This is an automatically translated article.
Cellulitis is an infection of the skin. If left untreated, the disease can spread quickly and be life-threatening. The most important thing is to get an early diagnosis.1. What is cellulitis?
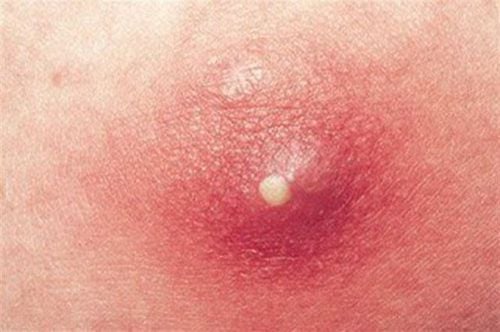
Cellulitis is a fairly common condition that can cause a serious skin infection that manifests as skin swelling, redness, heat, and blisters. The disease can spread quickly to nearby areas of the body. Cellulitis can occur anywhere on the body, but is most commonly found in the lower legs. Cellulitis can spread to the lymph nodes and blood. Cellulitis, if treated late, can spread quickly and lead to very dangerous sepsis. The cause of the disease is usually caused by bacteria such as Streptococcus and Staphylococcus that penetrate through the damaged skin,... In addition, it causes diseases such as S.pneumoniae, H. influenzae, P. aeruginosa,...
2. Symptoms of cellulitis
Local symptoms:
Sudden appearance of a swollen, hot, red and painful area of skin, unclear limits, easy to diffuse, may have blisters, hemorrhage. In severe cases, necrosis, subcutaneous abscess, myositis, myositis, sepsis and other serious infections may occur, especially in immunocompromised, diabetic, young children. children, the elderly,.. The most common location is the lower leg. Bacteria penetrate through superficial wounds, ulcers, interstitial inflammation causing cellulitis. Other possible sites such as: periocular cellulitis can cause ocular paralysis, vision loss, cavernous sinus vein occlusion, periorbital abscess, brain abscess, encephalitis - meningitis. Recurrence often results in long-term lymphatic damage causing lymphedema and venous insufficiency of the lower extremities. Systemic symptoms such as fever, fatigue.
Viêm mô tế bào trường hợp nặng triệu chứng có thể là nhiễm khuẩn huyết
3. Diagnosis of cellulitis
Diagnosis of blood cultures or taking samples from sores and cracks to determine the cause of the disease due to bacteria so that appropriate antibiotics can be determined. in retrospective diagnosis. In addition, leukocytes may be increased, erythrocyte sedimentation rate increased, and procalcitonin increased in blood.
4. Treatment of cellulitis according to the guidance of the Ministry of Health
Medical treatment:
Active antibiotic treatment according to the doctor's prescription, oral antibiotics can be used for mild cases. However, in severe cases such as suspected sepsis, arthritis, fasciitis, hospitalization is required for intravenous antibiotic treatment. It is possible to choose one of the antibiotic regimens such as Penicillin G, Amoxicillin-clavulanate, Ceftriaxon, Clearithromycin, .. In case of thrombophlebitis, anticoagulation should be used as indicated. Surgical treatment:
In severe cases of cellulitis, antibiotics are not effective, doctors can combine surgery to remove necrotic tissue.
5. Prevention
Clean personal hygiene Enhance nutrition, improve resistance Wounds need care, daily dressing changes, medication according to indications.
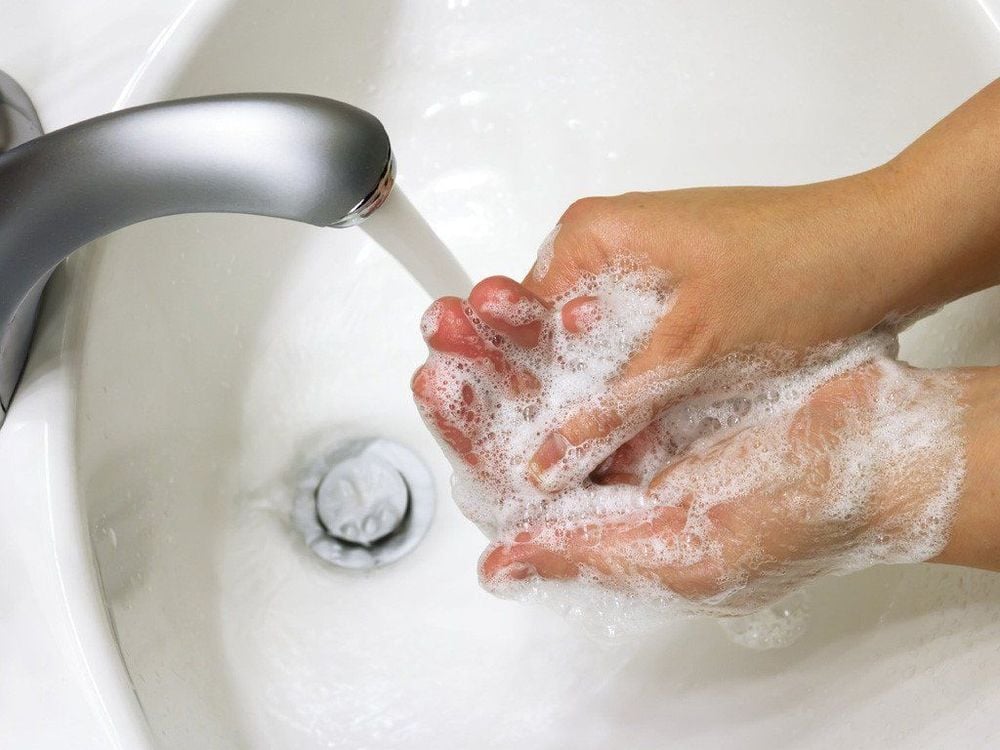

Cách phòng bệnh viêm mô tế bào là giữ vệ sinh cá nhân sạch sẽ