This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Dr. Do Minh Hung - Head of General Surgery Department, Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Inguinal hernias account for about 75% of all abdominal wall hernias. The inguinal canal is located in the groin area. In men, the testicles usually pass through the inguinal canal into the scrotum shortly before birth. In females, the inguinal canal is the site of the uterine ligaments.
1. What is an inguinal hernia?
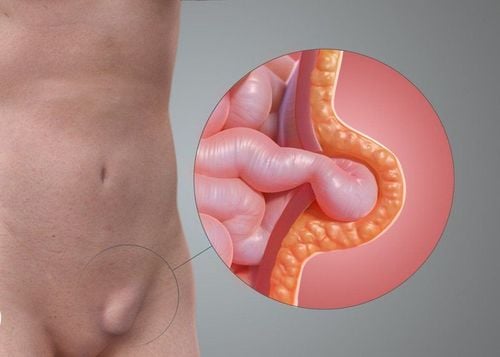
An inguinal hernia occurs in the groin area when fat (greater omentum) or bowel enters the inguinal canal. If you have a hernia, it creates a bulge in the groin or scrotum and can cause pain with movement.
Many people do not seek treatment for an inguinal hernia because it may not cause any symptoms. However, prompt treatment can help prevent the hernia from getting larger, causing obstruction and discomfort.
2. What are the symptoms of an inguinal hernia?
An inguinal hernia is the most noticeable type of hernia because of its appearance. The hernia causes a bulge along the inguinal crease (in the groin area), which can increase in size when you stand up or cough or strain (causes to increase intra-abdominal pressure). This type of hernia can be painful or sensitive to the touch.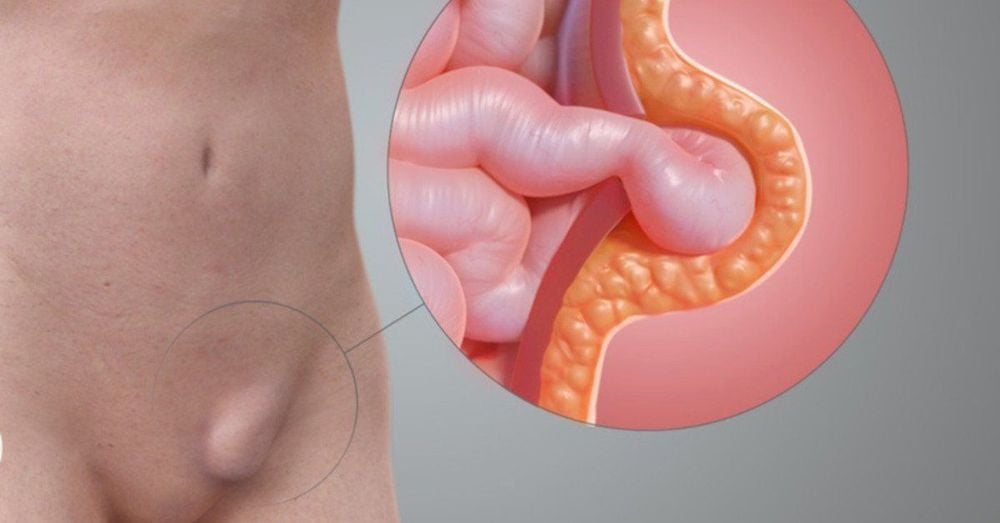
Thoát vị bẹn ở vùng háng khi lớp mạc nối lớn hoặc ruột chui xuống ống bẹn tạo khối thoát vị bẹn
Other symptoms may include:
Pain when coughing, exercising, or bending over Burning sensation Sharp pain Heaviness or tightness in the groin Swelling of the scrotum in men
3. What are the causes and risk factors of an inguinal hernia?
There is no known cause, but weakness in the abdominal and groin muscles is thought to play a large role in hernia formation. Along with high pressure in this area of the body can eventually cause a hernia. Some of the main causative factors include:
Risk factors that can increase your chances of getting an inguinal hernia include: Genetics; History of hernia; Male; Premature birth; Being overweight or obese... Factors that increase intra-abdominal pressure: Pregnancy, often standing for long periods of time, frequent constipation, straining to pass or urinate, lifting heavy objects, chronic cough count or sneeze A pre-existing weakness in the abdominal wall A combination of increased intra-abdominal pressure and a pre-existing weakness in the abdominal wall Abdominal fluid (ascites)
4. What are the complications of the disease?
Most inguinal hernias get bigger over time without surgery. Massive hernia puts pressure on surrounding tissues. In men, a large hernia can reach the scrotum, causing pain and swelling.
Inguinal hernias can also become trapped or strangulated. Trapped hernia occurs when the herniated organ is trapped in the groin area, the scrotum cannot get back into the abdomen. The strangulated inguinal hernia is more serious because the herniated visceral is tightened and cannot return, but the blood vessels supplying the visceral are also compressed, causing the herniated viscera to die. A strangulated inguinal hernia is a surgical emergency because it is life-threatening.
5. How many types of inguinal hernia are there?
Inguinal hernia can be indirect or direct. Indirect inguinal hernia is the most common type. It usually occurs in premature babies, before the inguinal canal can fully develop. However, hernias can happen at any time in your life.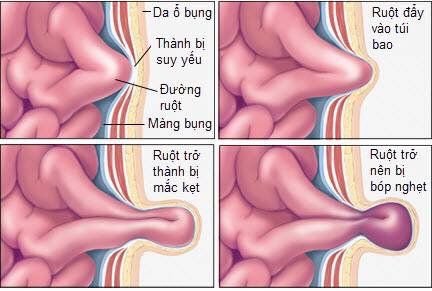
Thoát vị bẹn có 2 thể là thoát vị bẹn gián tiếp và thoát vị bẹn trực tiếp
Direct inguinal hernia is more common in adults, presumably due to weakening of the abdominal wall muscles in adulthood. This type of hernia is mostly seen in men.
6. How to diagnose inguinal hernia?
Diagnosis is mainly based on clinical examination. Your doctor will ask you to stand or cough while standing to check for the hernia when it is at its largest. Your doctor can easily push herniated organs back into your abdomen while you're lying down. However, if you cannot push the herniated organ in, you may have a trapped or strangulated inguinal hernia.7. How to treat inguinal hernia?
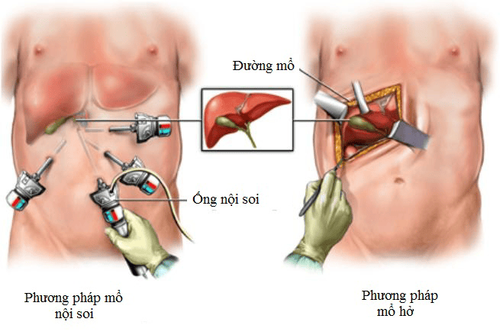
Surgery is the main treatment for an inguinal hernia. It is a very common surgery and has a high success rate when performed by a well-trained surgeon. Your doctor will recommend repairing the inguinal wall with open surgery or laparoscopic surgery.8. What is the prevention and prognosis of inguinal hernia?
Although you cannot prevent birth defects, you can slow the progression of a hernia by:
Maintain a healthy weight Diet high in fiber Do not smoke Avoid heavy lifting Treatment Early can help cure inguinal hernia. However, there is always a risk of recurrence and complications such as infection after surgery, scarring.