This is an automatically translated article.
Blood clot formation is a dangerous disorder and requires urgent treatment. In particular, in cancer patients and undergoing cancer treatment, there is a higher risk of blood clot formation.1. Thrombosis and formation mechanism
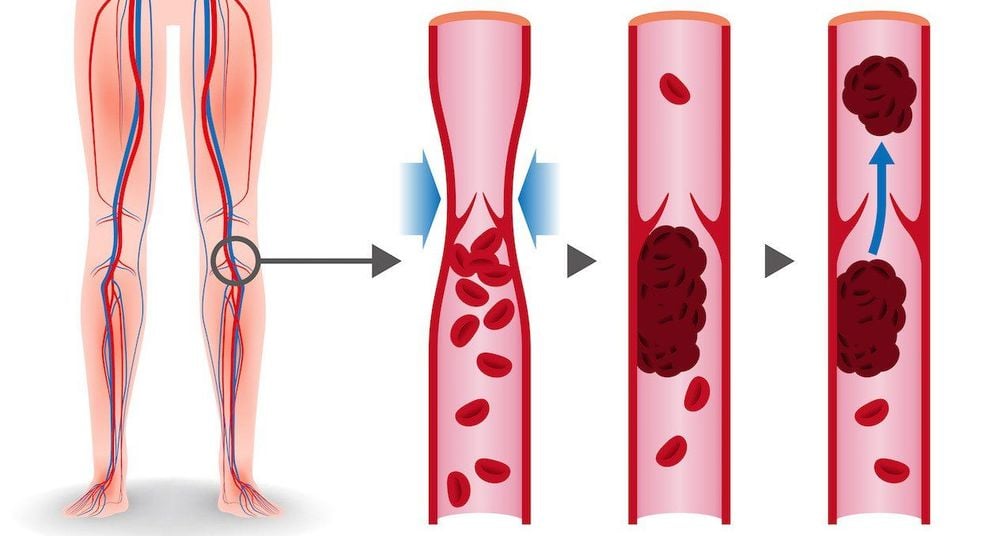
Thrombosis is a pathological condition caused by the unreasonable initiation and spread of the body's hemostatic coagulation response. This leads to the formation of blood clots in the lumen and causes a number of conditions such as semi-occlusive, complete embolism, or embolism. Thrombosis is classified into 2 types according to shape, composition and location. Therefore, the mechanism of formation and risk factors for each type of thrombosis are also different.
1.1 Cell pattern and composition Red thrombus: forms under conditions of slow blood flow. Red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets are covered in a purple-red fibrin network. White blood clots: form when endothelial cells are damaged. The main components are platelets, fibrin fibers, and a few white blood cells. Mixed thrombosis: this is the most common form. Mixed thrombus consists of 3 parts, the head is platelets attached to the vessel wall, the body has plaques of platelets interspersed with fibrin fibers, and the tail has a clot that is easily dislodged by blood flow. 1.2 Location of thrombus formation Arterial thrombosis: caused by damage to the vessel wall, increased platelet activation. Risk factors are diabetes, atherosclerosis, hyperlipidemia, hypertension,... Venous thromboembolism: formed when the flow is slow, damage to the vessel wall and the state of hypercoagulability. High-risk patients are often after surgery, postpartum or prolonged immobilization... increased activation of coagulation factors. The mechanism of coagulation formation is endothelial damage associated with increased platelet activation. In particular, cancer patients will increase the formation of blood clots.
MORE: Common types of blood clots
2. Thrombosis in cancer patients
Thrombosis is a dangerous disorder that requires urgent treatment. Especially in cancer patients and undergoing cancer treatment, there is an increased risk of blood clot formation. Causes may be due to the mechanism of cancer formation or due to the treatment process such as chemotherapy, steroid drugs, surgery or use of catheters for a long time.The process of thrombus formation in cancer patients is very complex. This is a consequence of the interaction between tumor cells, hemostasis and neovascularization. Cancer patients often have a state of hypercoagulability due to the synergistic effect of factors related to:
Blood stagnation: due to long-term bed rest or tumor compression. Vascular damage: caused by invasion of cancer cells, caused by drugs or other therapeutic interventions. Vascular damage can be caused by vascular compression from the outside by the tumor and by enlarged lymph nodes in cancer patients, or by the use of a central intravenous line during chemotherapy. The drugs used in chemotherapy are 4.5 to 6 times more likely to form blood clots. Hypercoagulability: due to the release of coagulation factors from cancer cells, it affects platelet function and coagulation cascade. The factors that play a major role in the pathophysiology of hypercoagulability in cancer patients are tissue factors, inflammatory cytokines, and platelets.
Trắc nghiệm: Thử hiểu biết của bạn về bệnh ung thư
Ung thư là nguyên nhân gây tử vong hàng thứ 2 trên thế giới. Thử sức cùng bài trắc nghiệm sau đây sẽ giúp bạn có thêm kiến thức về yếu tố nguy cơ cũng như cách phòng ngừa bệnh ung thư.
Bài dịch từ: webmd.com
3. Risk factors for blood clot formation in cancer patients
3.1 Patient-related factors Factors that increase the risk of thrombosis related to the patient's condition include:
Older age Obese people with BMI >35kg/m2 Homogeneous disease: infection , lung disease, kidney disease, mutations that cause hypercoagulability, chronic venous insufficiency,.... Cancer patients with a history of previous thrombosis have a 6-7 times higher risk than cancer patients without cancer. advance payment.

Drugs: Tamoxifen treatment increases the risk especially during the first 2 years when combined with chemotherapy. In addition, thalidomide is associated with thrombus formation at a rate of 12-28%, when used in combination with dexamethasone or chemotherapy. Similar to bevacizumab is an anti-angiogenic agent. Long-term central venous catheterization during chemotherapy or parenteral nutrition can cause local thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. In addition, use of erythropoiesis-stimulating drugs, red blood cell or platelet transfusions, and prolonged hospitalization are risk factors for thrombosis in cancer patients. In summary, thrombosis and blood clot formation is a dangerous condition. Especially in patients with cancer or undergoing cancer treatment will be at high risk. This condition is closely related to treatment methods, long hospital stay, etc. Therefore, cancer patients need to be treated with thromboprophylaxis and monitored during hospital stay.

Department of Oncology - Radiation Therapy of Vinmec system is focused on carefully investing in expertise and equipment, bringing satisfaction to patients.
The leading team of domestic and international doctors: the doctors are all highly qualified, experienced, conscientious and knowledgeable, having worked in major hospitals of Vietnam, Korea, Russia, are trained specialized training in the country and abroad to bring the most effective and new treatment regimens to patients. Intensive technique, effective treatment of difficult cases: is the first and only hospital in Vietnam to successfully deploy robotic surgery. CT scan accurately detects cancer even when there are no symptoms. Applying advanced gene technologies to early detect the risk of 16 most common cancers. Deploying autologous immunotherapy and thermotherapy in combination with cancer treatment to effectively prevent recurrence. Continuously working for the community: always accompanies the community in free screening programs for common cancers: Breast, cervical, colorectal, etc. Thousands of patients cannot be screened for cancer, join hands with the community to fight back the dreaded cancer. To register for examination and treatment with the leading doctors of the Department of Oncology - Radiation Therapy, please click the "Contact Us" button on the website, or register for an online examination.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.