This is an automatically translated article.
The article is expertly consulted by Doctor Head of Department of Medical Examination - Internal Medicine, Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.
Type 2 diabetes is one of the growing non-communicable diseases in Vietnam. According to the World Diabetes Federation (IDF) in 2017, Vietnam has 3.53 million people living with diabetes. In which, most of the patients belong to type 2 diabetes group.
1. What is type 2 diabetes?
Diabetes mellitus is a heterogeneous metabolic disorder characterized by hyperglycaemia due to defects in insulin secretion, insulin action, or both. Chronic elevation of glucose for a long time causes disturbances in carbohydrate, protein, and lipid metabolism, causing damage in many different organs, especially the heart and blood vessels, kidneys, eyes, and nerves.
2. The first mechanism at the onset of type 2 diabetes
It's insulin resistance, which means your body isn't using insulin properly or the insulin isn't working properly. At first, the pancreas makes extra insulin to make up for it. But over time, your pancreas can't keep up and doesn't make enough insulin to keep blood sugar levels normal.
In a simpler way, you can understand that insulin is the bridge that brings the most important food source in the body, glucose, into the cells, helping the cells produce energy.
When the body has a deficiency of insulin, sugar is not fully introduced into the cells, immediately your cells will starve, which means that the amount of glucose in the blood will increase. High blood glucose will cause many dangerous complications.
3. Common dangerous complications of type 2 diabetes
Chronic elevation of glucose for a long time causes disturbances in carbohydrate, protein and lipid metabolism, causing damage in many different organs, especially in the heart and blood vessels, kidneys, eyes, nerves and teeth. Complications of type 2 diabetes include:
Cardiovascular complications Cardiovascular disease is the most common cause of death in people with diabetes. The effects of hyperglycemia can cause coronary artery disease (leading to heart attack) and stroke. High blood pressure, high cholesterol, high blood glucose, and other risk factors contribute to an increased risk of cardiovascular complications.
Kidney complications Diabetes causes damage to the small blood vessels in the kidneys that lead to kidney failure or kidney failure. Kidney disease is more common in people with diabetes than in those without. Maintaining normal blood glucose levels and blood pressure significantly reduces the risk of kidney disease.
Peripheral neuropathy Diabetes 2 can cause nerve damage throughout the body when blood glucose and blood pressure are too high. This leads to digestive problems, erectile dysfunction and many other functions.
In the most affected areas are the extremities, especially the feet due to the different neurovascular anatomy and posture of the human body than other organs. Nerve damage in this area is called peripheral neuropathy and can lead to pain, itching, and loss of sensation. Loss of sensation is a particularly serious sign because it can distract you from injuries and lead to serious infections that can lead to amputation. People with diabetes are 25 times more likely to have a limb amputation than the general population.
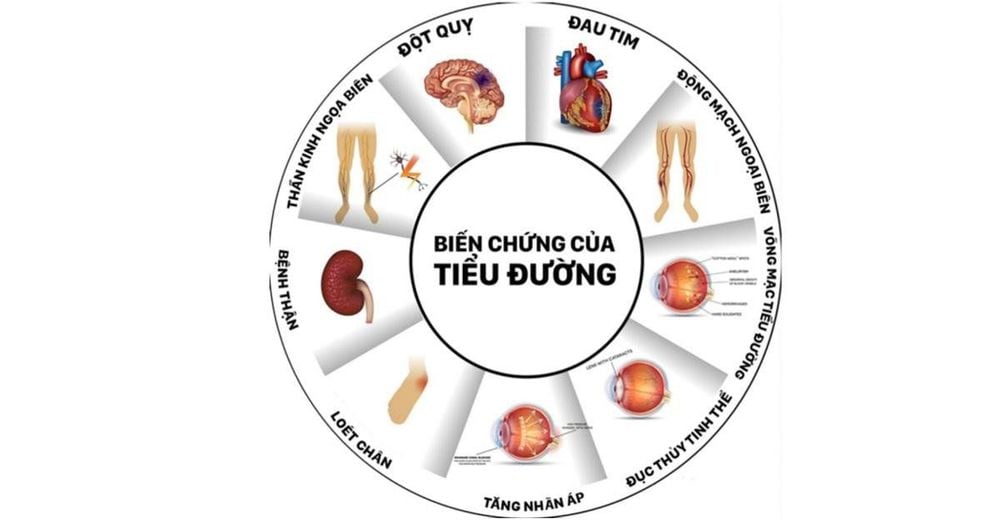
Retinopathy of the eye Most people with diabetes will develop some type of eye disease that causes vision loss or blindness. Persistently high blood glucose levels along with elevated blood pressure and high cholesterol are the main causes of retinopathy. This condition can be controlled through regular eye exams. Keep blood glucose levels and blood pressure near or normal.
Complications during pregnancy High blood glucose during pregnancy can lead to an overweight baby. This easily leads to birth complications and trauma for the baby and mother; Risk of sudden hypoglycemia in the newborn baby; Children exposed to high blood glucose during pregnancy are at higher risk of developing diabetes in the future than other children.
4. Subjects at high risk of developing type 2 diabetes
The following people have a higher than normal risk of type 2 diabetes:
Family history of diabetes History of gestational diabetes Advanced age Ethnicity Unhealthy diet and lifestyle Poor nutrition during pregnancy Physical inactivity Overweight, obesity High blood pressure Dyslipidemia Disorders of glucose tolerance: A condition in which blood sugar is higher than normal but not yet diabetes.

5. What should we do to reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes?
Unlike type 1 diabetes, it cannot be prevented, but when we change our behavior and lifestyle, we can significantly reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes. You can prevent type 2 diabetes by making the right lifestyle changes (diet and exercise):
Adjust your diet accordingly
The World Diabetes Association has compiled and put together makes recommendations for healthy diabetes prevention:
Choose water, coffee or tea instead of sugary, sweetened fruit juices, soft drinks or other sugary drinks. Eat at least 3 servings of vegetables every day. Eat up to 3 servings of fresh fruit per day. Choose a piece of fresh fruit or unsweetened yogurt for a snack. Limit alcoholic beverages. Choose lean white meat, poultry, or seafood instead of red or processed meat. Choose peanut butter over chocolate or jam. Choose wholemeal bread, rice, or pasta instead of white bread, rice, or pasta. Choose unsaturated fats (olive oil, canola oil, corn oil, or sunflower oil) instead of saturated fat (butter, animal fat, coconut oil, or palm oil)

Strength training
Need to check cardiovascular, eye, neurological complications, leg deformity before exercise. Do not exercise strenuously when plasma glucose > 250-270 mg/dL and positive urinary ketones Walk a total of 150 minutes per week (30 minutes per day), exercise should not be discontinued for 2 consecutive days. You should do resistance training 2-3 times a week (weight lifting, ..) The elderly, people with joint pain can do several times a day. Young people should exercise for about 60 minutes a day, doing resistance training at least 3 times per week.

Type 2 diabetes is not an infectious disease but is increasing in a very large number in our country because of the lifestyle associated with urbanization and the lack of information of the people. Through this article, we hope that readers will have an overview of type 2 diabetes as well as gain useful knowledge to prevent the disease.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: Ministry of Health