This is an automatically translated article.
The article is expertly consulted by MSc Nguyen Cong Canh, Head of Pediatrics - Neonatology Department, Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.
Thalassemia, also known as hereditary hemolytic disease, causes red blood cells to burst, the patient is constantly anemic. This is a preventable disease with thalassemia screening and premarital screening.
1. When to see a doctor?
When a patient has any of the following symptoms: Fatigue, weakness, shallow breathing, yellow skin, dark urine, bone deformities, growth retardation, enlarged spleen, it is necessary to go to a medical facility to be diagnosed. diagnose, diagnose and treat disease.
Or when there are risk factors such as having a family member with thalassemia . The patient lives in an area with a high incidence of the disease. Thalassemia is common in Southeast Asia, China, and the Philippines.
2. How to limit thalassemia
Avoid giving birth to children carrying 2 disease genes due to being received from both parents by measures such as:
2.1. Pre-marital examination With measures of testing, counseling, pre-marital examination. Couples who are about to become pregnant or are pregnant, especially families who have had Thalassemia patients, should be consulted, diagnosed, and examined before marriage.
Pre-marital genetic counseling with the goal of birth control between two carriers of the disease. Therefore, before getting married, couples need to be tested to see if they carry the disease gene or not and it is best to avoid marriage between two people carrying the same gene. Currently, due to the influence of the media, congenital hemolytic disease has received a lot of attention and knowledge, so many couples have come to medical centers for advice and pre-marital examination to avoid pre-marital examination. the case when going to the center, it was discovered that both people carried the disease gene. If a couple carrying the same form of Thalassemia becomes pregnant, prenatal diagnostic amniocentesis should be performed at specialized medical facilities. In these cases, medicine can intervene so that the person carrying the Thalassemia gene can completely give birth to healthy children, without carrying the disease gene.

Khám tiền hôn nhân để sàng lọc di truyền
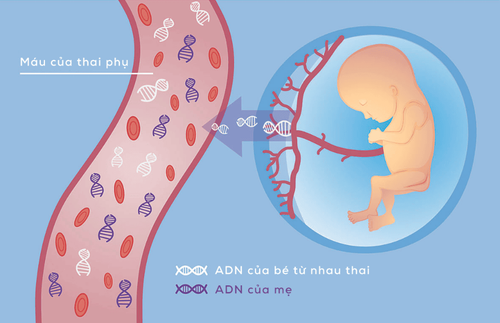
2.2. Thalassemia screening Screening for thalassemia with screening tests and diagnosing mutated genes during pregnancy. This is an effective and cost-effective measure. If both husband and wife carry the disease gene, the fetus has a 25% chance of having severe disease. In this case, prenatal diagnosis should be done by amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling and finding genetic mutations. .
Prenatal diagnosis in first trimester pregnant women. In the first 3 months of pregnancy, the mother will have blood drawn for testing to detect abnormalities.
Prenatal diagnosis is carried out with the following steps:
DNA test of 2 parents, mutation of each person. Amniocentesis or chorionic villus biopsies when the mother is pregnant. DNA test of amniotic fluid or placenta. Counseling for termination of pregnancy if the fetus is seriously ill. Use of pregnancy termination services (Obstetrics). With the above methods of antenatal thalassemia screening, some countries have achieved very good results, even preventing or not giving birth to children with severe congenital hemolytic disease. This not only limits the difficulties of families with patients, but also gathers resources to provide good treatment for existing patients with hemolytic anemia.