This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Doctor Nguyen Van Duong - Cardiovascular Center - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.
Giving an early and accurate diagnosis of myocardial infarction is very important, this will help patients quickly access appropriate treatment regimens, in order to minimize the serious complications of myocardial infarction and reduce mortality. To make an accurate diagnosis, doctors need to base on clinical symptoms combined with myocardial infarction tests.
1. What is a heart attack?
Myocardial infarction is a condition in which the heart muscle is damaged due to ischemia, causing the release of substances in the heart muscle cells into the blood. The signs to recognize a heart attack will help the patient get emergency care in time, and the tests will help accurately diagnose whether the patient has a heart attack or not and the extent of the damage.Therefore, people need to know the early warning signs of a heart attack. The warning signs of a heart attack in each person will have different manifestations and levels, besides the signs are also easy to confuse with other diseases such as respiratory disease, body weakness. However, heart attack patients still have common signs, there are two signs that every heart attack patient can have, that is:
The patient suddenly feels tired, feeling difficult Breathe even when doing things that you could do before. The patient feels restless, anxious, and insecure.

Biểu hiện của cơn nhồi máu cơ tim
Left chest pain may radiate to the jaw, to the medial border of the arm. This symptom is sometimes atypical, or there is no pain present. Dizziness, headache. Nausea, vomiting, indigestion. Sleep disorders . Sweating. Visual disturbances. Numbness in hands or arms, loss of appetite. Women and men will have different warning signs, such as breast pain in women less often, but symptoms of fatigue, anxiety, headache, and dizziness are more common.
However, these are only warning symptoms of a heart attack, and cannot confirm whether you have a heart attack or not. To confirm the diagnosis, it is necessary to rely on tests to detect myocardial infarction.
2. Tests to detect myocardial infarction
2.1. Electrocardiogram The electrocardiogram is a very valuable laboratory method. But many times the ECG is nonspecific and unclear. The ECG image of patients with myocardial infarction will have the following changes:ST segment elevation or depression T wave inversion New Q wave or newly discovered left bundle branch block 2.2. Echocardiography Echocardiography is very valuable in diagnosing myocardial infarction, it can help us see images of regional movement disorders related to the infarct site, such as: chamber thrombosis, pericardial fluid. ,...
Simultaneously, echocardiography also helps evaluate the function of the left ventricle and mechanical complications of myocardial infarction such as: regurgitation of the heart valve due to ligament rupture, or perforation of the heart wall causing ventricular septal defect.
ECG điện tâm đồ cho thấy các sóng có dấu hiệu bất thường
2.4. Biochemical tests Biochemical tests are essential and highly valuable in the diagnosis and monitoring of myocardial infarction. Up to now, there are 3 generations of biochemical tests applied to diagnose myocardial infarction:
1st generation: Creatin kinase (CK) total Aspartate amino transferase (ASAT) Alanin amino tranferase (ALAT) Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) 2nd generation: CK-MB and Myoglobin 3rd generation: Myocardial specific proteins (Troponin) These tests are further divided into 2 types:
Enzyme and isoenzyme tests : CK, LDH, ASAT, ALAT, CK-MB,... Protein tests: CK-MB mass, Myoglobin, Troponin T, Troponin I,... The diagnosis and assessment of myocardial infarction is based on the kinetics of myocardial infarction. These substances in the blood plasma:
Release from the tissue: slow release at first, then quickly, stimulate the infarct, concentration, solubility and localization of the substances determine the time of appearance of they are in the blood. Diffusion into the blood: because the location of the myocardium is not close to the capillary network, the time from the time the cells are injured until the substances appear in the blood takes hours. Elimination from the blood: the rate of elimination of the above substances is different.
Máu ngoại vi được sử dụng làm xét nghiệm hóa sinh
Myoglobin is a protein found in the cytoplasm of the myocardium, but also in skeletal muscle. Myoglobin has the following characteristics:
Is a protein containing O2 attached Hem, has a molecular weight of 17,800 Da, it plays a role in transporting and storing oxygen in muscle cells. Is a cytoplasmic protein, making up about 2% of the total cellular protein. Having a small volume, so when there is damage to myocardial infarction, myoglobin will soon appear in the serum, so it can be used for early diagnosis. The half-life is fast, only 10-20 minutes. Myoglobin was determined by immunoassay using electroluminescence technique.
Normally Myoglobin has a plasma concentration < 70 - 110 mcg/L. The concentration of Myoglobin in the blood plasma also depends on the glomerular filtration rate, when the amount of Myoglobin in the plasma increases > 200 mcg/L, myoglobinuria will appear.

Xét nghiệm Myoglobin tăng sau nhồi máu cơ tim
Myoglobin levels rise very early, about 2 hours after acute myocardial infarction, secondary myocardial infarction or when reperfusion is successful following streptolysin therapy. Myoglobin plasma concentrations peak after 4-12 hours, returning to normal after 24 hours. This index helps in early diagnosis of myocardial infarction but is not specific because it is also increased in musculoskeletal lesions. 2.4.2.2. CK-MB mass
CK-MB mass is an isoenzyme of CK, thought to be cardiac-specific CK.
CK-MB can be determined by immunoassay using enzyme, chemiluminescence, fluorescence, or electroluminescence techniques. CK-MB is determined by its combination with CK-B and CK-M-specific antibodies or with CK-MB-specific antibodies.
There are two methods to determine CK-MB:
Activity method (UZ/L) Mass method (mg/mL): this method is more specific than activity measurement method. Normal plasma CK-MB concentrations are < 5.3 - 8 mcg/L, depending on the test kit.
CK-MB has the following clinical significance:
Concentrations increase 4-5 hours after angina attack. This is a test used in the diagnosis of myocardial infarction and reperfusion. 2.4.2.3. Troponin
Troponin is a globular protein complex located in the thin fibers of the heart muscle, it is involved in the regulation of myocardial contraction. This complex consists of three components, which are Troponin C, Troponin T, Troponin I. In which Troponin C binds to calcium and it is present in both cardiac and skeletal muscle, while Troponin T and Troponin I are cardiac muscle-specific forms. .
When the heart muscle is necrotic, Troponin will be released into the blood, so the test to detect Troponin I or T in the blood plays an important role in accurately diagnosing myocardial infarction.
Troponin I (cTnI)
Normal plasma troponin I concentrations are < 0.1-0.2 μg/L.
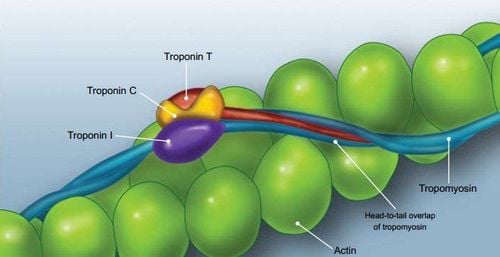
Troponin nằm trong sợi mảnh của cơ tim
During myocardial infarction: Troponin I increases with Troponin T after 3-4 hours of pain and peaks at 12-24 hours, this depends on coronary artery reperfusion. The sensitivity of Troponin I is similar to Troponin T in the first phase of acute myocardial infarction, increased with CK-MB, CK isoenzyme, Myoglobin. Troponin I has only one rising peak in the first phase. In other heart diseases: For patients after heart transplant, if there is no exclusion of heart palpitations, troponin I will return to normal very quickly, about 2-3 weeks. Unstable angina: troponin levels are associated with complications and mortality. Troponin T (TnT)
Normal plasma concentrations of Troponin T < 0.03 ng/ml.
Clinical significance of Troponin T index:
Troponin T test has 100% sensitivity (10 hours - 5 days). The specificity is greater than that of CK-MB carrying Myoglobin. The half-life of troponin is < 2 hours. After myocardial infarction, troponin T appeared early in the serum, reached its maximum value at day 4 and then gradually decreased until day 12, thus potentially diagnosing myocardial infarction until day 4. late. Troponin T is as sensitive as CK-MB, Myoglobin at an early stage, when the damaged area is reperfused, serum troponin T will have a second peak at 14 hours. Therefore, troponin T has the ability to monitor the effect. thrombolytic therapy. Troponin T can provide a preliminary assessment of the size and extent of myocardial infarction on values measured at 3 - 4 days after the pain. Diagnosis of myocardial infarction is confirmed when TnT > 0.1ng/ml. Differentiate myocardial infarction from trauma and other surgery, especially when TnT is consistently elevated 3 to 4 days after trauma or surgery.

Các xét nghiệm nhồi máu cơ tim cần được thực hiện tại cơ sở y tế uy tín
The above are the indicators of myocardial infarction test, depending on the condition of each patient and the physical conditions of the medical facility, the doctor will choose the appropriate tests to diagnose the heart attack. myocardial blood.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space. Customers when choosing to perform tests here can be completely assured of the accuracy of test results.
Dr. Nguyen Van Duong has many years of experience in the diagnosis and treatment of internal cardiovascular diseases and cardiovascular interventions; Perform other noninvasive functional investigations in the diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Currently working as a doctor at Cardiovascular Center, Vinmec Central Park Hospital from August 2017 aid.
MORE:
What to eat with ischemic cardiomyopathy? Acute myocardial infarction: Causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of cardiogenic shock in myocardial infarction