This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Do Van Manh - Emergency Department - Vinmec Ha Long International Hospital.
Knowing how to distinguish between edible mushrooms and poisonous mushrooms is the most effective measure to prevent poisoning by poisonous mushrooms. In addition, medical staff also need to know the diagnosis, initial management and early treatment of toxic mushroom poisoning to avoid severe disease progression and death.
1. Classification of poisonous mushrooms
Mushrooms contain toxins that will poison the human body or animals when eaten. To classify poisonous mushrooms, there are two ways to classify them:
1.1 Classification of poisonous mushrooms according to their toxin composition According to this division, poisonous mushrooms will have 8 groups:
Amatoxin (Cyclopolypeptide): Amanita verna, A. virosa, A. phalloides, Galerina autumnalis, Lepiota brunneoincarnata,... Gyromitrin (Monomethylhydrazin): Gyromitra esculenta, G. infula,... Orellanin: Cortinarius orellanus, C. speciosissimus, C. Splendens,... Muscarin: Inocybe fastigibeata, Cl dealbata,... Ibotenic Acid and Muscimol: Amanita muscaria, A. pantherina,... Coprin: Coprinus atramentarius, Coprinus disseminatus,... Psilocybin and Psilocin are found in fungi belonging to 4 genera: Psilocybe, Panaeolus, Conocybe and Gymnopilus Chlorophyllum molybdites, Russula foetens, Omphalotus nidiformis... causing digestive disorders:

Nấm ô tán trắng phiến xanh – Chlorophyllum Molybdites
1.2 Classification of toxic mushrooms according to the time of onset of toxicity Slow-acting poison: The time for poisoning symptoms to appear after eating poisonous mushrooms is usually 6 - 40 hours (average 12 hours) . Because the first symptoms of poisoning appear after eating for a long time, this type is often fatal. Mushrooms containing Amanita verna, Amanita virosa, Amanita phalloides,... will belong to the group of slow-acting poisons and have a mortality rate of about 50% or even higher. Rapid-acting poisons: In this case, the first symptoms The first will appear within 6 hours after eating the mushroom. Mushrooms containing Inocybe fastigiata, Chlorophyllum molybdites... will belong to the group of fast-acting poisons. Patients with this group of mushrooms, if they are treated promptly with toxic mushrooms and apply basic first aid measures, the survival rate and good recovery are relatively high.
2. Signs of toxic mushroom poisoning
Patients after eating mushrooms containing toxins, symptoms of mushroom poisoning will take place in the following stages:
Latent stage (from the time of eating mushrooms to the appearance of the first symptoms): Usually lasts a long time. from 6 to 24 hours (average 12 hours) and after eating mushrooms, the patient does not feel any abnormal signs. eat mushrooms. At this stage, the patient will have symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea (watery, milky stools like cholera) Pseudo-recovery phase: After about 1-3 days When symptoms of digestive disorders appear, these symptoms seem to be over. However, this stage is considered to be a period of worsening disease because this is the time for toxic substances to damage liver cells Stage of liver and kidney failure: Usually occurs on day 4 or 5 after eating mushrooms. The clinical manifestation of the patient in this period will be jaundice of varying degrees; gastrointestinal bleeding, brain, urinary tract, subcutaneous; edema; Oliguria or anuria; coma and lead to death due to liver failure, kidney failure, cerebral edema complications.

Một số dấu hiệu của ngộ độc nấm độc
3. Treatment and treatment of toxic mushroom poisoning
3.1 Treatment at home and in medical facilities It is necessary to quickly take measures to eliminate toxins from the body such as:
Try to make the patient vomit food containing mushrooms that have just been eaten within 1 the first hour In case the patient shows strange symptoms after 6 hours of eating mushrooms, activated charcoal can be given at a dose of: 1g/kg, time from 2-3 hours/time. Medical staff perform washing measures. stomach for the patient and and time after eating within 1-2 hours. 3.2 Treatment of toxic mushroom poisoning at the hospital Check the hematologic parameters: AST (GOT), ALT (GPT), bilirubin, protrombin content, PT, glucose, urea, creatinine, electrolytes, pH Perform routine blood test Perform urine test with 11 basic criteria.

Nước tiểu được xét nghiệm giúp đánh giá tình trạng ngộ độc của cơ thể
Toxic mushrooms containing amatoxin are treated with the following protocol at the hospital:
Give activated charcoal with a frequency of 3-4 hours/time, and sorbitol with it. To rule out gastrointestinal reabsorption of amatoxin, it is necessary to use activated charcoal and sorbitol for at least 3 days Aspiration drainage for 48 hours with a nasogastric tube Penicillin G at a dose: Adults 250,000 units/kg injection intramuscularly or intravenously twice a day for 5 days Children are prescribed with a dose of 300,000 - 500,000 units depending on weight 2 times / day for 5 days. Taking Legalon (Silymarin, Silibinin, Silybin) high dose: Adults take 600 - 1200 mg x 2 times/day, children 10 - 15 mg/kg body weight 2 times/day. When liver enzymes return to normal values, discontinue use Silibinin can be used instead of Legalon at a dose of 20 - 80mg/kg/day divided into 2 intravenous infusions over 2 hours Cimetidine: Adults take 400mg 3 times/day for 5 days. Children take a dose of 10 mg/kg body weight 3 times/day for 5 days. Use Vitamin C at a dose of 1g, 2 times/day, intravenously until biochemical indicators are close to normal. Infusion 0.9% sodium chloride solution or Ringer lactate with the volume of infusion according to the degree of toxicity, kidney status responding to diuretics.
Truyền dịch điều trị ngộ độc nấm
Furosemide (Lasix): 20mg IV tube, repeat if necessary to reach 150-200ml of urine/hour Anti-hypoglycemia by Glucose infusion (10% - 1000ml/24h) Restore liver function by administering N Intravenous acetylcysteine 70mg/kg first dose then 35mg/kg body weight every 4 hours. Discontinue when liver function is restored Monitor and correct electrolyte disturbances and correct acidosis with sodium bicarbonate Coagulation disorder or bleeding occurs: Intramuscular vitamin K injection at a dose of 10 - 20 mg or intravenous infusion 10 - 40 mg/24 hours, depending on the degree of coagulation disorder Fresh plasma infusion when protrombin < 40% when bleeding is present Treat brain edema: Mechanical ventilation Mannitol use: When threatened brain failure, IV infusion 400ml (20%) in 1 hour If there are cerebral - liver manifestations, then intubate to protect the airway. conduct hemodialysis, if diuretics are no longer effective Anti-infective: use broad-spectrum antibiotics (3rd generation cefalosporin), high dose Plasma exchange or artificial liver.
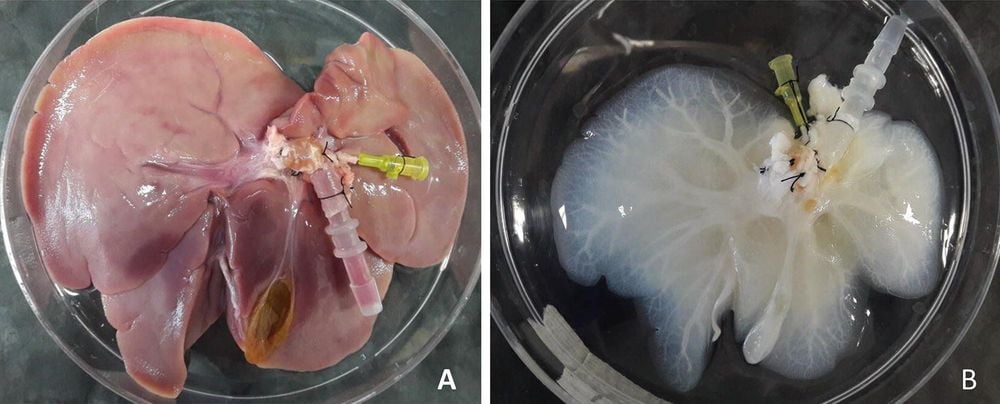
Hình ảnh gan nhân tạo được sử dụng thay thế
Specialist Doctor Do Van Manh has more than 10 years of experience in the field of Critical Care - Anti-poison. He used to be the Deputy Head of the Intensive Care Unit at Quang Ninh General Hospital before working at Vinmec Ha Long International Hospital.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health System nationwide for medical examination and treatment or contact to book an appointment online HERE.
SEE ALSO:
Notes when giving first aid to people with food poisoning Identify signs and first aid when having food poisoning Signs of stomach pain due to food poisoning