This is an automatically translated article.
Osteoarthritis, especially herniated disc, accounts for 45-60% of inpatients in neurology departments. The disease usually occurs in the age group of 20-50 years and tends to increase in young people. Treatment of herniated discs through the skin under enhanced X-ray is an effective method commonly used today.
1. Overview of herniated disc disease
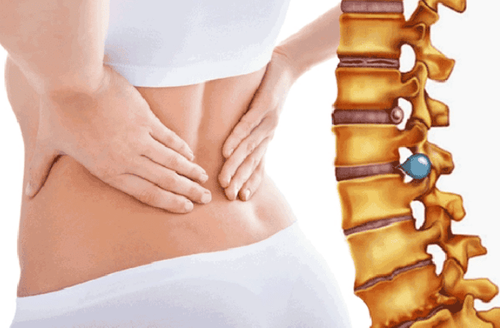
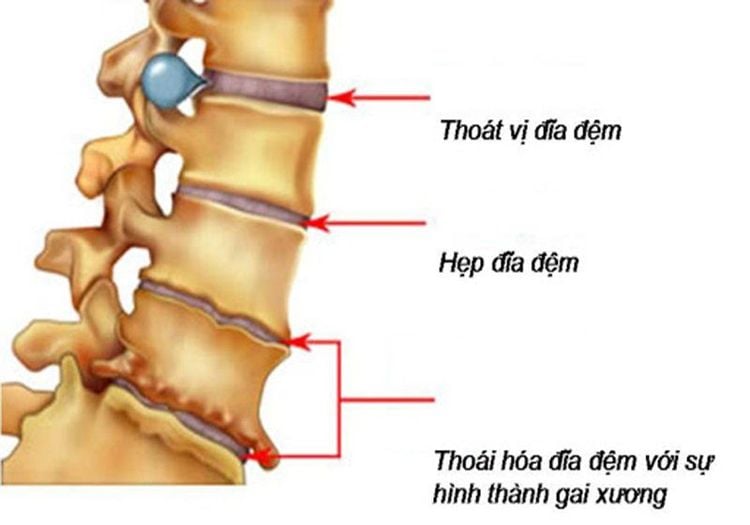
The disc is a cushion with a shock-absorbing role located between 2 vertebral bodies. Inside the disc are living cells that are constantly producing new cells. These cells get oxygen, nutrients, sugars, and proteins from the bones that help rebuild and keep the cells healthy. When the disc is constantly moved and torn, the fluid will escape into and out, causing a herniated disc. This fluid can press on nerve roots and spinal cord, causing back pain.
1.1 Causes of disc herniation
In addition to causes due to natural degeneration, trauma, and falls, people with herniated discs mostly suffer from diseases due to wrong living and working postures. For example: sitting with a curvature of the spine, sudden changes in posture, carrying heavy objects in the wrong way... leads to back vertebrae injury, disc herniation.
1.2 Symptoms of disc herniation
Patients should visit the doctor when they see signs of disc herniation such as:
Pain originating from the spine, spreading to the arms, shoulders or legs (depending on the location of the hernia in the back or neck). Pain is often felt after injuries, accidents, falls, etc. Muscle weakness: Feeling achy, weak muscles due to blocked nerves that transmit impulses from the brain. Feeling of crawling or numbness: In some areas of the skin that nerve roots govern. The method of treating disc herniation through the skin under enhanced X-ray has the following advantages:
Reduces the volume of the herniated nucleus by dissolving the mucinous nucleus with heat or chemicals. Television-enhanced radiographs help guide and track the percutaneous needle puncture into the disc directly and continuously, ensuring the safety and high accuracy of the procedure.
Đau cột sống là triệu chứng phổ biến
2. Treatment of percutaneous disc herniation under enhanced X-ray
2.1 Preparation for the procedure
To perform the treatment of herniated discs through the skin under the X-ray, it is necessary to prepare:
Implementation team:
Specialist doctor, auxiliary doctor; Nursing; Optical technician. Means of use:
Fluoroscopy; High frequency wave generator (if need use high frequency wave); Lead vest, apron to help shield from X-rays; Film, film printers and image storage systems. Drugs: Including local anesthetics, general anesthetics, water-soluble iodine contrast agents, skin and mucosal antiseptic solutions.
Common medical supplies: 5.10ml syringe, distilled water (physiological saline), surgical clothing; sterile intervention kit (knife, scissors, forceps, instrument tray, etc.), cotton gauze, surgical tape; medicine box and accident first aid box.
Special medical supplies:
17G disc puncture needle, anesthetic needle; Radiofrequency ablation needles (if radiofrequency treatment); Syringe pump 10ml, 20ml; Transfusion set. Patients need to prepare:
Be explained in detail about the procedure to coordinate with the doctor. Perform clinical examination before the procedure. Fasting, drinking before 6 hours. Do not drink more than 50ml of water. In the intervention room: The patient lies on his stomach or on his side depending on the doctor's instructions. The doctor installs a machine to monitor breathing, pulse, electrocardiogram, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation in the peripheral blood. Disinfect and cover with a sterile, perforated cover.

Trước khi làm thủ thuật, bệnh nhân không uống quá 50ml nước.
2.2 Percutaneous herniated disc treatment procedure
Steps to perform the treatment of herniated disc through the skin under X-ray luminosity:
Step 1: Anesthetize the patient locally with 2% Lidocaine (2-10ml). Step 2: Put the patient on the table to increase the light, place the intravenous line. Step 3: Locate the disc to be treated under the light curtain. Step 4: The doctor disinfects the injured area, spreads aseptic dressing with holes on the site to be biopsied. Step 5: Carry out local anesthesia in layers Step 6: Insert the needle through the skin into the disc to be treated, using the light curtain to control the puncture. Step 7: When the needle is inserted into the center of the intervertebral disc nucleus, depending on the treatment purpose, it is possible to inject chemicals or burn the intervertebral disc nucleus with high frequency waves. Step 8: Withdraw the needle and tape the puncture site.
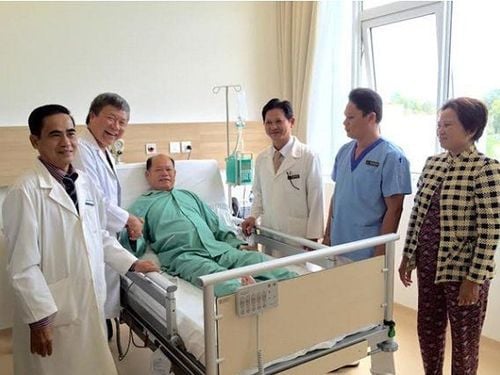
Điều trị thoát vị đĩa đệm qua da tại bệnh viện Vinmec
3. Complications after the procedure and treatment direction
Some common complications after the procedure include:
Bleeding at the needle puncture site: Apply compression at the puncture site. Hematoma in the soft tissue next to the needle puncture site: Further follow-up. Accidentally poking dangerous organs and structures: Consider handling on a case-by-case basis. No effective treatment: Carefully evaluate and consider a second treatment or surgical consultation. Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in medical examination and treatment, patients can rest assured to visit. and hospital treatment.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.