This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Le Van Quang - Ear, Nose Throat Doctor - Department of General Surgery - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital. BSCKI. Le Van Quang is an expert in the field of ENT with 15 years of experience.Otitis media in children is a complication of otitis media, which, if not treated early, can lead to dangerous conditions, even death. The treatment of mastoid otitis depends on the specific condition of the child and can be medically or surgically treated.
1. Overview of Acute Mastoid Otitis in Children
Mastoid bone is a small bone mass, located just behind the ear that can be palpated. The planar pole is the position where the mastoid bone connects to the ear canal.Acute mastoiditis is inflammation of the mastoid cells in the temporal bone. Because this canal communicates with the ear cavity, the main cause of mastoiditis is acute otitis media or a complication of chronic otitis media, which is why it is often called mastoid otitis.
Otitis mastoid can occur in all subjects, however, children are the subjects of otitis media and have poor resistance, so they are very often affected by mastoid otitis, especially children aged 6-13 months. .
The most common cause of mastoiditis is caused by bacteria such as: Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, group A streptococcus. Other bacteria that can be encountered but less often include green pus bacillus (Pseudomonas aeruginosa), anaerobic bacteria...
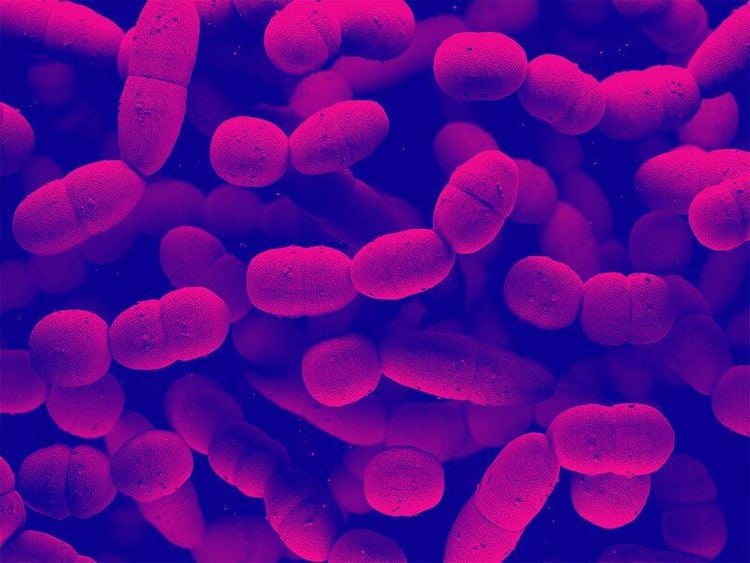
Liên cầu khuẩn nhóm A có thể là nguyên nhân gây ra viêm tai xương chũm
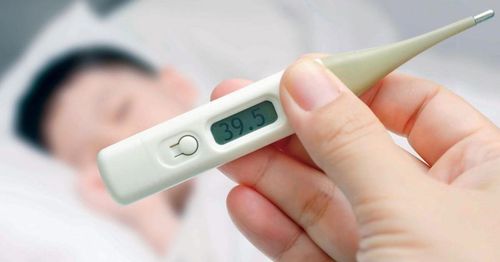
Signs of acute otitis media: Ear pain, hearing loss, purulent ear discharge. In the acute episode of otitis media, the symptoms of otitis will gradually decrease, and signs will appear such as: Pain at the beat of the beat, more purulent discharge, rapid decrease in hearing, mastoid position (behind the rim of the ear). ) pain and redness, pushing the earlobe forward. Systemic symptoms: Re-appearance of fever, which may or may not be high; eat poorly; tired; the child is irritable or fussy. Complications of mastoid otitis:
Blood infection: Mastoid otitis is often caused by highly virulent bacteria, or in children with poor resistance. If not controlled, it can lead to very dangerous bacteremia, showing high fever, shivering, tachycardia, and changes in blood pressure. If not diagnosed and treated early, the risk of death is high. Effects on Hearing: Hearing loss caused by labyrinthitis. Cranial nerve paralysis: Can cause VI or VII nerve paralysis. Due to the position of mastoid bone close to important components including brain, meninges, blood vessels, it can cause very dangerous complications such as: meningeal abscess, meningoencephalitis, lateral vein inflammation, brain abscess.
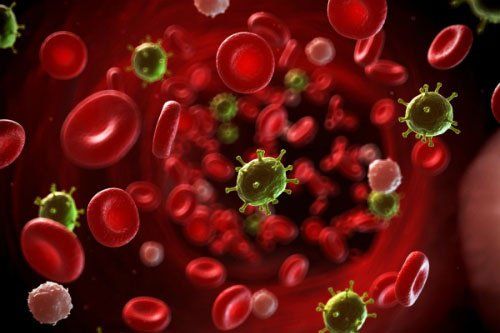
Viêm tai xương chũm không được điều trị kịp thời có thể dẫn đến nhiễm khuẩn huyết
2. Treatment regimen for acute mastoiditis in children
2.1 Treatment goals Treat as soon as possible with antibiotics, preferably with an antibiogram. In case if medical treatment does not respond or the condition is severe, it is necessary to have surgery early to prevent the risk of complications. Combined with a health-enhancing diet. 2.2 Medical treatment High-dose, broad-spectrum antibiotics are indicated for patients: Commonly used groups of antibiotics include second- and third-generation cephalosporins. Anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs: Steroid anti-inflammatory drugs Usually prescribed by injection for the first few days, then orally and gradually reducing the dose. Antipyretic drugs: Paracetamol dose is 10-15mg/kg body weight when the patient has a high fever over 38.5 degrees Celsius. If the fever is below 38.5 degrees Celsius, reduce the child's fever by physical methods such as warm compresses, wearing clothes. cool clothes. Ear drops: Often used are antibiotics aimed at local bacteria. Treatment of respiratory diseases: Use medicines to clear the nose and throat, reduce secretions. Regularly clean the nose and throat with antiseptic solutions, suck the nose if there is a lot of fluid. In addition: Need to puncture the tympanic membrane wider than the drainage hole in the tympanic membrane.
Bệnh nhân có thể điều trị bệnh bằng thuốc theo đơn của bác sĩ
Open the pole to drain the pus and clean the inflammatory tissue, create a communication between the middle ear and mast cells so that the fluid can escape through the tympanic membrane. Complete mastoidectomy is performed if antibiotic therapy has not had the desired effect. In addition, there are other surgical methods such as mastoidectomy and mastoid correction. 2.4 Measures to improve physical condition Children are given adequate rest, eat nutritious food, supplement with vitamin C, drink plenty of water. If the child is still breastfed, actively breastfeed the baby. Secure nutrition.
3. Prevention of mastoid otitis
The best prevention method is to not let the ear get otitis media by: Treating respiratory infections thoroughly, vaccinating, avoiding contact with people with infectious diseases. If you have otitis media, you need to have the right treatment regimen, follow up by a specialist doctor. Do not wean babies too early, before 12 months of age. Weaning children are provided with adequate nutrition, vitamins and minerals. Acute mastoiditis in children needs timely detection and treatment to prevent possible complications. So, if you find that your child has symptoms of otitis media after otitis media, it is necessary to take the child to a medical facility immediately.Vinmec International General Hospital examines and treats common ear, nose and throat diseases, head and neck tumors, congenital malformations of the ear, nose and throat area with the most optimal internal and surgical methods for patients, both children and adults. Coming to Vinmec International General Hospital, patients will receive a direct, dedicated and professional examination from a team of qualified and experienced medical staff.
If you have a need for consultation and examination at the Hospitals of the national health system, please book an appointment on the website for service.
Recommended video:
Incision of tympanic membrane to cure otitis media
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.