This is an automatically translated article.
The article was consulted with Dr. Vo Thi Thuy Trang, Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.Gastrin is an important hormone involved in the stimulation of secretion and regulation of gastric acid. This is an important mechanism to help break down protein in food. In addition, Gastrin is also involved in many other digestive hormone secretion processes.
1. What is Gastrin?
Gastrin was first discovered and proposed in 1905 by British physiologist John Sydney Edkins, and was isolated in 1964 by Hilda Tracy and Roderic Alfred Gregory at the University of Liverpool. In 1964, the chemical structure of gastrin was determined. Gastrin is a peptide hormone that is primarily responsible for enhancing gastric mucosal growth, gastric motility, and secretion of hydrochloric acid (HCl) into the stomach. It is produced and stored in the G-cells of the antrum of the stomach and the pancreatic islets of Langerhans and is released primarily in response to stimulation of the GRP peptide in the gastric juice. Gastrin binds to cholecystokinin B receptors to stimulate the release of histamines in enterochromaffin-like cells, and it causes inhibition of K+/H+ ATPase pumps into the basal membrane of parietal cells (thereby increasing the release H+ into the gastric cavity). Gastrin release is stimulated by peptides in the gastric lumen.Besides, Gastrin is also stimulated to secrete secondary after taking peptides, amino acids, or some diseases in the stomach and increasing gastric pH. In contrast, this release was inhibited by somatostatin and decreased gastric pH by a negative feedback mechanism. Gastrin produced and secreted into the blood is closely related to the secretion of hydrochloric acid, which is necessary for the conversion of inactive pepsinogen to active pepsin, which helps in the breakdown and digestion of proteins in the stomach, as well as the release of gastrin. cobalamin (vitamin B12) from the protein carrier R present in saliva. Gastrin circulating in the blood exists in two forms: bound to the sulfate base or not bound to the sulfate.
2. Physiological process of the hormone Gastrin
2.1. Gastrin synthesis Gastrin is a straight peptide hormone produced by the G cells of the duodenum, antrum, and pylorus of the stomach. Gastrin is secreted into the blood. After transcription, the first coding polypeptide formed is preprogastrin. They are then cleaved by active enzymes to progastrin (which is an intermediate, inactive precursor) and then gastrin is converted to the active form and comes in various forms, mainly the following three forms. :Gastrin-34 ("large gastrin") Gastrin-17 ("small gastrin") Gastrin-14 ("minigastrin") In addition, pentagastrin is an artificially synthesized form of gastrin, consisting of five amino acid sequences that resemble the last five amino acids at the C-terminus of gastrin.
2.2. Stimulation of Gastrin Release Gastrin is released in response to certain stimuli. These include:
Distension of the gastric antrum (eg, when food strains the antrum) X-nerve stimulation (mediated by neural bombesin, or GRP in humans) Presence of protein in partially digested food, especially amino acids, in the stomach. Aromatic amino acids are particularly powerful stimulants for gastrin release. Hypercalcemia (via calcium-sensing receptors) 2.3. Inhibition of Gastrin Release Gastrin release is inhibited by:
Presence of acid (mainly secreted HCl) in the stomach (negative feedback regulatory reflex) Somatostatin also inhibits release gastrin, along with secretin, GIP (Gastroinhibitor), VIP (vasoactice intestinal peptided), glucagon, and calcitonin.
3. Function of the hormone Gastrin
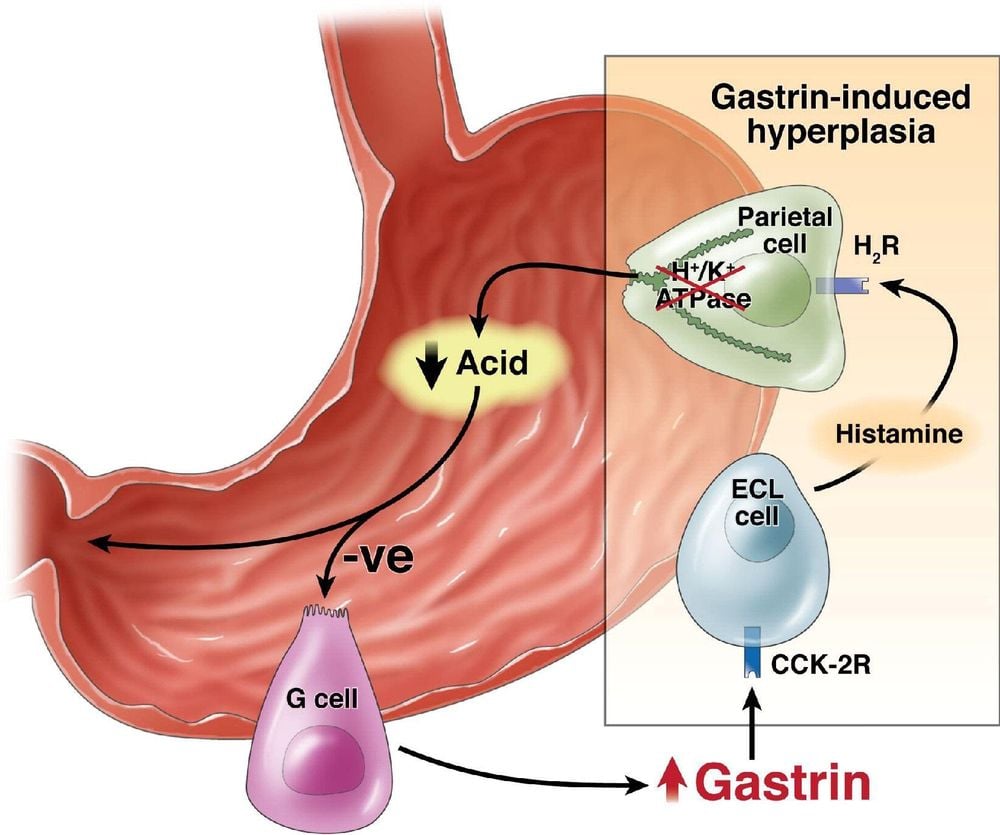
The presence of gastrin stimulates the parietal cells of the stomach to secrete hydrochloric acid (HCl) - gastric acid. This is accomplished through a direct mechanism of action on receptors present on gastric parietal cells and indirectly through binding to CCK2/gastrin receptors on gastric ECL cells. Cells respond by releasing histamine, which in turn acts in a parasecretory manner on parietal cells and stimulates them to secrete H+ ions. This is the main stimulant for the acid secretion of the parietal cells of the stomach.Along with the above mentioned function, gastrin has also been shown to have other functions such as:
Stimulates parietal cell maturation. Stimulates primary cells to secrete pepsinogen, which is a zymogen (inactive) form of the digestive enzyme pepsin. Increases motility of stomach muscles and stimulates stomach contractions and mixing of food. Stimulates contractions that push food through the pyloric orifice and relaxes the pyloric sphincter, increasing the rate of gastric emptying. Plays a role in dilating the ileal valve to allow food to enter the large intestine. Gastrin increases the secretion of pancreatic juice and increases the contractile secretion of bile from the gallbladder. May affect the tone of the lower esophageal sphincter, stimulating the esophagus to contract. However, this function was observed when pentagastrin (artificially synthesized gastrin) was used, not endogenous gastrin that had this effect. Gastrin contributes to the gastro-intestinal reflex.
4. The role of the hormone Gastrin in food digestion
This hormone is involved in the digestive process by. During meals, Gastrin stimulates the stomach to release stomach acid. This allows the stomach to break down protein from food and absorb some vitamins.Gastrin also acts as an antiseptic and kills most bacteria that enter the stomach with food, minimizing the risk of infection in the intestines
In addition, it can stimulate the gallbladder to increase contractions squeeze, secrete bile and pancreas to secrete digestive enzymes. Bile and pancreatic enzymes help hydrolyze and digest food in the small intestine.
5. Some disorders are related to the hormone Gastrin
Abnormally increased gastrin secretion can result from many medical conditions (eg, Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, peptic ulcer, duodenal ulcer, gastrin-secreting cell carcinoma, and Biermer pernicious anemia).In Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, gastrin is produced in excess, usually from a gastric tumor (gastrin-producing tumor, mostly benign) of the duodenum or pancreas. To check and evaluate for hypergastrinemia (hypergastrinemia), a test called a "pentagastrin test" may be performed.
In autoimmune gastritis, the immune system attacks the parietal cells leading to low gastric acid secretion (hypochlorhydria). This leads to increased gastrin levels due to a feedback mechanism to increase HCL acid secretion and decrease gastric pH. When this condition is in the late stages, all the cells of the stomach wall are attacked by the immune system and lead to a state of no acid in the stomach (achlorhydria) resulting in a loss of feedback to secrete gastrin.
Plasma gastrin levels are elevated in almost all individuals with type IV mucolipidosis (mean 1507 pg/mL; range 400-4100 pg/mL) (normal 0-200 pg/mL), this is an increased condition secondary to gastric acid aversion. This is a symptom that increases the likelihood of diagnosing patients with this neurological disorder.
In addition, increased gastrin levels may be present in chronic gastritis due to H pylori infection.
6. How is the Gastrin test done?
The test is performed on serum or plasma samples anticoagulated with heparin. In order for the test results to be accurate, it is necessary to ask the patient to fast before 12 hours and not drink alcohol for 24 hours. If possible, request discontinuation of all medications that reduce gastric acid secretion or gastric pH-lowering medications prior to blood sampling.Normal value: 13 - 115 pg/ml.
Increased levels are common in the following cases:
Elderly people over 60 years old often increase this hormone due to physiological reasons. Chronic gastritis. Helicobacter pylori infection. Use antacids. Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. Biermer anemia. After vagus nerve resection, vagal resection is incomplete. Rheumatoid arthritis. Chronic kidney disease. Gastrin cell tumor. Increased production of G cells by the antrum. Peptic ulcer . Short bowel syndrome due to bowel resection or from widespread enteritis. Stomach cancer. Stomach pyloric stenosis. Strong parathyroid. Diabetes. Adrenal myeloma. Decrease in concentration can be seen in the following cases:
There is polyacidic gastric juice. The antrum is too distended. Doctors often use the blood gastrin test in combination with gastrin stimulation tests to conduct differential diagnosis with gastric diseases:
Gastrin stimulation tests such as intravenous calcium gluconate or secretin injection are used for the differential diagnosis of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome with gastric and duodenal ulcers. Gastrin stimulation test after secretin injection is used in patients with suspected Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. Gastrin stimulation test after intravenous calcium infusion is used for patients with negative secrenin stimulation test, gastric acid hypersecretion, and the patient is still suspected to have Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. Abnormal levels of this hormone will greatly affect the digestive process, so when your digestive system has problems, you need to immediately go to medical facilities to conduct an examination to find out the cause. Only the most appropriate treatment can be determined.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination, consulting and service services. comprehensive and professional medical treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space. Customers when choosing to perform tests here can be completely assured of the accuracy of test results.
If you have a need for consultation and examination at Vinmec Hospitals under the national health system, please book an appointment on the website for service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: wikipedia.org, hormone.org, sciencedirect.com