This is an automatically translated article.
This article is professionally consulted by Master, Resident Doctor Tran Duc Tuan - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital. The doctor has many years of experience in the field of imaging and interventional internal and external blood vessels.Liver tumor is a disease with a high mortality rate if the patient is not detected and treated in time. Currently, a new treatment method for liver tumors is being used by many hospitals to capture and embolize liver tumors digitally erase the background, this is a method with many advantages and direct effects on liver tumors.
1. Signs to recognize liver tumors
The liver is known to be the largest organ in the human body, in an adult it weighs up to 3 pounds and has a triangular shape that extends most of the abdominal cavity.The liver plays an important role in the human body, the main functions of the liver are to produce bile, absorb and metabolize bilirubin, support blood clots, metabolize fats and carbohydrates, store vitamins and minerals, dialysis, protein metabolism...
2. Signs to recognize malignant liver tumors
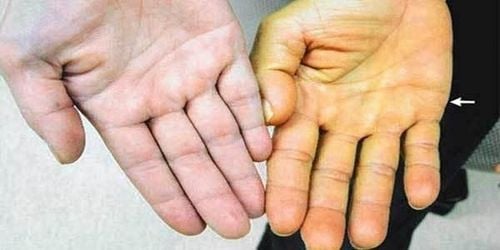
Signs of liver malignancy you need to pay attention to:Fatigue: This is the first and earliest sign of every liver tumor patient, the patient often feels tired even though he doesn't work hard. The patient's body deteriorated rapidly, the weight lost from 5-6 kg within a month. Digestive disorders: When liver function declines, it leads to digestive system disorders such as: Constipation, diarrhea... Patients always feel bloated, even though they eat little or nothing. . Malignant liver tumors when reaching the final stage will lead to broken stools, lots of mucus, the patient has to go many times a day. Abnormal bleeding: Malignant cells attack the liver, causing the liver's clotting function to be impaired, leading to frequent bleeding gums, abnormal bleeding under the skin. Prolonged low-grade fever: Malignant neoplasm causes necrosis of liver cells, leading to infection and prolonged low-grade fever. Jaundice: Due to high levels of bilirubin, the patient's skin is often yellower than the normal person. This is also thought to be the first sign of a malignant liver tumor.
3. What is the embolization method for liver tumors?
The method of embolization in the treatment of liver tumors, also known as chemoembolization, uses embolization drugs to block the blood supply from the artery to the tumor and at the same time to put chemicals in to treat the liver tumor.The embolization method has advantages such as: Focusing high concentrations of drugs on the tumor for a long time combined with the phenomenon of tumor necrosis to help the treatment process of liver tumors better, reduce the concentration of systemic chemicals should reduce cardiovascular risk, protect healthy liver parenchyma, and limit hair loss.
3.1 Indications The embolization method for liver tumors is indicated for use in primary or secondary liver tumor lesions without indications for surgery or percutaneous interventions such as radiofrequency ablation, absolute alcohol injection. opposite to.
3.2 Contraindications Patients in the following cases cannot use this method for treatment:
Patients with liver tumors with extrahepatic metastases The tumor is too large than 50% of the liver volume Invasion of the portal vein The patient had a porto-portal bypass (TIPS), the patient had hepatic encephalopathy, gastrointestinal bleeding The patient had thrombocytopenia, renal failure, infection, coagulopathy.

4. Imaging procedure and embolization treatment for digitized liver tumors, erasing the background
4.1 Prepare the patient Explain to the patient the procedure to coordinate with the physician. To perform this procedure, the patient or the patient's family must sign the consent form before the procedure. The patient must fast for at least 6 hours before the procedure, and at the same time limit water intake, do not drink more than 50ml of water. 4.2 Anesthesia Method The doctor administers anesthesia to the patient before performing the procedure, depending on the case, may prescribe anesthesia for the patient.4.3 Insertion of a catheter into the artery Usually placed in the right femoral artery, the doctor will conduct a puncture and insert a guide wire into the artery and then bring the wire to the aorta. The doctor then withdrew the needle to puncture the artery and inserted the tube into the artery through the wire. 4.4 Digitized liver tumor scan with background erasure Insert the catheter into the superior mesenteric artery and take the portal vein to confirm the absence of systemic thrombosis. A visceral angiogram was performed, then selectively inserted into the artery feeding the tumor with a small catheter.
4.5 Stopper Step 1: Mix 50mg Doxorubicin with 2ml distilled water and shake well to dissolve.
Step 2: Use a syringe and a fine needle to suck up all the solution in the vial containing the DC Bead beads, leaving the beads inside the vial.
Step 3: Use a syringe to suck up all the liquid in the bottle of Doxorubicin and then pump it into the bottle containing the DC Bead.
Step 4: Shake well the vial of DC Bead injected with solution in step 3 and wait for Doxorubicin to attach to the beads.
Step 5: After the waiting period, take the 10ml syringe to suck up all the liquid in the vial and add 2ml of contrast agent to monitor the granulation process.
Step 6: Carry out injecting the above solution into the artery feeding the tumor and performing a super-selective node of the tumor feeding vessel.
4.6 Post-vascular monitoring The patient stays in bed after the intervention for 6 hours and immobilizes the leg for femoral artery puncture and monitors the patient's pulse, blood pressure, and body temperature during that time.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
SEE MOREBenign and malignant liver tumors: What you need to know How to recognize benign liver tumors? Liver Tumor: When to Biopsy?