This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by an eye doctor - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Hai Phong International General HospitalThe structure of the eye socket is a pyramidal cavity, the top is towards the back, the base is extended to the front, made up of the skull and facial bones. Due to the special protective properties of the sensitive eye, the soft tissues of the orbit do not directly apply to the periosteum, but are covered by the fascia. Therefore, in general, orbital lesions or tumors usually develop in or out of the fascia.
1. Information about eye socket structure
Organizational anatomy of the orbit includes: the tenon wrap around the eyeball from the corneal margin to the optic nerve. From the tenonium capsule to the orbital wall is a fatty tissue with many fibers partly helping the eyeball to stand in a certain position and move flexibly when the muscles work; oculomotor system includes 4 rectus and 2 oblique muscles; orbital arteriovenous system; lymphatic system. Those are the factors that keep the eyeball standing in a certain position in the eye socket, when there is a change caused by orbital disease, it is easy to recognize it.2. Tumors, lesions around the eye socket are common
2.1 Thyroid eye disease Thyroid eye disease is often a complication that causes protrusion of the eyes. The patient feels no pain unless there is open corneal disease. The patient's eyes often bulge on both sides at the same time. Computed tomography showed thickening of oculomotor muscle but not associated with tendon and muscle injury.2.2 Pseudotumorrhea pseudotumorrhea pseudotumorrhea pseudotumor must be distinguished from specific inflammatory conditions such as thyroid gland disease (Graves), sarcoidosis, Wagener granulomatosis,...Based on clinical practice, it is difficult to distinguish between orbital disease. fake u and u real eye socket. Orbital true orbital tumors tend to grow slowly and often show no signs of inflammation, but some pseudotumors present without inflammation. Especially in children, there is inflammation in real tumors such as rhabdomyosarcoma, or ruptured dermoid cyst causing orbital inflammation.
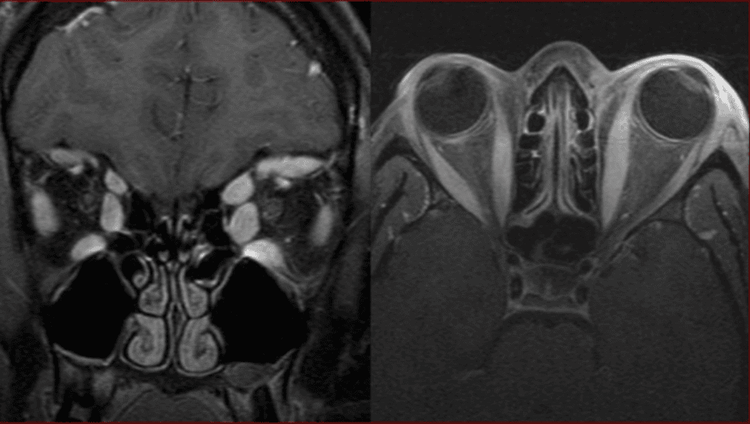
Hình ảnh giả u viêm hốc mắt trên phim CT
Treatment of pseudotumor orbital inflammation has 3 main methods: high-dose corticosteroids, radiation therapy and immunosuppressive drugs. Some pseudotumors that are inactive with corticosteroids or radiation respond well to chemotherapy such as chlorambucil or cyclophosphamide.
Orbital cellulitis: Common symptoms of this lesion are fever and leukocytosis. Computed tomography often shows sinusitis, especially the ethmoid sinus. Orbital tumor: When there are clinical signs, the doctor will examine and palpate the orbital tumor. The eyeball may be displaced away from the tumor site. The tumor mass is more clearly seen on computed tomography. When determining if an orbital tumor is dangerous, medical professionals point out that it can be benign or malignant. If it is a benign orbital tumor, there are dermoid tumors, fibrous dysplasia in children and meningioma, optic nerve tumors in adults.
Malignant orbital neoplasms include rhabdomyosarcoma, osteosarcoma in children, and metastatic melanoma and lymphoma in adults.
The cause of orbital tumor is the abnormal growth of the fundus or metastases to other parts, progressing slowly, for a long time
Primary orbital tumor accounts for 70%, from the next organization The most proximal accounts for about 23%, metastases from other distant organs account for 4%, from systemic diseases accounted for 3%.
The most common and considered major sign of orbital tumor is protrusion of the eye. The convex orientation of the eyeball can help suggest the location of the tumor. Careful assessment of the direction of convexity or deviation of the eyeball can be made relative to the location from which to predict tumor pathogenesis.
Visual loss is also an important symptom in the differential diagnosis of primary tumors affecting the optic nerve, often causing significant visual loss, while extra-orbital (oculomotor) tumors. affect vision only when the mass is large enough to compress the optic nerve.

Tình trạng suy giảm thị lực là triệu chứng giúp chẩn đoán phân biệt bệnh
MRI is a diagnostic imaging tool showing its superiority in the diagnosis of orbital tumors. Orbital MRI images provide details of the tumor's relationship to important delicate vascular and neuroanatomical structures in the orbit.
Treatment of orbital tumors usually includes common methods such as surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy.
Surgical treatment: Depending on the invasive condition, it is possible to only need surgery to remove the blinking membrane or to remove a large area when the disease arises and invades deep into the conjunctiva. Chemotherapy: This method uses drugs to kill cancer cells and slow down their growth. Chemotherapy combined with surgery can improve treatment efficiency, prolong life and quality of life for patients. Radiation therapy: This method of treatment of orbital tumors uses radiation to target the diseased tissue to destroy cells, destroy the cancerous tissue, thereby achieving the purpose of killing cancer cells. Orbital trauma: such as intraocular hemorrhage, foreign body in the eye socket.. Therefore, for accurate diagnosis, some supportive measures such as ultrasound or computed tomography are required. Orbital vasculitis: such as wegener's granulomatosis, nodular polyarteritis... When sick, patients often have systemic signs and symptoms, especially in the sinuses, kidneys, lungs, and disease in the lungs. skin, the patient has a fever, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate increases much. Mucorales disease: the disease manifests in the eye sockets, nose and sinuses in people with diabetes, immunocompromised or systemic weakness. Patients have a high risk of death.
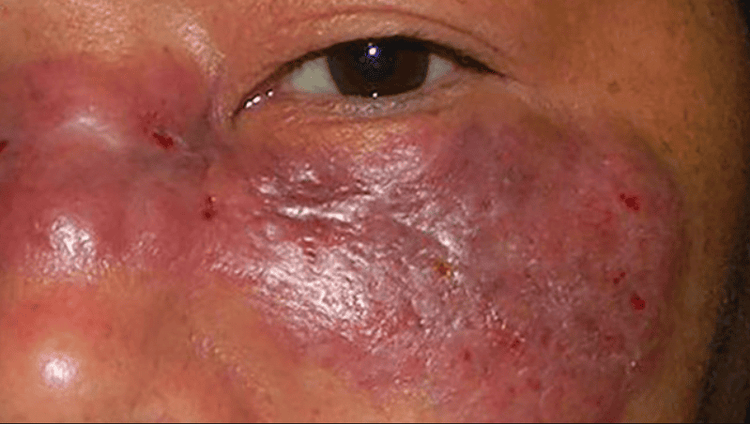
Hình ảnh bệnh nấm mucorales
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space. Customers when choosing to perform tests here can be completely assured of the accuracy of test results.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.