This is an automatically translated article.
Our muscular system consists of many different types of muscles and each type plays an important role in the function of the body. Muscles participate in many activities and functions of the body. Without muscles, we cannot live.
1. How many types of muscles are there in the muscular system?
The human muscular system has 3 types of muscles which are:
Skeletal muscle Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle All muscles are composed of one type of elastic tissue. Each muscle is composed of thousands and tens of thousands of small muscle fibers. Each muscle fiber is about 40mm long. Each muscle fiber is commanded by a nerve, which causes it to contract. Muscle strength depends mainly on the number of muscle fibers.
To fuel muscles, the body metabolizes food to produce Adenosine triphosphate (ATP), muscle cells convert ATP into mechanical energy.
1.1. Skeletal muscle
Skeletal muscles help to move the external parts of the body and limbs. Skeletal muscle covers bones and gives shape to our bodies.
For every striated muscle in the human body there is an identical muscle on the opposite side. There are about 320 pairs of identical bilateral muscles. When one muscle contracts, the other relaxes and this allows the bones to move.
Muscles are attached to tendons, tendons are attached to or directly connected to bone. The tendons extend over the joints, this helps keep the joints stable.
Skeletal muscle is the only type of muscle that can be consciously controlled. Most of our movements happen when striated muscles contract. Including eye movements, head, arms, fingers, running, walking and talking, facial expressions such as smiling, frowning, mouth and tongue movements are all controlled by striated muscles.
Skeletal muscles continuously make small adjustments to maintain posture, helping to keep a person upright or the center of the head in one position. The bones need to be held in place so that the joint does not dislocate. The striated muscles and tendons help with this.
Skeletal muscles also generate heat when they contract and release. This helps maintain body temperature. Up to 85% of body heat is due to muscle contraction.
Skeletal muscle is divided into different types, there are two main types:
Type I - red or slow twitch muscles: these are dense and capillary muscles. They are rich in myoglobin and mitochondria, which gives them their red color. This type of muscle can contract for a long time without much effort. Type I muscles can sustain aerobic activity by using carbohydrates and fats for fuel. Type II - nuclear twitching muscles: these muscles can contract quickly and with a lot of force. The contraction is strong but very brief. This muscle type is responsible for most of our muscle strength. These muscles can increase in mass after periods of weight training.
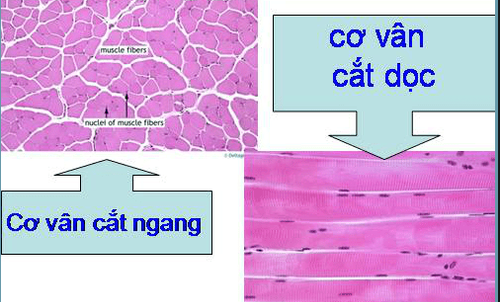
Cơ vân bao phủ xương và tạo hình dáng cho cơ thể.
1.2. Smooth muscle
Smooth muscle is responsible for movements in the stomach, intestines, arteries and hollow organs. The smooth muscles in the intestines are also called visceral muscles.
These muscles are activated automatically. We don't know if they are active or resting. Unlike striated muscles, they function independently of our conscious thinking.
Smooth muscles in the walls of the intestines contract to help push food forward. During childbirth, the smooth muscles in a woman's uterus contract to push the fetus out. Our pupils contract or dilate, depending on how much light hits the pupil. These movements depend on smooth muscle movement.
Smooth muscles are also present in the structures of the bladder, bronchi and pili plaques in the skin, making the hair stand up.
1.3. Cardiac muscle
Cardiac muscle is a unique type of muscle found only in our heart. The heart muscle is responsible for the contractions that produce the heartbeat.
The heart muscle works continuously without stopping, day and night. They work automatically, they produce electrical impulses that cause the heart's contractions, but hormones and stimuli from the nervous system can also affect these impulses. As you get scared, your heart rate increases.
The heart muscle contracts so that the heart can pump blood for us and releases so the heart can fill with blood again.
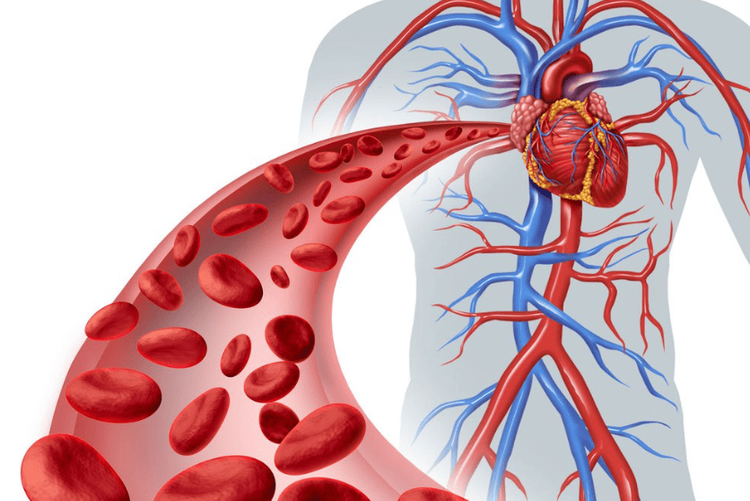
Cơ tim chịu trách nhiệm co bóp tạo ra nhịp tim
2. Muscle function
Muscles have many different functions, the main functions of muscles include:
2.1. Motor
Skeletal muscles are responsible for our movements. Skeletal muscle is attached to bone and is partly controlled by the central nervous system.
We use skeletal muscles whenever we move. Rapid-twitch skeletal muscles produce short, vigorous movements. Slow twitch muscles work better for longer movements.
When muscles contract, gross or subtle movements:
Gross movements include large, coordinated movements and include: Walking Jogging Swimming Subtle movements include small movements, such as: : Writing Speak Facial Expressions Smaller striated muscles are usually responsible for these activities.
Most muscle movements of the body are under conscious control. However, some movements are reflexive, such as withdrawing the hand from a heat source.

Cơ vân chịu trách nhiệm cho các chuyển động của cơ thể như chạy bộ
2.2. Stable
Tendons stretched over the joint contribute to joint stability. The muscle tendons in the knee and shoulder joints are important in stability.
The core striated muscles of the body include the abdominal muscles, the back muscles, and the pelvic muscles. This muscle group helps to protect our spine and helps with stability, it's like the trunk of a tree. The stronger the core muscle group, the more stable we can be.
In addition, the muscles in the calves also help us to stabilize.

Phần cơ ở bắp chân rất quan trọng trong việc ổn định.
2.3. Posture
Skeletal muscles help keep our body in control of posture such as sitting or standing. Flexibility and strength are key to maintaining proper posture.
Stiff or weak muscles can cause loss of control, leading to poor body posture and misalignment. Poor posture can affect parts of the body, leading to joint pain and weakening muscles. The most affected parts are:
Shoulders Spine Hips Knees
2.4. Circulate
The heart is like a pump, pumping blood throughout the body. The movement of the heart is not under our conscious control, but it works automatically, stimulated by electrical signals.
Smooth muscle in arteries and veins is also involved in blood circulation in the body. These muscles maintain blood pressure and circulation in the event of blood loss or dehydration.
These muscles relax to increase blood flow during intense exercise, when the body needs more oxygen.
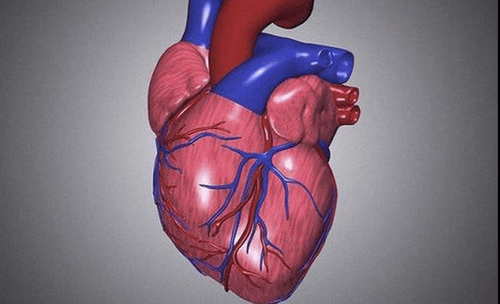
Cơ tim có nhiệm vụ đẩy máu lưu thông trong hệ tuần hoàn
2.5. Respiratory
Our breathing is related to the movement of the diaphragm. The diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscle located just below the lungs. When the diaphragm contracts, it pushes downward, causing the chest cavity to expand. Then the lungs fill with air. As the diaphragm relaxes, it helps push air out of the lungs.
When we need to breathe more deeply, we need the help of other muscles, called accessory respiratory muscles, including:
Abdominal muscles Back muscles Neck muscles
2.6 Digestion
The digestive tract extends from the mouth to the anus, and it is controlled by the smooth muscles in it.
Food moves through the digestive system with wave-like movements called peristalsis. Smooth muscles in the digestive tract contract and relax to create these movements, pushing food through the esophagus into the stomach.
The muscles in the stomach relax to allow food in, while the lower muscles help to mix the food with digestive juices.
Digested food moves from the stomach to the small intestine by peristalsis. Then the smooth muscles in the colon will contract to let the food residue - feces out of the body.
2.7. Vision
Six striated muscles around the eyes control facial movements. And the muscles inside the eye are made up of smooth muscles. These muscles work quickly and accurately, allowing the eye to:
Maintain a stable image Observe the surrounding area Track moving objects. If these muscles are damaged, our vision can be impaired.

Khi sáu cơ vân xung quanh mắt bị tổn thương sẽ ảnh hưởng đến thị lực
2.8. Peeing
The urinary system includes both smooth and striated muscles, both internal and external:
Bladder Kidneys Penile or vagina Prostate (men) Ureters Urethra Right muscles and nerves work together to hold and release urine from the bladder.
2.9. Birth
Smooth muscles in the uterus will grow and stretch during pregnancy. During labor, these muscles will contract and relax, which will push the baby through the vagina out. In addition, the pelvic floor muscles help guide the baby's head down into the vagina.
Các cơ trơn trong tử cung giúp đẩy em bé qua âm đạo ra ngoài
2.10. Protect internal organs
Muscles protect the internal organs in the front, sides and back of the body. The bones of the spine and ribs also help to better protect the internal organs.
The muscular system also protects bones and organs by absorbing force and reducing friction in the joints.
2.11. Regulate body temperature
Maintaining a normal body temperature is an important function of the muscular system. About 85% of the heat a person generates in the body comes from contracting muscles.
When the body temperature drops below the optimal level, the striated muscles will increase their activity to generate heat. Shivering is an example of this mechanism. The muscles in the blood vessels also contract to maintain body temperature.
Body temperature can be brought back to normal through smooth muscle relaxation in blood vessels. Show

Cơ bắp còn có chức năng điều chỉnh nhiệt độ cơ thể
3. Interesting things about the muscular system you may not know
Muscles make up about 40% of total body weight. The heart is the hardest working muscle in the body. It pumps about 5l of blood per minute. The gluteus maximus is the largest muscle in the body. It helps us maintain an upright posture. Our ears contain the smallest muscles in the body along with the smallest bones. The bite muscle is the strongest muscle by weight. It allows the teeth to bite back with a force of up to 55 pounds on the front teeth or 200 pounds on the molars. The muscular system is a complex and important network for the human body. Muscles are involved in many bodily functions. They control heart rate and breathing, help with digestion, and allow us to move.
Muscles thrive when we exercise and eat smart. However, if we exercise too much, it can also cause muscle pain. Muscle pain can also be a sign of a more serious condition affecting the body. Some conditions that affect the muscular system include:
Muscular Dystrophy Multiple Sclerosis Parkinson's Disease Fibromyalgia References: healthline.com; medicalnewstoday.com