This is an automatically translated article.
Birth defects are something that any pregnant woman does not want to encounter. In particular, bone defects put the fetus at high risk of death or if born, it will not develop normally as other children. Currently, ultrasound of malformations in general and ultrasound of bone malformations in particular are chosen by many pregnant women to perform.1. Why should go for fetal malformation ultrasound?
Every child is born with the expectation and love of parents and family. Everyone wants their baby to be born healthy and free of any birth defects, but according to statistics from the Ministry of Health, in Vietnam, one in every 33 children has a birth defect. this represents 3% of the total number of babies born each year. Birth defects can occur in any child or simply any fetus is at risk of having a birth defect.There are different types of fetal malformations including chromosomal abnormalities leading to congenital heart disease, down syndrome, human body defects such as extra fingers, legs, cleft palate, malformations malformations of the anus, malformations of the bones or certain malformations of one or more other organs.
If in the past the technical means were not developed, early detection of fetal malformations was still difficult, now the screening for malformations becomes simpler and the cost is not too expensive.
Fetal malformation ultrasound helps doctors find fetal abnormalities early and give the most appropriate advice to pregnant women. Currently, ultrasound for fetal malformations depends mainly on machines and under favorable conditions, the doctor's level and analytical ability, up to 90% of ultrasound results are accurate.

Việc siêu âm dị tật thai nhi giúp bác sĩ sớm tìm ra các bất thường của thai nhi và đưa ra những tư vấn thích hợp nhất cho thai phụ
2. What abnormalities does ultrasound in bones help detect?
2.1 Cartilaginous aplasia This is a type of bone malformation with a high risk of death with the characteristic that the trunk and extremities are shorter than normal, the fetal head is quite large compared to the limbs. Cartilage aplasia is rare and is equally common in male and female fetuses. Cartilage aplasia can be diagnosed as early as 12 weeks of pregnancy thanks to certain telltale signs.Signs of cartilaginous aplasia:
In some cases, lymphatic cysts or edema may be seen Typical signs are soft tissue thickening in the arms Abdomen and fetal head are very large compared to the chest and extremities Occasionally There are cases of rib fractures The limbs of the fetus are often very short. For a fetus diagnosed with aplasia of cartilage, the doctor will advise pregnant women to abort the pregnancy for the following reasons:
Most of the fetuses die. before birth If born, the baby usually dies within 24 hours of pulmonary hypoplasia 2.2 Chondrodysplasia Chondrodysplasia is mostly heterozygous dysplasia, which is a non-fatal skeletal malformation, However, when children are born, they often have short limbs, a large head, and in adulthood, the height ranges from 1.16m to 1.4m. Chondrodysplasia can be accurately diagnosed after 24 weeks, the most reliable indicator being the quotient between femoral length and biparietal diameter.
>>> The first pregnancy was diagnosed with osteochondrosis and the pregnancy was terminated, will the next pregnancy be again?
Signs to recognize cartilage dysplasia through ultrasound:
The fetal body is underdeveloped and disproportionate, short limbs, large head, when viewed from the side, the forehead is protruding and the nose is flat. The signs of short limbs are obvious. more in the 2nd trimester, short, stout hands and feet Measurements of long bones below the 5th percentile Polyhydramnios in the last trimester Some cases of ventricular dilatation Babies Children with dysplasia after birth have a normal life like other children, their intelligence is not limited, but some neurological complications can occur, especially in the neck bones. Children reaching adulthood will be very short, which can be treated with leg lengthening surgery.
2.3 Amniotic band syndrome This is an asymmetrical abnormal syndrome with amputation and separation defects such as abdominal wall defect, brain herniation, cleft palate, small chin, and some superficial muscle malformations. body.
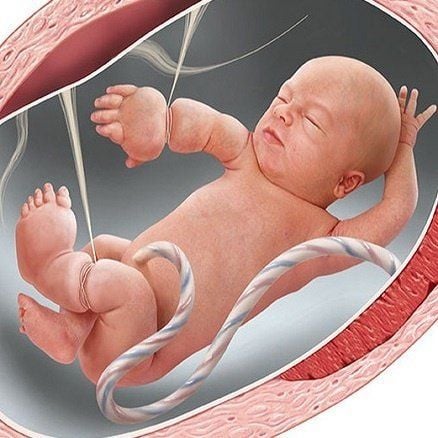
Hội chứng dải sợi ối là hội chứng bất thường không đối xứng với cắt cụt chi và các khiếm khuyết tách, chẻ như khiếm khuyết thành bụng, thoát vị não, chẻ mặt, cằm nhỏ và một vài dị dạng bề ngoài cơ thể
2.4 Polyarticular spasticity This is a heterogeneous group of disorders that cause spasticity of the joints at birth, the fetal limbs are typically immobilized in the extended and flexed legs, and the arms are flexed. curved. An ultrasound will show fetal hands clenched, feet stretched out or clubbed.
Some other signs on ultrasound such as:
Obvious muscle hypoplasia, fetal movement is limited or completely lost. The prominent feature of polyarticular spasticity is edema of the limbs and the symptoms are usually obvious in the third trimester. the last month of pregnancy When the fetus is diagnosed with polyarticular spasticity, depending on the severity of the disorder, the doctor may recommend abortion or appoint orthopedics for minor defects after the baby is born. .
2.5 Diastrophic Dysplasia This is a form of skeletal dysplasia with short limbs, crooked feet, enlarged ears, joint and spine deformities. Recognizing signs on ultrasound include:
All limbs are short, hands are deviated in the middle, fingers are short, thumbs are crooked out, feet are crooked. Small chin, one third of fetuses have cases. split face Loudspeakers as big as broccoli, cervical scoliosis Deformities in elbow and knee flexion Pregnant woman with polyhydramnios limited maturity. Although neonatal mortality is rare, most babies die after a while or die before adolescence.

Thai nhi bị Diastrophic Dysplasia sau khi sinh có cuộc sống giống như người bình thường, tuy nhiên chiều cao khi trưởng thành bị hạn chế
Femoral hypoplasia is often recognized by ultrasound:
The proximal portion of the femur including the head of the bone is missing. The femur is frequently bent or bowed, and the fibula and tibia can also be bent. Long bones or fingers may be partially or completely lost. Children after birth can have orthopedic surgery to correct this condition. The success rate depends on the accompanying abnormality, if there is only one abnormality, the success rate is high.
2.7 Cartilaginous hypoplasia The child was born with this malformation after birth with an average growth condition with disproportionately short limbs, increased head circumference. This will be easily noticed during an ultrasound.
Children with this deformity after birth have a healthy life like a normal person, except for their less developed height and short limbs.
2.8 Curvature Dysplasia This is a typical bony curvature of the femur and tibia with relatively low frequency. Signs identified by ultrasound are as follows:
Short and curved lower limb bones, hypoplasia of the fibula Pregnant woman has polyhydramnios in many cases The fetus has a bell-shaped rib cage, heart abnormalities, umbilical hernia , dilated renal calyx , clubfoot Often seen hermaphrodite. Most of the fetuses with this birth defect die in the neonatal period due to respiratory failure, physical and mental retardation.
2.9 Clubfoot A clubfoot is an angled foot at the sole of the foot, turned and turned inward. This malformation is often accompanied by musculoskeletal abnormalities of the lower extremities. Through ultrasound, the doctor will see the longitudinal section, the long bones of the lower limb and the foot can be seen in the same plane, the foot is flexed.
Children with this deformity after birth from 6-12 months can undergo orthopedic surgery to restore normal foot function.
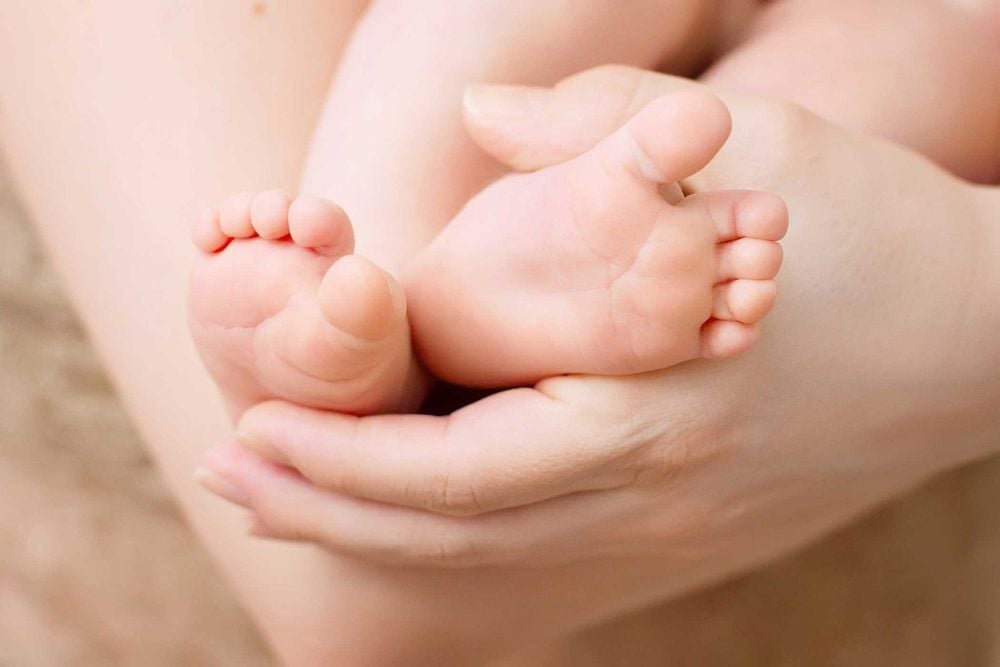

Trẻ với dị dạng bàn chân khoèo sau khi sinh từ 6-12 tháng có thể tiến hành phẫu thuật chỉnh hình để chức năng chân có thể phục hồi bình thường
Type 1: Can be diagnosed soon after birth with features of fracture, sclera, and hearing loss Type 2: There are many signs right before birth with high mortality prognosis Type 3: Fetal growth retardation and severe disability Type 4: This is a mild form with a high tendency to fracture, normal sclera :
For types 1 and 4 the fetal bones are long and short and fracture forming calluses, long bones are curved and meandering Type 2 can be recognized by ultrasound from 14 weeks of gestation, usually there is a decrease in mineralization bones causing rib deformities, short extremities and multiple fractures. 2.11 Extra-toes Children are born with extra fingers or toes. Ultrasonography of the deformity may not be detected if the bony part of the extra toe is not visible. This defect almost does not affect the health of the child, the child still develops normally after birth. It only has a certain effect on the aesthetic factor of the viewer.
2.12 Radial aplasia, radial hypoplasia This syndrome is usually complete, partial or terminal loss of the radial bone. This malformation usually occurs alone with a relatively low incidence. Ultrasound signs of malformation include:
Rotating bone or complete loss of ulna which may be shortened, arched or missing. Fetal hand is crooked and missing thumbs Lower extremities may also be affected 2.13 Syndrome Short ribs This is a syndrome with many malformations including short ribs, extra fingers, and short limbs. Ultrasound signs of malformations that can be seen include:
Large fetal head Short ribs and narrow rib cage Spinal malformations Pregnant women with polyhydramnios, which can be seen from the second trimester Posterior axial adhesions Most of the fetus If you have malformations due to pulmonary hypoplasia, your doctor can advise you and your family to terminate the pregnancy if detected early.
Vinmec International General Hospital offers a Package Maternity Care Program for pregnant women right from the first months of pregnancy with a full range of antenatal care visits, periodical 3D and 4D ultrasounds and routine tests to ensure that the mother is healthy and the fetus is developing comprehensively. Pregnant women will no longer be alone when entering labor because having a loved one to help them during childbirth always brings peace of mind and happiness.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.