This is an automatically translated article.
Helminth infection is a fairly common medical condition worldwide, especially in underdeveloped countries. There are many types of worms that can parasitize in the human body, each of which will cause different symptoms.
1. Worms parasitic in the human body
Worms, also known as helminths, are a common parasite. There are several types of worms that infect and eat humans. Some of the species of worms that people have can be very large - more than 3 feet (0.91m) long, while there are also very small species. The worst parasitic worms are usually found in warm tropical or subtropical regions of the world, but there are also some species of worms that are also common elsewhere. And anyone can get worms.
2. How did you get parasitic worms?
You can get worms in different ways, depending on the type of worm.
Many people become infected with worms by accidentally ingesting them or their eggs. Certain types of worms can get through your skin when they're young. Sometimes you get worms when you are bitten by an infected insect. You can also get worms when you eat the meat of an infected animal. Worms are usually transmitted through the urine or feces of an infected animal or person.
Bạn có thể bị nhiễm giun theo nhiều cách khác nhau
3. Common types of parasitic worms in the human body
3.1. Pinworms Pinworms are a common worm in the United States and around the world. They are very small in size, body length usually no longer than 1/2 inch.
You can get pinworms when you swallow their eggs. The pinworm eggs will then hatch in your intestines. At night, the female pinworm exits your body and lays thousands of tiny eggs around your anus. If those eggs are passed on to other people, those people will also become infected. Pinworm infections most commonly occur when children pass them on to other children.
When infected with pinworms, patients are usually asymptomatic but they can cause symptoms such as:
Itching anus Pain Nausea 3.2. Ascariasis Ascariasis is common in warm places where sanitation is poor. When a person swallows roundworm eggs, the worms hatch in the intestines. The young worm then travels to the lungs. After a week or two, the worms will reach the throat and are usually swallowed back into the intestinal tract. Roundworms are spread by contaminated soil contaminated with feces or by eating infected raw meat.
Symptoms of roundworm infection may include:
Dry cough Wheezing Abdominal pain Vomiting Diarrhea Fatigue Weight loss 3.3. Hookworms Hookworms are also common in tropical regions. When the feces of an infected person mix with the soil, the eggs will hatch. At a certain stage, hookworms can pass through the skin to enter the human body. This can happen if people walk barefoot in contaminated soil.
An itchy rash is often the first sign of a hookworm infection. Other symptoms include:
Abdominal pain Diarrhea Weight loss Loss of appetite Fatigue Anemia
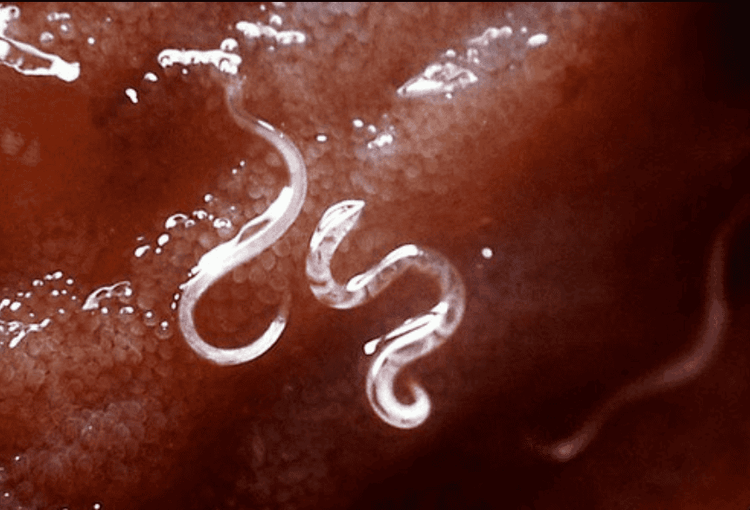
Giun móc có thể đi qua da để vào bên trong cơ thể người
3.4. Strongyloides stercoralis (Strongyloides stercoralis) People are mainly infected with strongyloides when young worms in the soil burrow through the skin into the body. Once inside the human body, strongyloides will find their way to the small intestine and lay eggs. Those eggs hatch before being excreted in the feces, and the worms can infect others.
Usually when infected with strongyloides, the patient will not have any symptoms. However strongyloides can also cause the following symptoms:
Abdominal pain Enlarged heartburn Diarrhea Constipation Dry cough Dermatitis 3.5. Pinworms You get roundworms by eating infected meat, especially raw or undercooked pork. When a person eats infected meat, stomach acid dissolves the cysts in the meat to release the helminth larvae. The helminths, after being released, will enter the intestines, grow, mate and lay eggs. After the eggs hatch, the young worms travel through the bloodstream to the muscles. Symptoms of helminthiasis include:
Nausea and vomiting Diarrhea Fatigue Fatigue Fever Headache Swelling Muscle and joint pain 3.6. Hairworms (Trichuris trichiura) Hairworm larvae (Trichuris trichiura) and adults can live in your intestines. Hairworms are so named because of their hair-like shape. Like many other parasitic worms, they spread through contaminated soil in warm climates. When infected with pinworms, patients are usually asymptomatic unless the infection is severe. Symptoms of severe ringworm infection include:
Diarrhea with mucus, water or blood Thin, stunted people Rectal prolapse: when part of the large intestine separates and slides out of the anus 3.7. Tapeworms You can get tapeworms from food or water contaminated with tapeworms or their eggs. If you swallow tapeworms, they will grow in your intestines. Tapeworms can live in a person's intestines for 30 years. If you swallow eggs, they can travel through your intestines into other parts of your body to form cysts. Symptoms of tapeworm infection depend on their location, symptoms of tapeworm infection include:
Nausea Weakness Loss of appetite Abdominal pain
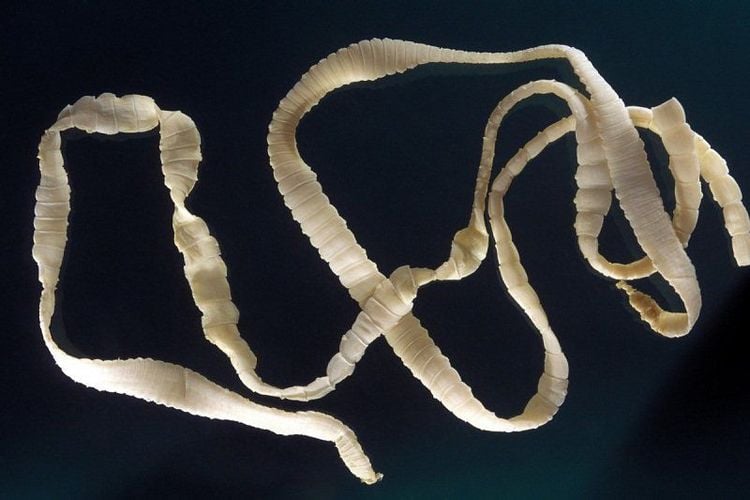
Bạn có thể bị nhiễm sán dây từ thức ăn hoặc nước bị nhiễm sán hoặc trứng của chúng
Diarrhea Feeling dizzy Salt cravings Weight loss Headache Convulsions 3.8. Schistosoma A schistosomiasis is a flat tapeworm that causes a condition called schistosomiasis (also known as tick fever or snail fever). People get sick if they come into contact with fresh water where schistosomiasis-infected snails live. The disc-shaped schistosomes emerge from snails and can then pass through a person's skin and enter the bloodstream as they mature. When the female lays eggs, it can cause:
Abdominal pain Diarrhea Blood in urine Chronic schistosomiasis infection can cause:
Anemia Stunt growth Damage to organs where schistosomiasis resides 3.9. Lymphatic filariasis Three types of small threadlike worms cause lymphatic filariasis. It is common in tropical and subtropical regions. Adult worms can live up to 7 years in a person's lymphatic system. The disease is only spread from person to person through mosquitoes. When mosquitoes bite an infected person, they can spread these tiny worms to other people they bite later. When infected with filariasis, the patient may have no symptoms, but filariasis can cause:
Damage to the lymphatic system Swelling The patient has difficulty fighting the infection
4. How to diagnose helminth infection in human body?
If your doctor suspects you have worms in your system, they will run tests to see if you have a helminth infection and find out what type of worm you have. Those tests may include:
Looking for signs of worms or eggs in your stool Endoscopy : Inserting a tube into your mouth or rectum to look at your intestines. Blood tests X-rays or other imaging tests.

Bác sĩ tiến hành các xét nghiệm để phát hiện và chẩn đoán tình trạng nhiễm giun sán
5. Treatment of helminths in the human body
If you have worms in your body, certain medications can kill them, commonly known as dewormers. You may sometimes need other treatments for symptoms related to the infection, including:
Anti-inflammatory drugs (steroids) Pain medications Anti-seizure medications If you have a cyst in your muscle, you may need surgery.
6. Prevention of parasitic worms in the human body
You've been treated for worms, but there's still a good chance you'll be re-infected. To avoid getting infected with worms, do the following:
Wash your hands often. Avoid contact with soil contaminated with human or animal feces. Do not eat raw or undercooked meat. Handle any pets with worms. Be extra careful if you travel to places where worms are common. Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in neurological examination and treatment, patients can completely rest in peace. examination and treatment center at the Hospital.
To book an appointment, please come directly to Vinmec medical system or register for an online examination on the website for service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: webmd.com