This is an automatically translated article.
Tuberculosis of the lymph nodes or peripheral lymph nodes is a common extrapulmonary disease in our country. Tuberculosis of the lymph nodes can occur at any age. The disease needs to be differentiated from some other diseases, so it is quite difficult to diagnose.
1. What is peripheral lymph node tuberculosis?
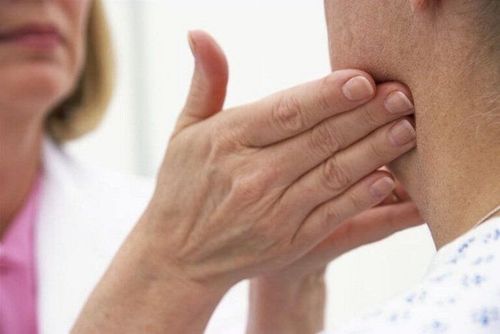
Tuberculosis of the peripheral lymph nodes is a chronic inflammatory condition in the peripheral lymphatic system caused by tubercle bacilli, common in children and young adults. Peripheral tuberculosis lymph nodes may be encountered, including cervical lymph nodes, axillary lymph nodes, and inguinal lymph nodes. In which the cervical lymph node is the most common site, the inguinal lymph node is the rarest The lymph node is associated with TB lesions of other organs such as meningitis, pulmonary tuberculosis,... The disease manifests as enlarged lymph nodes, which may be slightly painful. , often has a series of lymphadenopathy progressing in waves at intervals of years, possibly longer. The lymph nodes that leak out are residues, fibrosis and calcification for a long time, leaving behind ugly, ugly scars. The cause of lymphadenitis is caused by the tuberculosis bacteria that cause lymph node tuberculosis, which is M. tuberculosis, M. bovis, M. africanum, of which mainly M. tuberculosis.
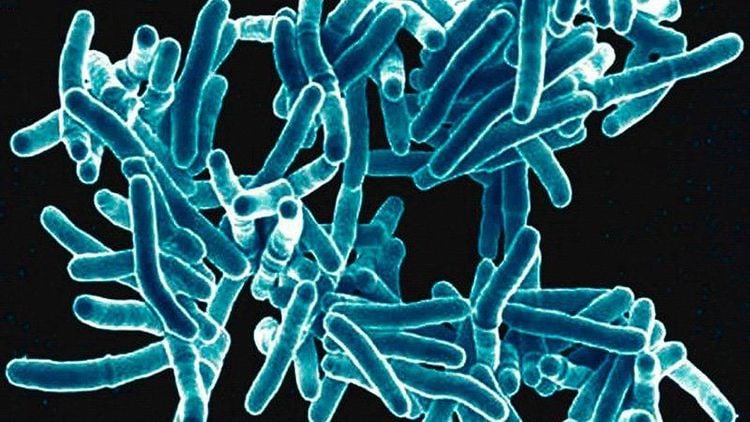
Lao hạch bạch huyết ngoại vi do vi khuẩn lao gây ra
2. Symptoms of Tuberculosis Peripheral Lymph nodes
Systemic symptoms
Mild fever in the afternoon, fatigue, poor appetite, weight loss... There are cases of no systemic symptoms. Attention should be paid to the history of old lymph node tuberculosis and old pulmonary tuberculosis. Local symptoms
Typical
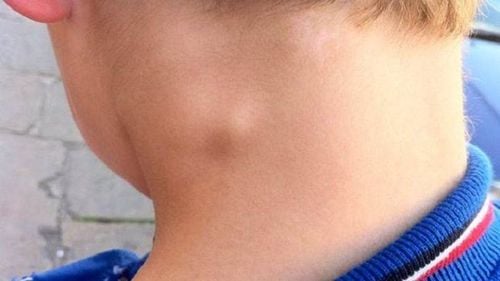
Common locations in the cervical group are the lymph nodes along the sternocleidomastoid muscle, then the supraclavicular and submandibular nodes. In which, the right cervical lymph node is more common than the left cervical lymph node, or TB lymph node is found on one side of the neck. The characteristics of the lymph nodes are from 1 to several cm in diameter, the lymph nodes are firm, mobile, maybe slightly painful, often have a chain of nodes, the skin in the lymph nodes is usually normal. After that, the lymph nodes are usually smooth, the skin outside the lymph nodes is often edematous, red, then burst with yellow pus, when squeezed out, you can see bean paste, the edges of the fistula are jagged, oozing yellow water continuously and for a long time. After a long time, it can heal on its own, but the scar is small, sometimes there is a leak of pus. The disease progresses for a long time, then the lymph nodes stick together and the surrounding organization, the skin outside the fistula may have fistula and many scars.
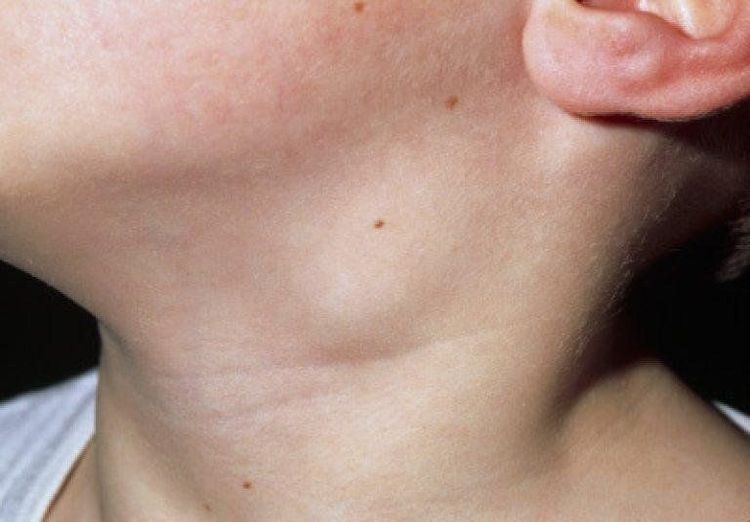
Lao hạch thường xuất hiện ở một bên cổ
Atypical form: The lymph nodes are floating all over the body and internal organs, accompanied by prolonged high fever, rapid weight loss.
Pseudotumor: Peripheral lymph nodes are swollen, solid, like a tumor.
Subclinical symptoms:
Strong positive Mantoux reaction. It is an important test in the diagnosis of lymph node tuberculosis and in the differential diagnosis of Hodgkin's disease, sarcoidosis, and lymphoma. Lymph node biopsy is an important diagnostic test. Laboratory tests found tuberculous cysts with specific inflammatory cells and central pox necrosis. Inoculation of BK from fluid, aspirated pus in the lymph nodes inoculated with Loewenstein's medium found tuberculous bacilli. Lymph node biopsy found the components of the tuberculous cyst and concluded that the lymph node was tuberculosis. Chest X-ray: has diagnostic significance when there are swollen lymph nodes and associated tuberculosis lesions.
3. Treatment
Medical treatment is the main . Based on the principle:
Combination of anti-tuberculosis drugs, from 3 drugs or more. The attack phase uses a combination of 3 to 4 anti-TB drugs, the maintenance phase uses 2 anti-TB drugs. The duration of treatment for lymph node tuberculosis lasts 9-12 months because of the recurrence or recurrence of lymph node tuberculosis.
Điều trị bệnh nội khoa bằng cách kết hợp các loại thuốc chống lao
Surgical treatment
Drainage of pus. Indicated in the case of lymph nodes softening, turning pus and potentially bursting pus, so it is advisable to actively extract pus to avoid leaving bad scars. After the incision, local treatment such as isoniazid or rifampicin powder is sprinkled daily until the wound is dry and the scar heals. In addition, drainage of pus is also indicated in cases where the lymph nodes leak pus not yet, drain the pus by making an incision to widen the fistula, draining all the pus. Surgery to remove the lymph nodes. Indicated in case the lymph node is too big to press on the surrounding tissue, needing lymphadenectomy. The surgical process should be careful not to damage blood vessels and nerves. Remove all lymph nodes. Indicated in cases of purulent lymph nodes, cold abscesses that respond poorly to treatment, need to remove the entire peripheral lymph nodes and then continue to treat tuberculosis. Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consulting services. and comprehensive, professional medical treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.