be encountered during laparoscopic surgery to place an artificial mesh to treat inguinal hernia
Complications that can be encountered during surgery and after surgery to install an artificial mesh to treat inguinal hernia are:
Peritoneal tear is the most common complication during surgery. If the tear is small, a peritoneal decompressor is used to create space and no further treatment is required. If the peritoneal tear is extensive, the tear can be secured with sutures or sutured. Postoperative fluid collection: Meet with the rate of 0.5-12.2%, the wall will clear up after 6-8 weeks. No drainage is required to avoid postoperative fluid accumulation. Hematoma: Occurs with the rate of 5.6-16%, much lower than open surgery. Bleeding is so rare that it requires a blood transfusion. If the hematoma is large, causing a lot of pain, anesthesia can be used to make an incision and take the hematoma. Postoperative urinary retention occurs in less than 3%, bladder injury is rare in <1%. Bladder injury usually occurs when cutting into the hernia sac directly. Complications of the mesh such as folding and moving cause hernia to develop. Prevent this situation by using a large net, at least 10x15cm in size, spread the net flat, not folded. Prevent infection of the mesh by using prophylactic antibiotics and aseptic handling. Other complications such as damage to blood vessels, nerve damage, damage to the vas deferens, testicular blood vessels and orchitis, etc. can occur but the rate is low and usually not serious.

Biến chứng viêm tinh hoàn sau phẫu thuật nội soi rất hiếm khi xảy ra
4. Caring for patients after laparoscopic surgery with artificial mesh to treat inguinal hernia
After surgery for inguinal hernia, the patient needs to rest completely, avoid movement, early post-operative movement will affect the incision and slow recovery. Re-examination according to the doctor's schedule or when detecting abnormal signs such as pain in the groin area, high fever, bleeding,...
Patients should drink a lot of water, eat a diet rich in green vegetables and fresh fruits to provide many minerals, vitamins, help increase resistance. A diet rich in fruits and vegetables also helps patients with laxatives, preventing constipation. Having a bowel movement when constipated will increase abdominal pressure, causing pain, discomfort, and even poking the wound.
Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in examination and treatment, patients can rest assured to visit. and hospital treatment.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.
READ MORE
What is an inguinal hernia? Can it be cured? Treatment of inguinal hernia: Should laparoscopic or open surgery? Is surgery for inguinal hernia dangerous?