This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Tran Thi Ngat - Department of General Surgery - Vinmec International General Hospital Da Nang. Dr. Ngat has over 15 years of experience as an Anesthesiologist.Total parotid glandectomy in preservation of 7th nerve is a type of surgery to remove the entire tissue area of the parotid gland outside the body but does not affect the VII nerve. They work to maintain sensation and movement of facial muscles. Surgery to remove the entire parotid gland preserving the 7th nerve under laryngeal mask anesthesia is increasingly popular in difficult cases.
1. Overview of pregnancy total glandectomy while preserving the VII nerve
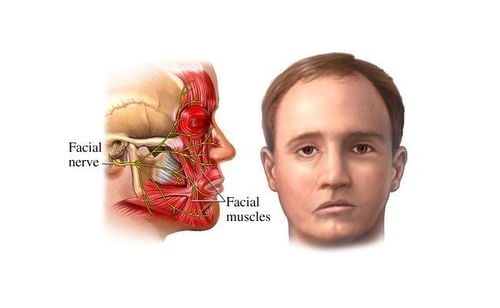
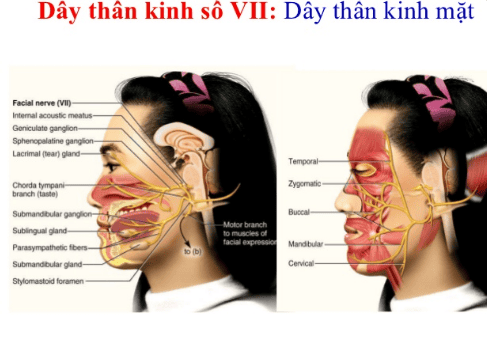
The parotid or parotid salivary gland is one of the major salivary glands in the human body. The parotid gland is located under the skin in front of the ears and has an opening that drains the duct into the oral cavity. The parotid gland is the largest salivary gland in the human body, playing an important role in the process of chewing and digesting primary food in the oral cavity.VII or facial nerve is a mixed nerve that supplies sensation and movement to most facial muscles. After exiting the skull, the seventh nerve branches to the ear region. At the position of the gestational gland, the facial nerve divides into two large branches, the one that innervates the facial neck region and the one that supplies the temporomandibular region. Then they divide again into many small branches and form the parotid plexus.
Parotid gland stones that do not respond to treatment with drugs Large parotid cysts causing compression Tumor Parotid gland area Acute parotid gland inflammation is a common disease, but is contraindicated for surgical removal of the entire parotid gland.
2. Procedure for performing anesthesia with laryngeal mask mask to cut the entire parotid gland to preserve nerve VII
Laryngeal mask anesthesia is one of the general anesthetic techniques in which the laryngeal mask is used as a respiratory protection device for the patient during surgery. Total parotid glandectomy to preserve the VII nerve can be performed in many different forms of anesthesia, however, the choice of laryngeal mask anesthesia is preferred in the following cases:patients unable to intubate or difficult intubation Patients with many serious underlying medical conditions affecting the respiratory system Patients need to control airways and airways during surgery. Facilities that do not have enough facilities to use anesthesia for resuscitation should not choose laryngeal mask anesthesia for total parotidectomy.
To ensure patient safety and effectiveness for the surgical process, laryngeal mask anesthesia for surgical removal of the entire parotid gland to preserve the VII nerve should be performed in the correct order of the following steps:
Prepare medical staff: the surgical team includes odonto-stomatology or otolaryngologists trained in parotid gland surgery and anesthesiologists who take on the role of anesthesiologists. strength. Preparation of equipment and instruments: it is necessary to have all the basic tools used in surgery such as scissors, cold knife, electric knife, surgical forceps, Kelly, ball, microscope, blood-soaked cotton swabs, needle, thread. Laryngeal mask anesthesia kit is also prepared in advance including the system of machines used in anesthesia, laryngeal mask with many sizes, mask, canule Patient preparation: the surgeon should advise and explain Educate the patient about the surgery and possible complications. Clinical examination, taking medical and medical history as well as ordering laboratory tests to provide an accurate diagnosis before intervention.

3. Follow-up of patients after total parotidectomy with preservation of nerve VII
After a surgery with general anesthesia such as total parotid gland resection, preserving the 7th nerve under laryngeal mask anesthesia, the patient should be closely monitored in the postoperative period through signs and symptoms. such as:Pulse, temperature, blood pressure Amount of fluid from drains Swelling of local tissues Check and change wound dressings daily Use medications to reduce inflammation and edema of tissues at the incision If If progress is good, drains can be removed in one to two days Wounds heal well, with no inflammatory or bleeding complications can be sutures removed after 7 days of surgery Total gillectomy Ears with preserved nerve VII can cause some unwanted complications such as:
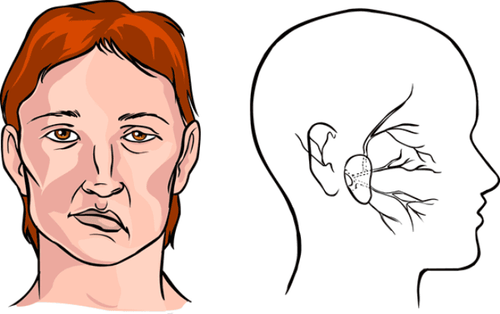
Bleeding: the maxillofacial region is rich in blood vessels. Postoperative bleeding may be due to damage to the branches of the external carotid or superficial temporal arteries. Detect bleeding complications through the amount of fluid from the drain and the patient's hemodynamic status. Infection: swelling, redness, and pus discharge from the incision. Facial paralysis due to damage to the small branches of the VII nerve
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that strictly applies safe surgical anesthesia practice standards according to international guidelines. Vinmec has a team of experienced anesthesiologists and nurses, modern equipment such as: nerve detectors, ultrasound machines, Karl Storz's difficult airway control system, comprehensive anesthesia monitoring system GE's AoA (Adequate of Anesthesia) including monitoring of anesthesia, pain and muscle relaxation will provide high quality and safety, helping patients to have adequate anesthesia, not wake up, and do not have residual muscle relaxants after surgery.
Vinmec Health System is also proud to be the first hospital in Vietnam to sign with the World Anesthesiology Association (WFSA) towards the goal of becoming the safest hospital for surgical anesthesia in Southeast Asia.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.