This is an automatically translated article.
Food allergies are extremely common, affecting about 5% of adults and 3% of children (this percentage is increasing). Any type of food can cause an allergic reaction, but the majority of food allergies focus on the eight common foods below.What is a food allergy?
A food allergy (food allergy) is a condition in which one or certain foods cause an abnormal immune response. That's because the body's immune system mistakenly recognizes certain proteins in food as harmful, thereby triggering a series of defense mechanisms (including the release of chemicals like histamine) that cause inflammation.For people with food allergies, even contact with a very small amount of the allergenic food is enough to cause an allergic reaction. Symptoms may appear minutes to hours after exposure and include:
Swelling of the face, mouth, tongue Difficulty breathing Low blood pressure Vomiting Diarrhea Urticaria In severe cases, a real allergy product may cause anaphylaxis. Symptoms will appear and progress very quickly and include an itchy rash, swelling of the throat or tongue, difficulty breathing, and low blood pressure. Anaphylactic reactions can be life-threatening.
Many cases are just food intolerance but mistaken for a food allergy. Food intolerance has nothing to do with the immune system, so while it can have a big impact on quality of life, it's not life-threatening.
Food allergies can be classified into two main categories: IgE allergies and non-IgE allergies. IgE is a type of antibody. An antibody is a protein in the blood that has an immune role in recognizing and fighting off infections. In IgE allergy, IgE antibodies are released by the immune system. In non-IgE allergy, IgE antibodies are not present, instead other components are present.
Dị ứng thức ăn có thể phân thành hai loại chính: dị ứng IgE và dị ứng không IgE
The Eight Most Allergenic Foods
1. Cow's milk Cow's milk allergy is most common in young children, especially those exposed to cow's milk protein before 6 months of age.Cow's milk allergy is the most common food allergy in children, affecting 2-3% of young children. However, about 90% of children with allergies go away by the time they are three years old, making cow's milk allergy less common in adults.
Cow's milk allergy can present in both IgE and non-IgE allergy forms, but IgE allergy is the most common and also carries the greatest risk of progression.
Cases of IgE cow's milk allergy usually show the first signs of reaction 5 to 30 minutes after ingestion, including: edema, rash, urticaria, vomiting, and in rare cases is an anaphylactic reaction.
Non-IgE cow's milk allergy typically presents with gastrointestinal symptoms such as vomiting, constipation, or diarrhea, as well as enteritis. Non-IgE milk allergy is difficult to diagnose, because the symptoms resemble an intolerance and there is no blood test that can be used to make a differential diagnosis.
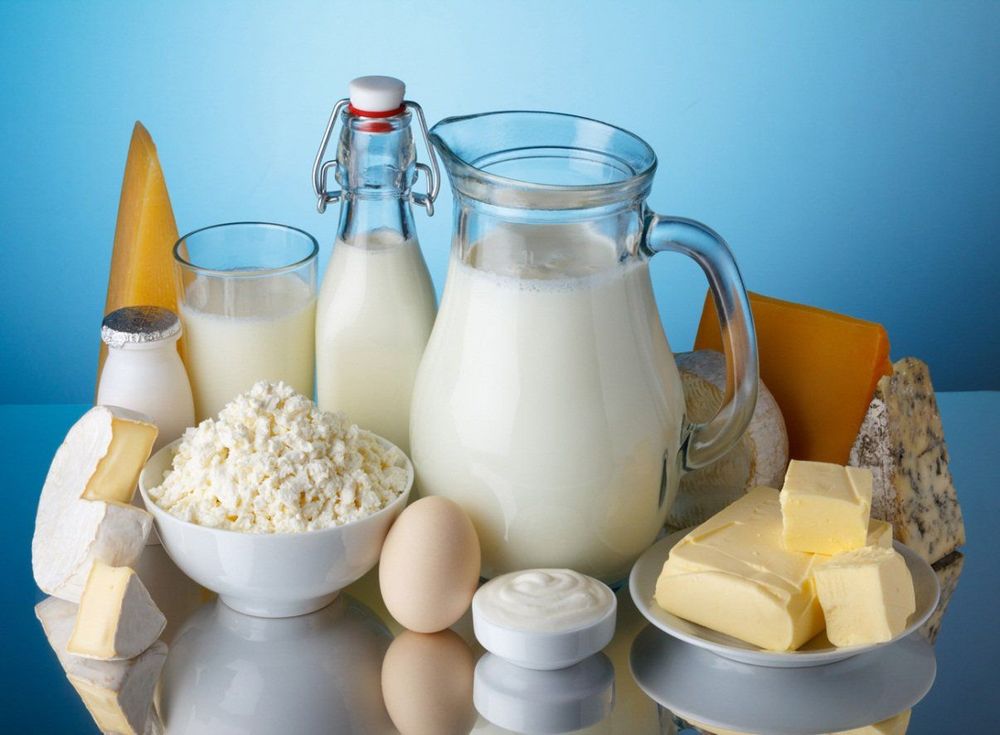
If you really have a cow's milk allergy, the only way to treat it is to avoid cow's milk and cow's milk products, including foods and drinks such as:
Fresh milk Milk powder Cheese Butter Vegetable oils Milk Sour Cream Breastfeeding mothers may need to avoid cow's milk and cow's milk products if their child has allergies.

Nếu thực sự bị dị ứng sữa bò, cách duy nhất để điều trị là tránh sữa bò và các chế phẩm từ sữa bò
Egg allergy symptoms include:
Digestive disturbances, such as abdominal pain. Skin reactions, such as redness, hives. Breathing problems. Anaphylactic reactions (rare). There is a special point, is that a person can be allergic to egg white but have no problem with egg yolk, and vice versa, because the protein in white and yolk is slightly different. However, allergies to egg whites are still more common.
The treatment for egg allergy is still to eliminate eggs from the diet, but you may not need to avoid all foods related to eggs, because the protein in eggs after undergoing heat processing will be denatured, causing the immune system to no longer see it as a threat and not respond.
In fact, some studies show that children with egg allergies use baked goods (cakes, cookies, etc. containing eggs) can make egg allergies go away sooner. completely. But this isn't true for everyone, and food allergies can have serious consequences, so consult your doctor carefully.
3. Nuts and Nuts Allergies to nuts and seeds are also common, they include:
Brazil nuts Cashews Almonds Macadamia nuts Pistachios Pine nuts Walnuts People who are allergic to nuts of hard shells are also allergic to products containing them (nut butters, vegetable oils, etc.). Also, although people may be allergic to only one or two nuts, people with allergies are still advised to avoid all nuts, as these people are at risk of developing an allergy to nuts. other.
Allergies to nuts and seeds can be so severe that a life-threatening anaphylactic reaction occurs. And this type of allergy usually lasts a lifetime.
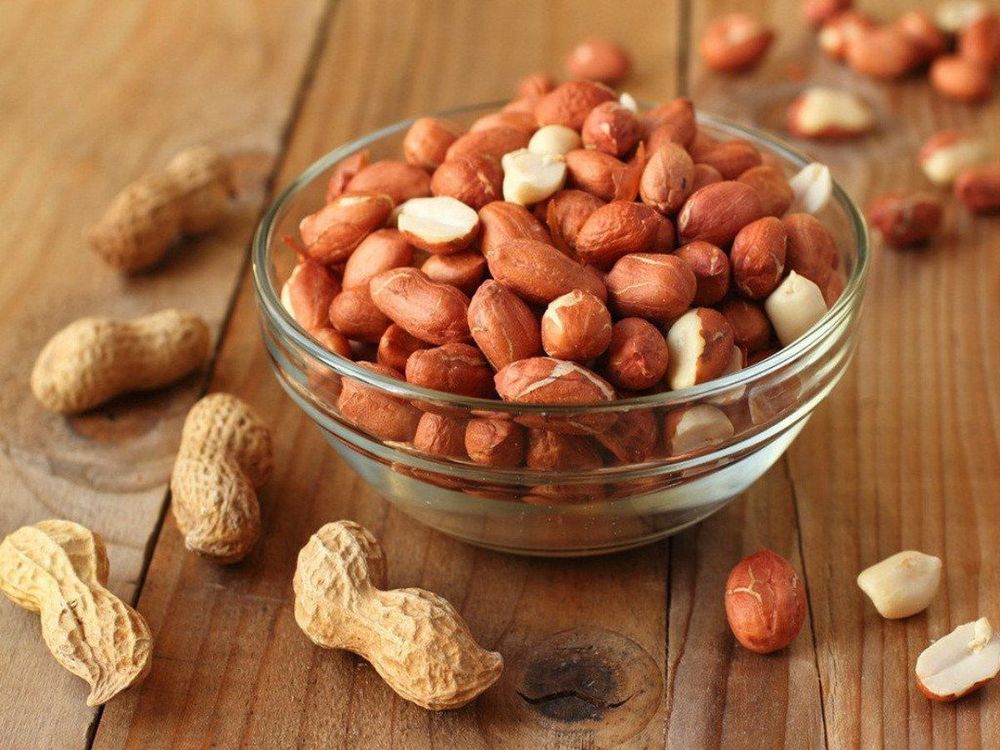
4. Peanuts

Dị ứng với đậu phộng là loại dị ứng rất phổ biến và có thể đe dọa tính mạng
Peanut allergy affects about 4-8% of children and 1-2% of adults, however about 15-22% of children with peanut allergy will outgrow their allergy by the time they are teenagers. .
People who are allergic to peanuts have only one treatment that is to completely eliminate peanuts and peanut-containing products from the diet.
5. Shellfish A shellfish allergy is an allergy to foods from crustaceans and molluscs, for example:
Shrimp (shrimp) Prawn (crayfish) Crab Squid Scallop The symptoms of a shellfish allergy are often rapid and similar to those of other IgE food allergies. A special feature of shellfish allergy is that for some people, just smelling the smell during food preparation is enough to show signs of an allergy.
Allergy to shellfish usually lasts a lifetime, so people with allergies need to eliminate all shellfish from their diet.
6. Wheat Wheat allergy is caused by an allergic response to one or several proteins in wheat. Wheat allergies most commonly affect children, although the allergy usually goes away by the age of 10.
A wheat allergy can be confused with celiac disease and non-celiac gluten sensitivity, but an allergy to wheat can be life-threatening, and the other two are not.
People who are allergic to wheat only need to avoid wheat (food, cosmetics contain wheat) but can still use other grains.
7. Soy Soybean allergy affects about 0.4% of children and is most common in children under 3 years of age, however 70% of children with allergies will clear up on their own as they get older.
A special feature of soy allergy is that some children who are allergic to cow's milk are also allergic to soy.
Because soy is a common ingredient in many foods, it is important to read product labels carefully, because people with allergies need to eliminate soy from their diets.
8. Fish Allergies to fish are also relatively common, affecting about 2% of adults. Unlike other allergies, allergies to fish can appear after adulthood.

Dị ứng với cá cũng tương đối phổ biến, ảnh hưởng tới khoảng 2% người trưởng thành
At Vinmec International General Hospital, there is a package of examination and advice on treatment of atopic dermatitis to help customers assess the overall condition of the disease and advise on measures to help prevent recurrence.
When registering for a package of examination and consultation for treatment of atopic dermatitis, customers will receive: Dermatology specialist examination. Perform tests such as: quantitative IgE, fresh mycobacteria, specific IgE quantification with respiratory allergens - food (Panel 1 Viet), test Rida Allergy Screen (panel 1)...
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Article referenced source: Healthline.com