This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Minh Son - Interventional Cardiologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Nha Trang International General HospitalAtherosclerosis is a common medical condition today. They can cause many serious cardiovascular and vascular events.
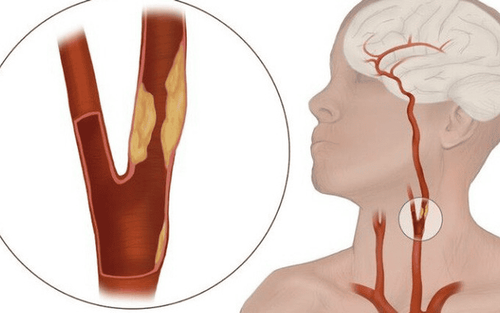
Arteries are blood vessels that help circulate oxygen-rich blood throughout the body, from the brain to the tips of the toes. Good arteries will have smooth inner walls and blood can flow through them easily. However, in some people, their arteries become blocked. An artery is blocked by a plaque buildup of substances called atheroma inside the artery wall. These plaques impede blood flow or, in some cases, block arteries.
Atherosclerosis will significantly increase the risk of heart attack, stroke and even death. Therefore, no matter how old you are, it is extremely important to be aware of the dangers posed by atherosclerotic plaques and to have a treatment strategy to avoid serious consequences.

Đột quỵ là biến chứng nguy hiểm của bệnh lý xơ vữa động mạch
1. What causes atherosclerotic plaques?
Atherosclerotic plaques that accumulate in the inner walls of arteries are formed from various substances circulating in the blood. These include calcium, fat, cholesterol, cellular waste, and fibrin (a substance involved in blood clotting). In response to the plaque buildup, cells in the artery walls multiply and secrete more substances that make the blockage worse.
Plaque deposits on the inner walls of arteries causing atherosclerosis. This disease causes the arteries to narrow and harden.
Although experts do not know exactly what is at the root of atherosclerosis. This process can originate from the damage of the endothelium of the arteries, allowing plaque to accumulate, which can originate from:
The body contains more bad cholesterol and less good cholesterol. High levels of bad cholesterol, or low-density lipoprotein - LDL, are the main contributors to the formation of atherosclerosis. However this is not to say, we also have good cholesterol, or high density lipoproteins, circulating in our blood. High-density lipoproteins (HDL) are thought to remove bad cholesterol from the atherosclerotic plaques in the arteries and return them to the liver, where they are eliminated.
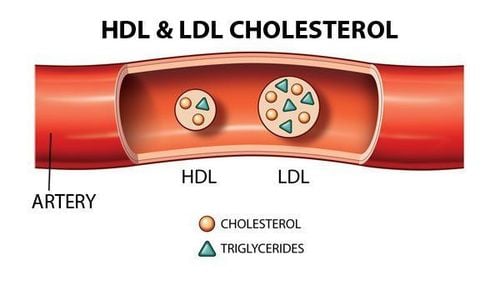
Nồng độ cholesterol xấu cao làm gia tăng mắc bệnh xơ vữa động mạch
Hypertension: High blood pressure will increase the rate of accumulation of atherosclerotic plaques. This also promotes the hardening of plaque inside the arteries. Smoking: Smoking is considered to be the cause of an increased rate of atherosclerosis in the coronary arteries, blood vessels of the extremities, and the aorta (the main and largest artery in the human body). Diabetes, or hyperglycemia, is also one of the main culprits. Even people who have just had high blood sugar without diabetes, such as metabolic syndrome, are at risk for atherosclerosis. Other causes include family history, stress, sedentary lifestyle and obesity. Knowing your family history is extremely important. Atheroma usually begins to form in childhood or adolescence. Strong dynamic obstruction then develops from middle age or later.
Đái tháo đường là một tác nhân gây xơ vữa động mạch
2. What are the dangers of atherosclerosis and blocked arteries?
This depends on where the atherosclerotic plaque accumulates. Blocked arteries in many parts of the body can lead to many diseases at the same time, including:
Coronary artery disease: Atherosclerotic plaques build up in the lining of the arteries that carry blood to the heart. This causes coronary artery disease, or heart disease. Coronary artery disease causes chest pain and shortness of breath. Heart attack is the leading cause of death in the United States. Carotid artery disease: The carotid artery is an artery that travels up the sides of the neck. They help deliver oxygen to the brain. Atherosclerosis in the carotid arteries can cause a stroke. Peripheral artery disease: If atherosclerotic plaques build up in the vessels that carry blood to the legs, they reduce the amount of oxygen transported. Impaired blood flow causes pain, paralysis, or serious infection in the legs and feet.
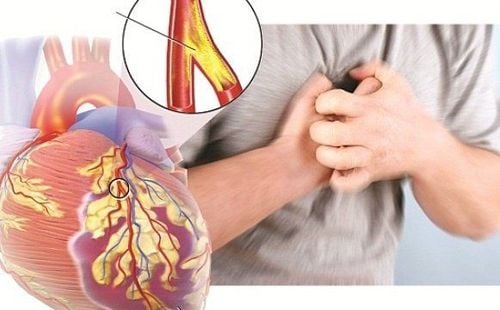
Bệnh động mạch vành khiến người bệnh dễ xuất hiện các cơn đau ngực
3. Does obstructive artery disease cause any symptoms?
In many cases, a blockage in an artery doesn't cause any symptoms until a major event occurs, such as a heart attack or stroke.
In other cases, especially when an artery is 70% or more blocked, the buildup of atherosclerosis can cause symptoms including:
Chest pain Shortness of breath Fast heartbeat Body failure weakness or lightheadedness Nausea Sweating The first symptom, chest pain, is also known as angina. Caused by reduced blood flow to the heart due to plaque buildup in the coronary arteries of the heart.
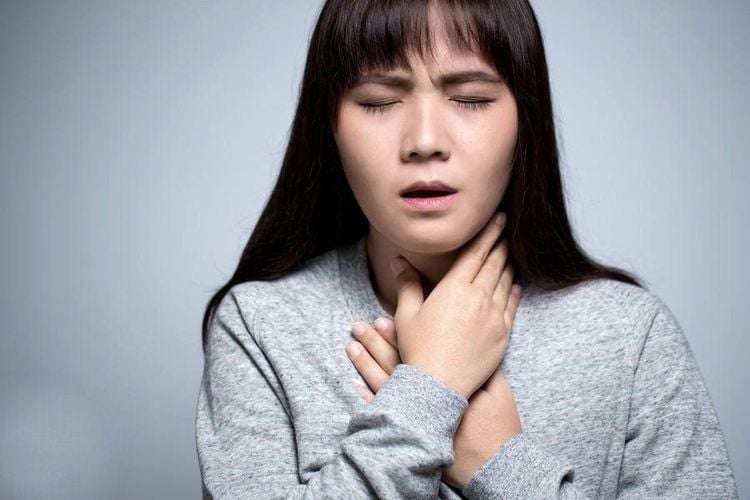

Khó thở là triệu chứng thường gặp ở bệnh nhân tắc nghẽn động mạch
A feeling of weakness and numbness in a part of the body. Inability to move an arm or a leg Loss of vision on one side Impaired language function Peripheral artery occlusion will cause:
Leg pain Slow healing of foot injuries Feet cold gangrene
4. Are there any tests to diagnose obstructive artery disease?
The answer is yes, there are several tests for occlusive disease. Your doctor will decide which test is appropriate based on your symptoms and medical history. Tests may include:
Blood cholesterol test Chest X-ray CT scan (computed tomography) Doppler vascular ultrasound Echocardiogram and stress echocardiogram Magnetic resonance imaging or positron emission tomography Angiography Angiography Contrast-injected blood
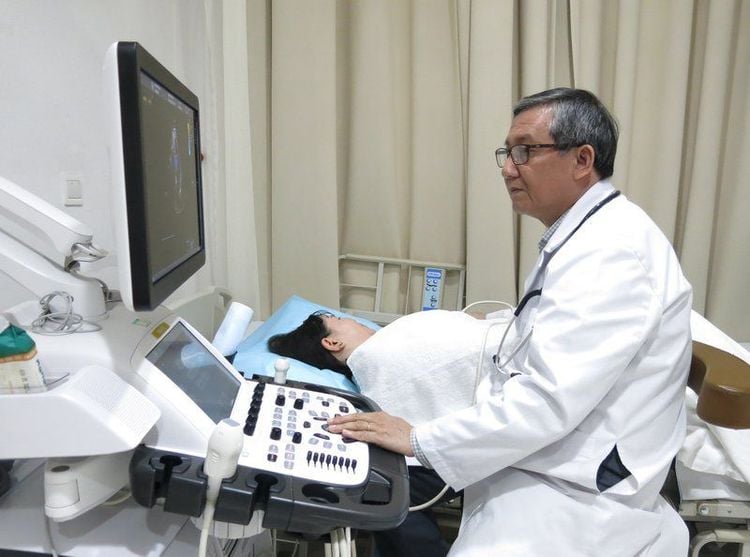

Siêu âm tim cho phép chẩn đoán bệnh tắc nghẽn động mạch
5. How can coronary artery disease and atherosclerosis be treated?
There are many prevention and treatment options for blocked arteries. The way to reduce plaque and prevent blood vessel blockage that the doctor prescribes will depend on the severity and medical history of the patient. Your doctor may prescribe one or more of the following:
5.1. Lifestyle changes
A healthy lifestyle is essential for the management of atherosclerosis and the progress of arterial occlusion.Includes:
Diet low in saturated fat and cholesterol, low in sugar and rich in fruits and vegetables Maintain a healthy weight Don't smoke Exercise regularly Manage stress Keep your blood healthy moderate blood pressure and cholesterol Keep blood sugar in moderation

Duy trì thói quen tập thể dục giúp ngăn ngừa bệnh xơ vữa động mạch
5.2. Surgery or other interventions.
In many cases, the patient will need surgical measures to treat the blockage of the blood vessel and prevent further accumulation of plaque. Interventional modalities may include:
Stenting: A holder called a stent, which can contain medication, is placed in an artery to maintain adequate blood flow. A cardiac catheter is used through the leg artery to connect to the heart, and a stent is placed through the heart catheter to the site of the blockage. Arterial bypass surgery: In this type of surgery, arteries from other parts of the body are cut to bypass blocked arteries and help deliver oxygen-rich blood to designated locations. Balloon angioplasty: This procedure opens up partially or completely blocked arteries with a device that pushes the plaques against the vessel wall.
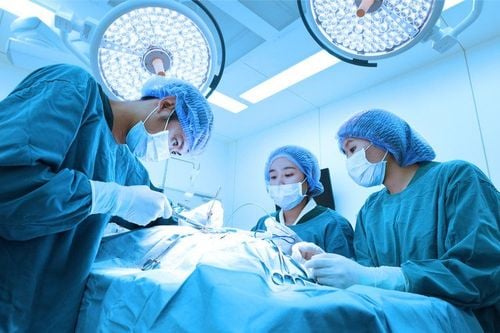
Phẫu thuật bắc cầu động mạch là phương pháp điều trị hiệu quả bệnh xơ vữa động mạch
5.3. Use drugs.
Many medications can help control factors that contribute to the buildup of atherosclerotic plaques. These drugs include:Cholesterol-lowering drugs Blood pressure-lowering drugs Aspirin or other anti-thrombotic drugs, which help reduce the likelihood of dangerous blood clots forming Vinmec International General Hospital With a system of facilities, modern medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in medical examination and treatment, patients can rest assured for examination and treatment at the hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: webmd.com