This is an automatically translated article.
An acute ischemic stroke, also known as a cerebral infarction, occurs when an area of the brain is deprived of blood, usually due to a narrowing or blockage of an artery in the brain. Cerebral edema is an acute neurological complication that can occur in patients with acute ischemic stroke.
1. Signs of cerebral edema in acute ischemic stroke
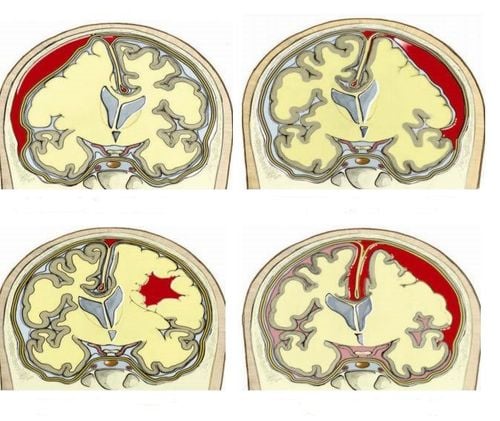
Cerebral edema is an acute neurological complication in ischemic stroke, this condition usually appears 2-3 hours after stroke, reaches its maximum level after 24 hours and persists for 5-10 days. Consequences of cerebral edema are increased intracranial pressure, decrease in cerebral perfusion pressure, which can cause depression, brain jam, which is dangerous to the patient's life. That's why it needs to be treated aggressively.
Manifestations of cerebral edema may coincide with symptoms of ischemic stroke, making detection difficult. Symptoms of cerebral edema may include:
Patient has a headache, neck feeling Nausea or vomiting Patient feels dizzy Patient has memory loss, consciousness Patient has difficulty speaking or moving Patient has convulsions jerk The patient lost his sight

Đau đầu, cổ là một trong các dấu hiệu xảy ra sớm
In addition to the above clinical manifestations, doctors will rely on brain CT images or brain MRI to predict the possibility of brain edema in patients with acute ischemic stroke. In which, brain CT scan without contrast is the first choice to diagnose and monitor patients with cerebral edema due to cerebral hemisphere or cerebellar infarction. Follow-up CT during the first 2 days is a useful measure to identify patients at high risk of developing symptomatic edema. Patients are predicted to have cerebral edema when: CT brain at 6 h has hypoattenuating images, infarct area ≥ 1/3 of MCA and midline deviation is useful in predicting cerebral edema. On brain CT images, if more than 50% of the perfusion area of the middle cerebral artery is damaged within 12 hours of the stroke. Measurement of MRI DWI volume in the first 6 hours is useful, if the volume is > 80 ml, it is predictive of very rapid disease progression.
2. Treatment of cerebral edema caused by ischemic stroke
2.1. Non-specific treatments
Place the patient with acute ischemic cerebral edema in a supine position of 300 to avoid obstruction of venous return. This method can reduce intracranial pressure by 7-10 mmHg.
Control patient temperature: Keep patient temperature below 360C and room temperature between 22 - 260C. The purpose of this is to reduce energy metabolism, inhibit the release of Glutamate and free radicals in the body.
Provide enough oxygen to the patient: Aim to achieve SpO2 > 95% or measure arterial gas PaO2 > 65mmHg.
Anti-excitation and convulsion: Because the more excited the patient, the more convulsive, the more hypoxic, leading to increased cerebral edema, causing metabolic disorders, becoming a pathological spiral. Barbiturates can be used at a dose of 5-6 mg/kg/day, not more than 3-5 days. This drug has both anticonvulsant effects and reduces intracranial pressure by reducing metabolism, reducing cerebral blood flow, reducing oxygen use, redistributing blood from healthy brain areas to brain areas. damaged by Robin Hood's reverse volume effect, stabilizing cell membranes, reducing cerebrospinal fluid secretion, neutralizing free radicals, etc. However, it is necessary to pay attention to respiratory failure and cardiovascular collapse.
It is necessary to maintain cerebral perfusion pressure > 70 mmHg to keep intracranial pressure < 20 mmg. Keep arterial pressure and plasma osmolality at reasonable levels.
Cho người bệnh thở oxy
2.2. Specific treatments against cerebral edema
Osmotic therapy with mannitol: This is the drug with the best effect against cerebral edema. Mannitol pulls water from the intercellular space into the vascular lumen, thereby reducing blood viscosity, causing increased blood flow, and it also has the effect of increasing blood pressure.
Hypertonic saline serum: It has the effect of absorbing intercellular water, thereby reducing intracranial pressure, reducing blood viscosity, increasing blood flow. Many opinions suggest that 3% saline serum should be used for many days to combat cerebral edema in stroke patients.
Drainage of cerebrospinal fluid: This is a method of inserting a catheter into the ventricles to drain. However, the effectiveness of this method is limited and there is a potential risk of encephalitis - meningococcal infection, which is life-threatening.
Decompressing craniotomy: In the case of an ischemic stroke at the base of the middle or anterior cerebral artery causing extensive cerebral edema, craniotomy to reduce intracranial pressure should be considered, when Medical treatments were unsuccessful.
Phẫu thuật mở hộp sọ
Reasonable pulmonary hyperventilation reduces intracranial pressure, this method has the effect of cerebral vasoconstriction and brain volume reduction. Experts recommend keeping PaCO2 between 30-35mmHg. However, if the pulmonary ventilation is excessively PaCO2 < 30 mmHg, there is a risk of vasoconstriction and a decrease in cerebral perfusion pressure.
Cerebral edema in acute ischemic stroke is one of the acute neurological complications that endanger the patient's life, therefore, it should be detected and treated promptly. Patients with cerebral edema can be accurately diagnosed as soon as the above symptoms are detected by examining and combining other modern laboratory diagnostic methods such as: physical examination of the head and neck, neurology, imaging CT or MRI of the brain, blood tests.
Stroke is an extremely dangerous disease and can cause many complications in addition to cerebral edema such as heart complications, pneumonia, venous congestion, depression,... Therefore, we should get screened early. stroke so that appropriate treatment options can be given and future complications can be avoided. Currently, Magnetic Resonance Imaging - MRI/MRA is considered a "golden" tool to screen for brain stroke. MRI is used to check the condition of most organs in the body, especially valuable in detailed imaging of the brain or spinal nerves. Due to the good contrast and resolution, MRI images allow to detect abnormalities hidden behind bone layers that are difficult to recognize with other imaging methods. MRI can give more accurate results than X-ray techniques (except for DSA angiography) in diagnosing brain diseases, cardiovascular diseases, strokes,... Moreover, the process MRI scans do not cause side effects like X-rays or computed tomography (CT) scans.\
Vinmec International General Hospital currently owns a 3.0 Tesla MRI system equipped with state-of-the-art equipment by GE. Healthcare (USA) with high image quality, allows comprehensive assessment, does not miss the injury but reduces the time taken to take pictures. Silent technology helps to reduce noise, create comfort and reduce stress for the client during the shooting process, resulting in better image quality and shorter imaging time. With the state-of-the-art MRI system With the application of modern methods of cerebral vascular intervention, a team of experienced and well-trained neurologists and radiologists, Vinmec is a prestigious address for stroke risk screening and screening. reliable goods.
In the past time; Vinmec has successfully treated many cases of stroke in a timely manner, leaving no sequelae: saving the life of a patient suffering from 2 consecutive strokes; Responding to foreign female tourists to escape the "death door" of stroke;...
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide. , or register online HERE.