This is an automatically translated article.
Transcranial doppler ultrasound is one of the commonly applied methods for the purpose of studying and checking brain health... In emergency resuscitation, transcranial doppler ultrasound is used. for diagnosis and monitoring of brain death, vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage, increased intracranial pressure,...
1. What is transcranial doppler ultrasound?
Doppler ultrasound is a method of using ultrasound waves to investigate patterns of movement inside the body such as the movement of red blood cells (changes in frequency, speed) or arterial pressure.
When performing a doppler ultrasound, the doctor sends a beam of ultrasound waves of the right frequency through moving objects in the body. The computer then receives the signals and converts them into parameters. Finally, the doctor reads the obtained readings and makes a diagnosis for the patient.
Transcranial doppler ultrasound is also a procedure performed similar to conventional doppler ultrasound. A transcranial ultrasound procedure sends exploratory ultrasound waves into areas where the skull is thinner than elsewhere. The waves will collect information related to the image of the whole skull, especially the fluid-filled chambers in the brain.
There are 3 key locations to perform transcranial doppler ultrasound:
Transcranial Doppler in the temporal region: Examine the anterior, middle, and posterior cerebral arteries; Orbital transcranial Doppler: Examine the ophthalmic and carotid arteries; Transcranial Doppler in the suboccipital region: Record the blood flow rate in the vertebral and basilar arteries. Transcranial doppler ultrasound is a non-invasive method, so it is very safe, low cost, can be performed many times in patients or for continuous monitoring and can also be performed at the bedside.
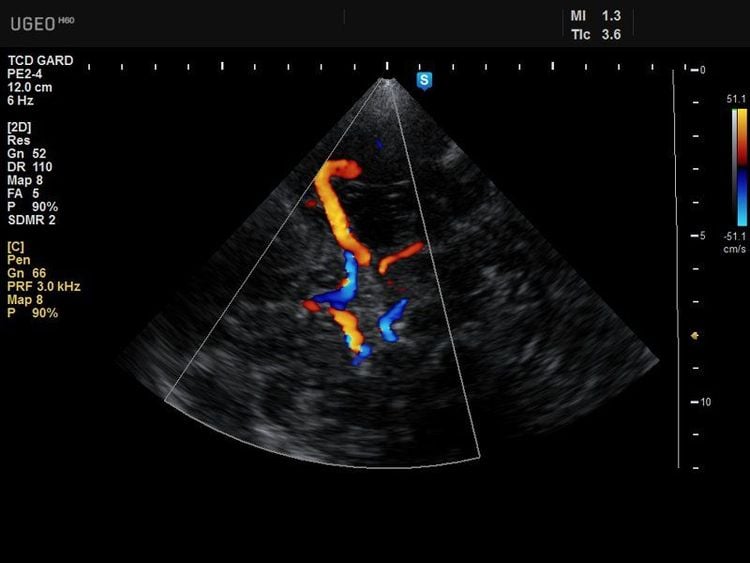
Siêu âm doppler xuyên sọ an toàn và dễ thực hiện
2. Transcranial doppler ultrasound procedure in emergency resuscitation
2.1 Indications and contraindications
Indication
Diagnosis of brain death; Monitor and diagnose increased intracranial pressure; Monitor and diagnose vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage; Intraoperative monitoring; Performed when the patient is seriously ill, has difficulty moving. Contraindications
Transcranial doppler ultrasound is a non-invasive and non-hazardous technique, so there are no contraindications.
2.2 Preparation
Implementation personnel: Doctors and nurses; Technical facilities: Transcranial doppler ultrasound machine, cleaning cloth, transducer lubricating gel, patient table or chair, computer, printer; Patient: The procedure is explained, placed in the supine position, clean and well exposed of the ultrasound window; Medical record: Specify necessary information such as name, age, address, gender, clinical diagnosis, date and time of transcranial doppler ultrasound and name of doctor performing ultrasound.
2.3 Implementation process
Check records
Name, age, clinical diagnosis, reason for doing transcranial doppler ultrasound.
Check the patient
Check the vital functions of the patient: Respiratory status, temperature, pulse, blood pressure. At the same time, it is necessary to check whether the ultrasound probe window areas are clean and well exposed;
Perform the technique
Ultrasound in 3 key positions:
Ultrasound through the temporal window: The thickness of the temporal bone varies between ethnicities or gender, so the doctor will consider the following factors: before specifying to perform ultrasound at this site. When performing, the doctor will place the probe above the cheekbone area in front of the ear, perform the test and select the best probe position. The computer will record the signal of the anterior, middle and posterior cerebral arteries as soon as the ultrasound waves reach the appropriate depth; Ultrasound through the orbital window: Before performing the procedure, the doctor will instruct the patient in technique because the orbital ultrasound technique requires the patient's eyeball to be stationary. When performing, the patient focuses his vision forward, the doctor will place the transducer on the eyelid, use a light force just enough for the ultrasound gel to contact the skin surface and record the ultrasound results. minus; Transoccipital suboccipital window ultrasound: The occipital bone is the bone located at the bottom right of the skull, covering the occipital lobe. When performing ultrasound, the patient needs to coordinate with the doctor to find the transducer place, then ultrasound and record the results.
Theo dõi huyết áp của người bệnh sau khi siêu âm
2.4 Monitoring and dealing with complications after ultrasound
It is necessary to monitor the patient's vital indicators such as pulse, temperature, blood pressure, respiration,...; No complications occurred due to transcranial ultrasound. In order to shorten the transcranial doppler ultrasound time and obtain the most accurate results, the patient needs to coordinate with the doctor's instructions during the procedure.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE