This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Master, Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Gastrointestinal Endoscopy - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International HospitalDiverticulitis is a common disease in the elderly, the disease often has no obvious symptoms. If not examined and diagnosed early, the patient's health can be seriously affected. Colonoscopy is the most useful method to determine the presence and extent of diverticular disease to guide effective treatment and management.
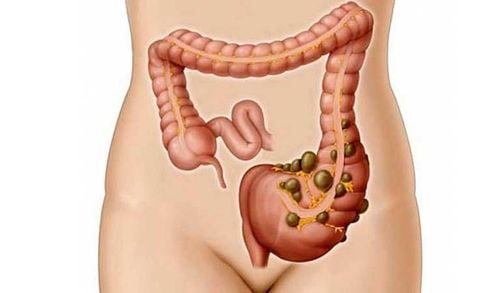
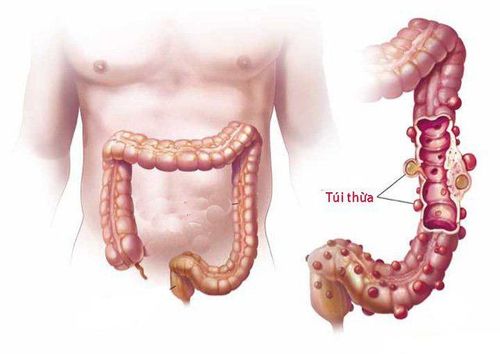
1.What is a colonic diverticulum? Diverticula are small, bulging pouches that can form anywhere in the digestive tract, from the esophagus to the stomach, small intestine, and large intestine. However, they are usually found in the large intestine. Diverticulosis is a fairly common disease, often seen in patients over 40 years of age.
Colonic diverticula are pouch-like structures that develop in the wall of the colon, most commonly in the sigmoid and left colon, but can also involve the entire colon. When these diverticula become inflamed, it causes diverticulitis.
2. An overview of colonic diverticulosis Diverticulitis, which encompasses a wide range of clinical manifestations and possible complications. The disease is common in clinical practice. Accordingly, colonoscopy is an important tool in the diagnosis and management of diverticular disease.
Colonic diverticula are the most common incidental finding during routine colonoscopy and their prevalence increases with patient age.
3. Role of Colonoscopy in Diverticulitis Colonoscopy is the most useful method for determining the presence and extent of diverticular disease and may be important for the diagnosis and diagnosis of diverticulitis. management of diverticular diseases. For example, diverticular bleeding can be localized and treated with timely bowel preparation. Following endoscopic hemostasis, the colonic strictures associated with diverticulitis can be stented to bridge the obstruction to resect a segment of the bowel. Acute diverticulitis should be followed up with diagnostic colonoscopy approximately two months later to rule out other entities presenting with diverticulitis (eg, colon cancer, Crohn's disease, cancer) lymph nodes). In addition, it is imperative for clinicians and endoscopists to recognize that severe (i.e., dense) diverticulitis in the sigmoid colon and complications of previous acute diverticulitis can make Because colonoscopy becomes technically difficult and the risk of colonic perforation is higher, sometimes a change in conventional technique is required for effective treatment.
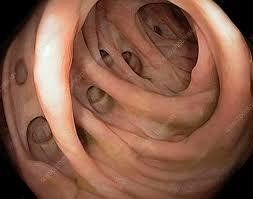
4. The Role of Colonoscopy in Diverticular Bleeding Diverticulitis is a common cause of acute lower gastrointestinal bleeding, accounting for 20% to 65% of such episodes. Erosive ulcers of the colon wall affecting the blood vessels passing through the neck and arch of the diverticulum can lead to rapid, forceful bleeding.
Laparoscopic management of diverticulitis can be difficult for a variety of reasons including the inconvenience of rapid bowel preparation, the difficulty of carefully examining each diverticulum in the colon, identifying actual signs and symptoms. recent bleeding and achieved hemostasis of small lesions in the diverticulum.
5. Treatment of active hemorrhagic diverticulitis 5.1. Urgent Endoscopy In hemodynamically stable patients with lower gastrointestinal bleeding, urgent endoscopy should be performed within 8 to 24 hours of presentation (or earlier, if possible) after Complete bowel preparation. The likelihood of identifying bleeding from a diverticulum is higher with early colonoscopy, thus increasing the chances of definitive hemostasis. Two meta-analyses in 2017 comparing early and late colonoscopy in patients presenting with lower gastrointestinal bleeding did not reduce recurrence rates, transfusion requirements, and key outcomes. different, but showed an increased rate of endoscopic intervention.
5.2. Identification of a bleeding diverticulum Recent bleeding signs of bleeding from the diverticulum are similar to those of the upper gastrointestinal tract. Active bleeding, blood vessels, blood clots, and pigment spots associated with diverticula can be seen. The location of such lesions can be difficult due to the potential for multiple diverticula throughout the colon. This requires investigation, inadequate bowel preparation, and the fact that diverticulitis usually stops spontaneously or may be intermittent. The recently published bleeding site identification rates vary widely, with one notable study reporting the identification of a bleeding site in 17% of cases. Niikura et al's study also found factors useful in locating recent bleeding, including urgent colonoscopy, professional colonoscopy, use of transparent flaps (CAP - cap-like device attached to) the tip of the bronchoscope and uses a water jet.
During a colonoscopy, the doctor must carefully examine it using a transparent cap attached to the colonoscope that is rinsed with water and infused with fluids as needed. Another technique that may be tried is inversion of the diverticulum by suction on the clear flap (CAP) at the tip of the laparoscope. Using these methods, diverticula in the colon can be examined for signs of recent diverticular bleeding.

5.3. Laparoscopic treatment Current American College of Gastroenterology practice guidelines recommend the use of endoscopic vascular clips (TTS) for the treatment of diverticular bleeding due to their safety and ease of use compared with other methods. other methods such as tying with an elastic band. The current American Gastroenterology Association Gastrointestinal Endoscopy Practice Guidelines recommend using a thermal probe or bipolar coagulation device alone or in combination with epinephrine, followed by proximal marking of the lesion for identification. later in case of recurrent bleeding. Endoscopic clipping and endoscopic elastic band ligation (EBL) are alternatives to thermal coagulation. The clamping site near the suspected bleeding diverticulum can also be used as a marker if DSA background angiography is used to localize the bleeding site.
6. Role of endoclips in diverticulostasis and stop bleeding recurrence. Attention to the anatomy of the diverticulum and adjacent arteries is important in hemostasis. Clamps can be used in many ways, for example clamping on the neck or arch of a diverticulum or clamping at the mouth of a diverticulum. If the site of recent bleeding is not visible or accessible, it is recommended that you use a clear endoscope cap (i.e. distal attachment) to improve navigation and examination of the diverticulum and create favorable conditions for treatment.
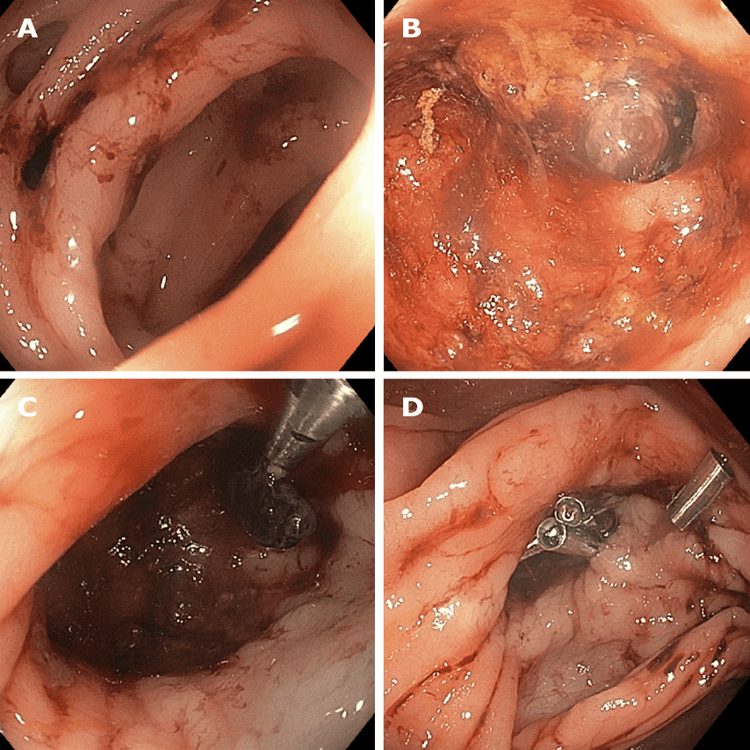
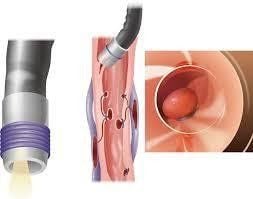
Elastic band ligation is another available treatment modality. If the site of recent bleeding can be identified, an endoscopic clip is placed to mark the site and the colonoscope is withdrawn to place the elastic device. After returning to the site of bleeding, the diverticulum was inverted into the cap of the rubber-ringed tube and an elastic band was ejected to enclose the diverticulum. This technique may be limited or not feasible in the case of diverticula with a narrow stoma or in the presence of a diverticulum in the right colon.

7. Intestinal obstruction due to acute diverticulitis Diverticulitis can cause colonic stenosis leading to partial or complete bowel obstruction with clinical presentation similar to other causes of obstruction. such as malignancy, megacolon and inflammatory bowel disease. Large bowel obstruction is thought to be caused by diverticular disease in about 10% of cases, although this number can vary considerably depending on study design.
Several studies have mentioned the use of colonic stents for diverticulitis-associated stenosis as a bridge to surgery or for palliation in patients no longer indicated for surgery. Much of the literature on this topic has combined colonic complaints associated with diverticular disease with a larger cohort of patients with other benign and often malignant causes of colonic stricture. A meta-analysis examining the technical and clinical success of self-expanding metal stents (SEMS) for benign causes of colorectal obstruction concluded that the rate of stent complications Benign obstruction is too high to warrant use.
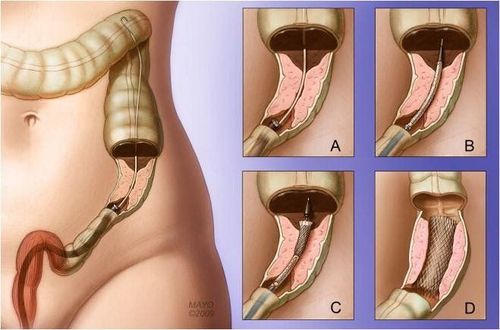
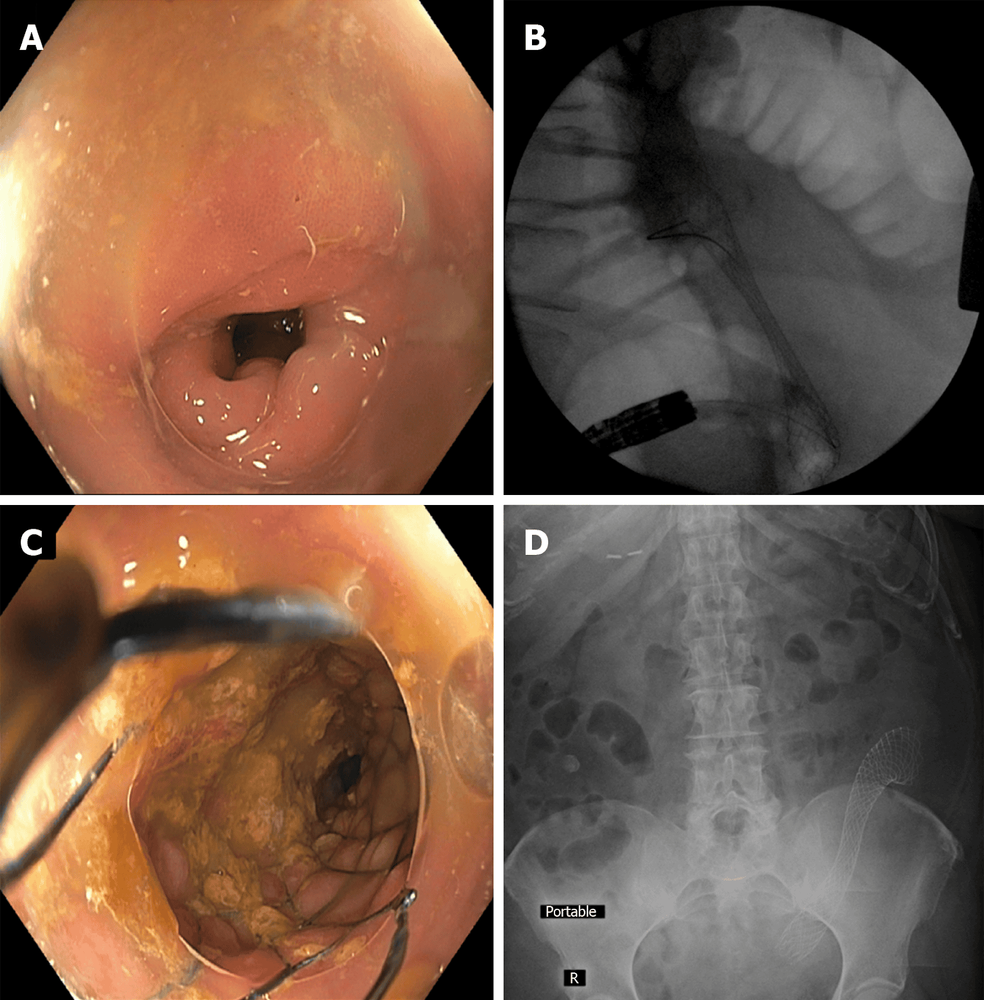
This treatment may allow successful bowel preparation and a first-stage colectomy instead of an emergency colectomy with a temporary colostomy and a second colostomy.
8. Follow-up colonoscopy after diverticulitis Current guidelines recommend diagnostic colonoscopy after resolution of acute diverticulitis if a colonoscopy has not been performed recently. Colonic wall thickening on imaging may also result from processes other than diverticulitis, such as ischemia, inflammatory bowel disease, or malignancy. The rationale for follow-up colonoscopy is to avoid underdiagnosing any of these conditions, especially malignancy. This is usually done 6-8 weeks after improvement of acute diverticulitis in patients who have not had a colonoscopy in the previous 1-2 years, although the optimal timing of colonoscopy remains unclear.
Vinmec International General Hospital is a prestigious address trusted by many patients in performing diagnostic techniques and treating colon diverticula... Accordingly, at Vinmec, the diagnostic implementation through colonoscopy with Olympus CV 190 endoscope, with NBI function (Narrow Banding Imaging - endoscope with narrow light frequency band) results in clearer images of mucosal pathology analysis compared to endoscopy. Conventional endoscopy detects abnormal mucosal lesions at an early stage. With modern facilities and equipment and a team of experts, experienced doctors, always dedicated in medical examination and treatment, customers can rest assured with the gastrointestinal endoscopy service at General Hospital. Vinmec International Faculty.
Customers who are interested in the diagnostic service of colon diverticulum at Vinmec and need advice and support, please contact to register for an online examination.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References
Brian West A. The pathology of diverticulosis: classical concepts and mucosal changes in diverticula. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2006;40:S126-S131. [PubMed] [DOI]
Everhart JE, Ruhl CE. Burden of digestive diseases in the United States part II: lower gastrointestinal diseases. Gastroenterology. 2009;136:741-754. [PubMed] [DOI]
Peery AF, Dellon ES, Lund J, Crockett SD, McGowan CE, Bulsiewicz WJ, Gangarosa LM, Thiny MT, Stizenberg K, Morgan DR, Ringel Y, Kim HP, DiBonaventura MD, Carroll CF, Allen JK, Cook SF, Sandler RS, Kappelman MD, Shaheen NJ. Burden of gastrointestinal disease in the United States: 2012 update. Gastroenterology. 2012;143:1179-1187.e3. [PubMed] [DOI]
Strate LL, Naumann CR. The role of colonoscopy and radiological procedures in the management of acute lower intestinal bleeding. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;8:333-43; quiz e44. [PubMed] [DOI]
M Phillip Fejleh, James H Tabibian, Colonoscopic management of diverticular disease. World J Gastrointest Endosc. Feb 16, 2020; 12(2): 53-59