This is an automatically translated article.
Intracranial hypertension needs to be accurately diagnosed and treated promptly to minimize the complications that cause later as well as the risk of death for the patient.1. Diagnosis of increased intracranial pressure
Patients will be carefully diagnosed about the raised intracranial pressure as well as the cause of the syndrome. Specific diagnoses to be made of a person with signs of increased ICP include:1.1 Confirmed ICP diagnosis Increasing headache Nausea or vomiting Possible disturbances of consciousness accompanied by ophthalmoscopy: There is papilledema. 1.2 Differential diagnosis of elevated intracranial pressure Coma: Hyperosmolar coma, ketoacidosis, hypoglycemia, hepatic coma... Blurred vision: ocular physical diseases Headache: Neurological causes Peripheral nerves, vasomotor disorders 1.3 Diagnosis of increased intracranial pressure caused by traumatic brain injury: CT scan patients can see images of brain bleeding, brain damage due to contusion, skull fracture. Due to brain bleeding: Image of bleeding in brain parenchyma, ventricle, subarachnoid hemorrhage when CT scan Brain tumor: Image, location, size, number of brain tumors can be detected when taking MRI or CT Due to hydrocephalus: CT scan and MRI show images of dilated ventricles. meningitis, brain abscess, MRI scan can clearly see encephalitis, brain abscess. In addition, the diagnosis of increased intracranial pressure is also through other signs such as hypercapnia, hypoxemia, mechanical ventilation using PEEP, hyperthermia > 40°C, continuous prolongation, and hyponatremia. Through the electrolyte test, the convulsion state in the blood chemistry test has elevated CK blood.
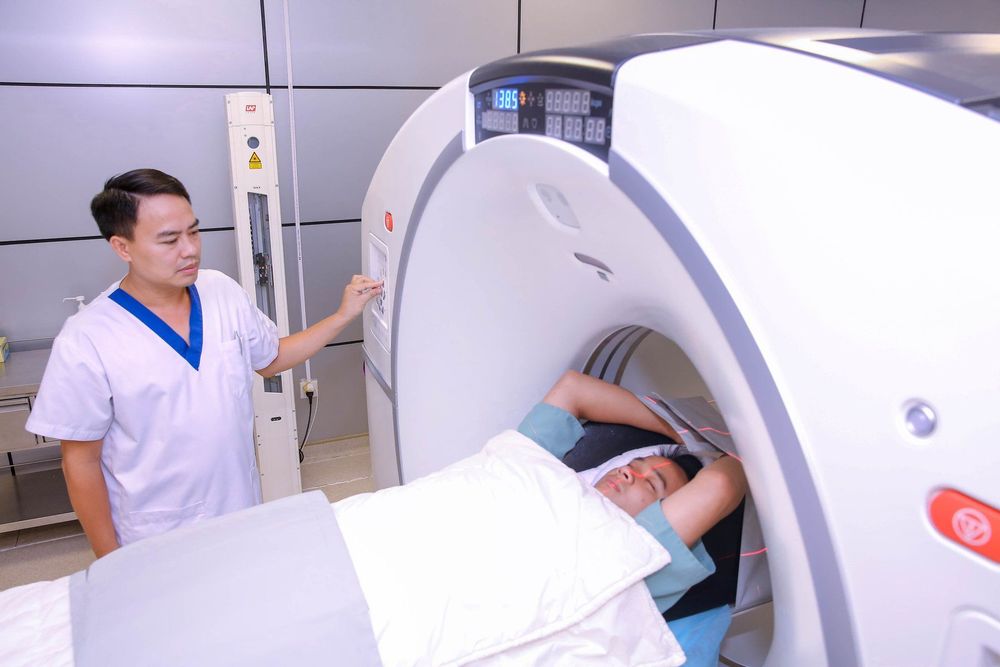
Chẩn đoán tăng áp lực nội sọ bằng CT scanner
2. Treatment of increased intracranial pressure
Surgical treatment of raised intracranial pressure is applied in the state of hypertension caused by brain tumors, traumatic cerebral hematomas, hematomas and extensive cerebellar edema, some brain abscesses depending on the indications and circumstances. specific case of the patient.Surgical treatment is necessary to treat respiratory, or metabolic disorders, hypertensive crisis to maintain cerebral perfusion pressure (60 - 80 mmHg). Antibiotics in purulent meningitis, acute abscess, antiviral as in herpes simplex encephalitis. In the treatment of increased intracranial pressure, patients should avoid sudden position changes.
Patients with increased intracranial pressure will be treated symptomatically including:
Eliminate extracranial factors such as reducing venous pressure by placing the patient in supine position, raising the head about 10-30 0 to avoid pressure Squeeze the jugular vein, avoid strenuous stimulation with sedation. Treat respiratory disorders to combat hypoxia, increase CO2, lower osmotic pressure, so limit water and avoid using osmotic hypotonic solutions. Anti cerebral edema by using corticosteroids, usually dexamethasone (Soludecadron tube 4mg) at first bolus 10mg, then 4mg every 6 hours. Usually 16-24mg/day or Synacthen (Tetracosaclide) 1-2mg/24 hours. Treatment to reduce fluid in the brain with diuretics, increase ventilation...
Corticoid được dùng trong điều trị tăng áp lực nội sọ
Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in neurological examination and treatment, patients can completely peace of mind to examine and treat raised intracranial pressure at the Hospital.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.
MORE:
Dealing with severe traumatic brain injury Injuries caused by traumatic brain injury How is traumatic brain surgery?