This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Tong Diu Huong - Radiologist - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.Thyroid ultrasound is the use of sound waves to create images of the thyroid gland located in the neck area. This is a commonly used means of examining an enlarged thyroid gland, tumors or nodules found in this area, or when a patient has hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism.
1. What is ultrasound for thyroid pathology?
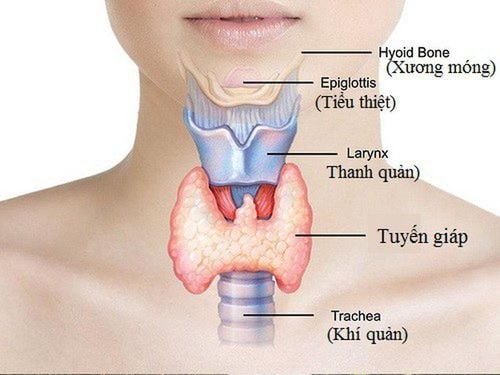
Ultrasound is by nature a safe and painless imaging medium that produces images of the inside of the body using sound waves. Likewise, ultrasound for thyroid disease is to create images of the thyroid gland and nearby structures in the neck.The thyroid gland is located in the front of the neck, shaped like a butterfly, with two lobes on either side of the neck and is connected by a narrow band of tissue. This is an endocrine gland that produces and releases thyroid hormone into the bloodstream, which helps regulate the body's metabolic functions. This organ is also often found to be enlarged, with abnormal lumps or nodules. Therefore, the role of ultrasound at this time is very sensitive to diagnose thyroid disease.
Observationally, nodules are seen on ultrasound for thyroid pathology in 70% of adults. The majority of these are benign thyroid areas that pose no health risk. The small remainder are true tumors of the thyroid gland and may require specialized diagnosis or specific treatment, including thyroid cancer.
2. Indications for ultrasound for thyroid disease
Thyroid pathology ultrasound will be performed when the patient has the following indications:To confirm the presence of a thyroid nodule when the physical examination is not clear. To characterize the nodule(s) in the thyroid gland, i.e. to measure the exact size and determine the internal structure and blood vessels.
3. How to prepare before ultrasound for thyroid pathology?
Wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothing. Remove all clothing and jewelry from the neck area. A gown may be changed during ultrasound for thyroid disease. For older children, parents should explain the procedure to the child before the ultrasound to help the child cooperate better. For young children, parents need to hold the baby and bring a small toy to help distract the child and make the ultrasound easier.4. Thyroid pathology ultrasound procedure
The patient needs to lie on his back on a table and turn to his sides according to instructions for a complete imaging survey of the thyroid gland.
5. The benefits and limitations when diagnosing thyroid disease by ultrasound
Ultrasound for thyroid disease is non-invasive and does not cause any pain, although sometimes pressing the transducer on the neck can cause transient discomfort. Ultrasound is readily available and easy to use, and less expensive than most other imaging modalities. The images obtained through ultrasound are extremely safe and do not use radiation. Ultrasound gives clear images of soft tissues while not showing well on radiographic images.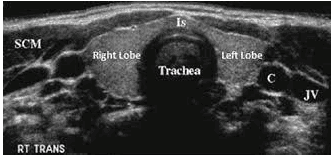
If one or more nodules are detected in ultrasound of thyroid pathology, determining the nature of the lesion may be subjective, sensitive and the specificity for distinguishing between benign and malignant nodules is limited. At this point, the determination must be based on biopsy. However, in some cases, your doctor may consider follow-up and repeat ultrasound after several months. Ultrasound for thyroid disease cannot determine thyroid function and differentiate between hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism. To determine that, your doctor may order a blood test or a radioactive iodine uptake test. In conclusion, ultrasound of thyroid pathology has become a common and useful tool in the diagnosis and monitoring of thyroid diseases. Besides the above advantages, ultrasound also has certain limitations, requiring the level and experience of the sonographer to make accurate judgments.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.