This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Cardiologists and Interventional Cardiologists - Cardiovascular Center - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Atrial fibrillation is one of the leading causes of stroke, accounting for about 25% of all cases. Stroke is the second leading cause of death in Vietnam, after cardiovascular disease.
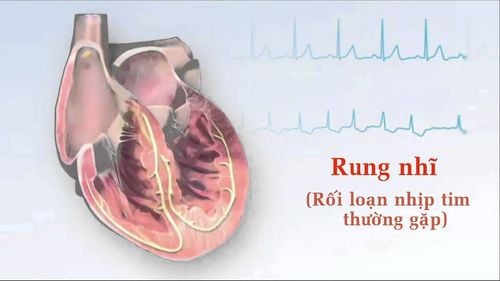
1. What is atrial fibrillation?
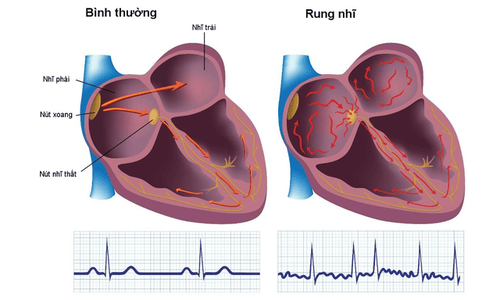
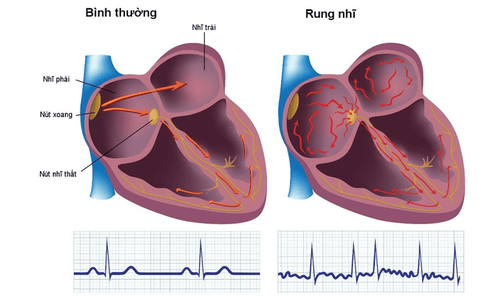
Atrial fibrillation is one of the most common clinical arrhythmias. In a normal person, the heart has 4 chambers, including 2 atria at the top and 2 larger ventricles at the bottom, receiving blood from the atria and pumping blood to the lungs for gas exchange if it is the right ventricle or pumping oxygen-rich blood. nourish other organs in the body. To ensure their function, the heart chambers must work rhythmically and synchronously, thanks to their ability to spontaneously beat and conduct impulses to all heart muscle cells. The sinus node is the pacemaker node with a pulse rate of about 60-100 beats/min, but in atrial fibrillation, the role of pacemaker belongs to many different points in the two atrial chambers. They spontaneously pulse with an irregularly high frequency, about 350-600 beats/min, causing the atria to enter a state of constant excitation, the atria to vibrate and contract ineffectively. These impulses, when carried down the ventricles, also cause the ventricles to contract at a faster rate than normal. Decreased blood flow to the body because the ventricles do not contract rhythmically and synchronously, causing a sudden, life-threatening drop in blood pressure. In practice, however, only a fraction of the impulses are transmitted through the atrioventricular bundle to the ventricles, the rate of contraction of the ventricles is irregular and rapid, often <200 beats/min.2. Subjects at risk of atrial fibrillation
To date, the etiology and pathogenesis of atrial fibrillation are not really understood. However, many factors have been shown to be associated with an increased clinical likelihood of atrial fibrillation. Risk factors for atrial fibrillation are not considered to be direct causes of atrial fibrillation. People with the following factors are considered at risk for atrial fibrillation, including:Older adults, usually over 60 years of age Hypertension Coronary artery disease Heart valve disease After heart surgery, thoracic failure heart Diabetes Chronic lung disease Alcoholism, use of stimulants Thyroid disease such as hyperthyroidism Other systemic diseases
Nhiều bệnh nhân rung nhĩ không có bất kỳ yếu tố nguy cơ nào
However, clinically, many patients with atrial fibrillation do not have any risk factors. Therefore, even young people, who are leading a healthy and active lifestyle, are also likely to have atrial fibrillation and need to go to a medical facility as soon as there is an abnormality.
Diagnosis of atrial fibrillation is not difficult, but treatment and prevention of atrial fibrillation complications is challenging. As atrial fibrillation progresses over a long period of time, symptoms are often more persistent and difficult to treat.
3. The relationship between atrial fibrillation and stroke
Stroke and atrial fibrillation are closely related. According to many statistics, atrial fibrillation increases the risk of stroke by up to 5 times compared to the general population. Atrial fibrillation is the leading cause of stroke, accounting for about 25% of all cases.Brain stroke is a dangerous complication of atrial fibrillation, leaving heavy consequences on the patient's quality of life afterward. It is also the leading cause of long-term neurological damage in adults, the second leading cause of death in Vietnam, after cardiovascular disease.
In atrial fibrillation, the muscle mass of the atria falls into a state of fibrillation instead of effective contractions due to the continuous stimulation of multiple sites in the two atrial chambers. Blood is not brought down to the ventricles and stagnates inside the two atria. This condition stimulates hypercoagulability, which forms small blood clots in the atria. These blood clots, once pumped into the circulatory system, will have the opportunity to travel to the cerebral blood vessels, causing embolism and leading to a stroke in the form of cerebral infarction, causing death of brain parenchyma due to insufficient blood supply.
Some patients present only transient neurological symptoms, not more than 24 hours, known as transient ischemic attack. These patients are more likely to experience an actual stroke in the future.
In addition, when reaching other organs in the body, they can all cause serious consequences such as myocardial infarction or pulmonary infarction.
Đột quỵ não và bệnh rung nhĩ có mối liên hệ mật thiết với nhau
4. Diagnosis of atrial fibrillation
Diagnosis of a patient with atrial fibrillation is not too difficult. Doctors often rely on both clinical and laboratory symptoms to conclude whether a patient has atrial fibrillation or not. Atrial fibrillation is usually detected when the patient has a feeling of palpitations due to a rapid heart rate, accompanied by shortness of breath and shortness of breath. When atrial fibrillation has a rapid ventricular response, the patient is often prone to dizziness, chest pain, hypotension, and sweating. Chronic untreated atrial fibrillation will lead to heart failure due to enlarged heart chambers, reduced contractile function. At this time, the feeling of shortness of breath increases, the ability to exercise is reduced, and edema may also appear. The electrocardiogram (ECG) is a simple tool commonly used clinically for the diagnosis of atrial fibrillation. Electrodes are placed in suitable locations to record the electrical activity of the heart. A typical electrocardiogram of a patient with atrial fibrillation observes the replacement of the normal P wave by small, very rapid f-waves with a frequency of about 350-600 beats/min. The QRS complex is irregular and variable depending on the ventricular response or other associated arrhythmias. The Holter electrocardiogram works with the same mechanism as the electrocardiogram, but the electrical activity of the heart is recorded over a longer period of time, ranging from a day to weeks. Therefore, the electrocardiogram holter is capable of detecting episodes of atrial fibrillation or other arrhythmias.
5. Treatment of atrial fibrillation
Treatment of atrial fibrillation is not as simple as diagnosis, it is necessary to simultaneously adhere to the following principles:Heart rate control: Conversion from atrial fibrillation to sinus rhythm is necessary. In the case of episodes of atrial fibrillation, cardioversion can be performed by various methods such as electric shock, medication or radiofrequency ablation intervention that destroys the impulse generators of the atrial muscle. The likelihood of successful cardioversion decreases with the duration of a patient's atrial fibrillation. Prevention of complications of atrial fibrillation: This is the first priority treatment goal in atrial fibrillation. Blood clots are easy to form and cause blockage of important blood vessels in the body such as cerebral embolism causing stroke, coronary occlusion causing myocardial infarction, ... Common methods used to prevent thrombosis are anti-thrombotic drugs. Oral anticoagulants such as vitamin K antagonists, thrombin inhibitors or factor X inhibitors. Patients using anticoagulants need to follow the advice and follow up with the doctor on time, absolutely do not self-medicate. change the dose of the drug. Patients will be evaluated for additional risk factors. The cardiologist will plan to treat your atrial fibrillation and minimize your chances of developing atrial fibrillation.
Oral anticoagulants are the most common method of inhibiting blood clotting in patients with atrial fibrillation. The decision to choose a drug depends on the current status of atrial fibrillation, age, general health and comorbidities. Patients taking anticoagulants should be consulted by their doctor about the benefits and risks of the drug, avoid stopping or increasing the dose of the drug while taking it, and need to be re-examined to check the blood clotting function regularly. period.
Stroke prevention is the preferred goal when managing a patient with atrial fibrillation. Currently, Magnetic Resonance Imaging - MRI/MRA is considered a "golden" tool to screen for brain stroke. MRI is used to check the condition of most organs in the body, especially valuable in detailed imaging of the brain or spinal nerves. Due to the good resolution and contrast, MRI images allow to detect abnormalities hidden behind bone layers that are difficult to detect with other imaging methods. MRI can give more accurate results than X-ray techniques (except DSA angiography) in diagnosing brain diseases, cardiovascular diseases, strokes,... Moreover, the process MRI scans do not cause the side effects seen in X-rays or computed tomography (CT).
Vinmec International General Hospital currently owns a 3.0 Tesla MRI System, which is equipped with state-of-the-art equipment by GE Healthcare (USA) with high image quality, allowing a comprehensive assessment, without omitting the injury without leaving any damage. and reduce shooting time. Silent technology helps to reduce noise, create comfort and reduce stress for the client during the shooting process, resulting in better image quality and shorter imaging time. With the state-of-the-art MRI system With the application of modern methods of cerebral vascular intervention, a team of experienced and well-trained neurologists and imaging specialists, Vinmec is a prestigious address for stroke risk screening and screening. reliable goods.
In the past time; Vinmec has successfully treated many cases of stroke in a timely manner, leaving no sequelae: saving the life of a patient suffering from 2 consecutive strokes; Responding to foreign female tourists to escape the "death door" of a stroke ;...
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.