This is an automatically translated article.
This article is professionally consulted by Master - Doctor Huynh An Thien - Department of Medical Examination and Internal Medicine, Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.Currently, the prevalence of diabetes is increasing, in this disease, insulin hormone plays an important role in the pathogenesis and treatment measures. So what is insulin hormone? What is the role of insulin in the human body?
1. What is insulin hormone?
Insulin is a hormone secreted by the beta cells of the pancreas that is responsible for lowering blood sugar. Insulin has a molecular weight of about 5808 Dalton and is composed of two polypeptide chains: A and B.2. Effects of Insulin?
Insulin is the only hormone in the body that lowers blood sugar. This effect is due to the effect of insulin on the metabolism of glucose, lipids and proteins in the body.2.1. Effects of insulin on glucose (starch) metabolism
- Insulin increases glycogen stores and muscle glucose breakdown. After a meal, an increase in blood glucose (blood sugar) will stimulate insulin secretion, leading to increased glucose transport into cells. If the muscle is inactive, glucose is converted to a stored form, glycogen.
- If blood glucose is high, but glucose cannot enter the cells, it will lead to an increase in blood osmotic pressure that can lead to coma and death. When there is a lack of insulin, the cells do not have enough glucose to convert into energy, the metabolism in the cells follows the lactic metabolic pathway, which can cause acidosis.
- One of the most important effects of insulin is to convert most of the glucose in the liver into glycogen for storage. When blood glucose is reduced, insulin secretion is inhibited, and glycogen is broken down to release glucose into the blood.
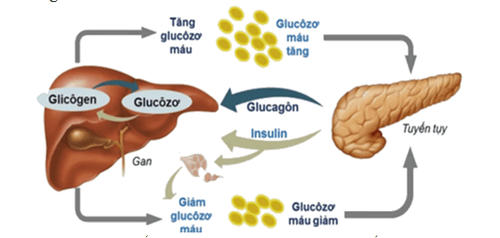
Insulin giúp chuyển glucose ở gan thành dạng glycogen để dự trữ.
- In addition, insulin also inhibits the process of creating sugar in the body (new sugar is the process of using amino acids in the body to form glucose).
2.2. Effects of insulin on lipid (fat) metabolism:
- Insulin increases fatty acid synthesis from glucose and transports them to adipose tissue.
- When there is a lack of insulin, it will lead to increased glycerol and fatty acids in the blood (hyperlipidemia). Increased levels of lipids (fats) in the blood lead to atherosclerosis in patients with diabetes.
2.3. The effect of insulin on protein (protein) metabolism
Insulin increases protein synthesis and storage in most cells of the body. If there is a lack of insulin, the breakdown of proteins increases, reduces protein in tissues, and the body loses weight. That's why people with diabetes have symptoms of drinking a lot, eating a lot, but losing weight quickly.3. How does insulin work?
To be effective, insulin needs to be attached to target cells through insulin receptors on the cell surface.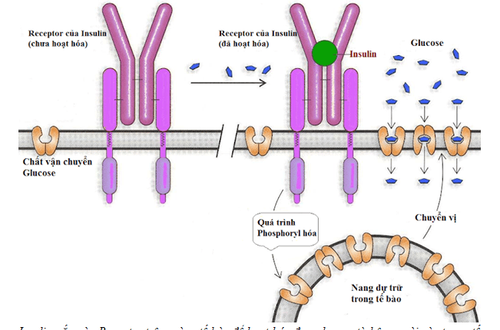
Insulin gắn vào Receptor trên màng tế bào để hoạt hóa đưa glucose từ bên ngoài vào trong tế bào.
4. Insulin and diabetes
- In patients with type 1 diabetes, the beta cells of the pancreas are destroyed leading to a complete lack of insulin. Therefore, patients with type 1 diabetes need to be treated by adding insulin from outside into the body.
- In patients with type 2 diabetes, the body can still produce insulin but there is resistance to insulin in the target cells. In the early stages of the disease, the body responds by increasing insulin secretion, as the disease progresses, the beta cells of the pancreas are reduced, leading to patients with type 2 diabetes needing combination therapy, even having diabetes. may include insulin therapy.
5. Application of Insulin in the treatment of diabetes
From information about the effect and role of insulin in diabetes, we can realize its important role in the treatment of diabetes.
Hình ảnh Insulin
Currently, insulin is mainly produced by recombinant technology. Based on the duration of action of insulin, people divide insulin into 3 main types:
There are also a number of insulin preparations that combine insulins with different durations of action such as: Mixtard (NPH/regular) 70/30
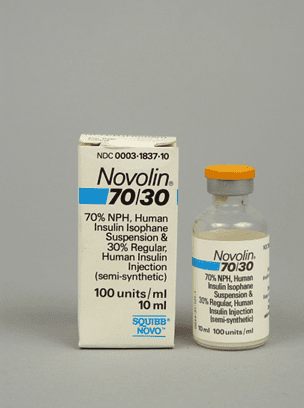
Insulin dạng phối hợp 70% bán chậm và 30% nhanh
There are also some other forms of insulin
- Oral insulin: Nowadays, in some countries, insulin has been studied in oral form, when it reaches the small intestine, it is released and not destroyed by gastric juice.
- Insulin spray: Can be sprayed into the mouth or nose, the drug penetrates the respiratory mucosa causing lower blood sugar faster.
- Insulin Pen: Convenient, precisely control the amount of insulin injected.
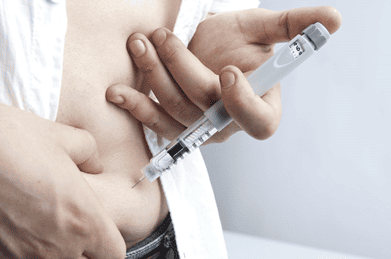
Dạng Insulin tiêm điều trị đái tháo đường vẫn là dạng phổ biến nhất hiện nay
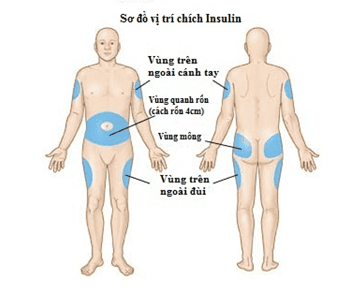
Sơ đồ vị trí tiêm Insulin trên cơ thể
6. When is the patient prescribed insulin treatment?
Indications for insulin treatment
- Type 1 diabetes is required to be treated with insulin
- Emergency pre-coma or coma due to diabetes
Type 2 diabetes has been treated with a combination of types Oral drugs are ineffective
- Diabetic patients are suffering from severe infections or are underweight, have a lot of weight loss, are malnourished
- Diabetic patients have complications with target organ damage (heart, kidney, brain) such as: stroke, myocardial infarction, kidney failure due to diabetes...
- Diabetic patients need to stabilize blood sugar before, during and after surgery
- Diabetes in women has thai
7. Notes when using insulin
When using insulin, the patient should pay attention to the following things
- Inject the correct dose as prescribed by the doctor, inject at the prescribed time
- The injection site should be rotated to avoid insulin lipodystrophy
- Ensure Store insulin in the refrigerator compartment
- Have a suitable diet and exercise for people with diabetes, avoid skipping meals that cause low blood sugar.
Above, we have provided the most general information about the role of insulin in human health, to learn more about insulin injections, the diabetic diet, please read Readers welcome to read useful articles on the website of Vinmec Hospital.
See more:
Instructions for using an insulin pen What is insulin? What is the role, side effect, note when using according to the guidance of the Ministry of Health Diabetes screening and why should diabetes screening?