This is an automatically translated article.
The article was consulted professionally with Master, Doctor Do Thi Hoang Ha - Doctor of Biochemistry - Laboratory of Laboratory - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.Blood lipids or "blood fats" are an important component of the body consisting of many different structures in which the most important component is cholesterol. Dyslipidemia will increase the amount of cholesterol, triglycerides or both, or decrease the concentration of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) or increase the concentration of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) affecting the process of atherosclerosis. Dyslipidemia tests or “fat tests” will help identify these disorders to diagnose medical conditions caused by dyslipidemia.
1. Overview of lipid components in the blood
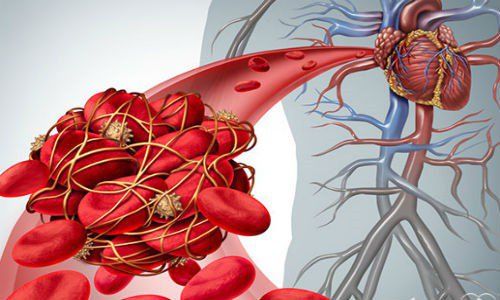
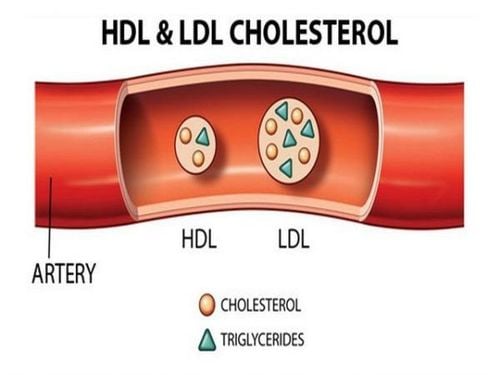
LDL Cholesterol: This is a low-molecular-weight lipoprotein that is considered the “bad” component of cholesterol. This bad cholesterol can cause dangerous diseases for the body such as stroke, atherosclerosis, kidney stones, heart attack, etc., causing death of the patient because the increased LDL in the blood will lead to deposition. Their accumulation easily in blood vessels causes atherosclerotic plaque. Atheroma when forming can cause narrowing or blockage of blood vessels (especially in the heart and brain) or rupture of blood vessels, causing dangerous diseases such as myocardial infarction or cerebrovascular accident.LDL cholesterol in the blood can be increased due to factors such as family, diet and exercise, tobacco use, medical conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure and is a very important indicator in the follow-up. Monitor and treat dyslipidemia.
HDL Cholesterol : accounts for 25-35% of total cholesterol in the blood and is called good cholesterol, plays a protective role in the heart because it transports cholesterol from the blood to the liver and transports cholesterol away from atherosclerotic plaques. reduce the risk of atherosclerosis and avoid dangerous cardiovascular complications. HDL decreases due to risks such as smoking, being overweight and obese, and being inactive.
Triglycerides: This is also a form of body fat, synthesized in the liver from fatty acids, glucose and protein. Triglycerides are stored in fat and muscle tissues, used by the body as an energy source when needed, and are often increased in subjects who are obese, sedentary, smoker, alcoholic, or have diabetes. Elevated blood triglycerides will often be accompanied by elevated total cholesterol
2. Results of dyslipidemia test
The values of blood lipid components will help to assess the status of lipidosis as follows:For total cholesterol:
< 200 mg/dl: low risk of coronary artery disease 200-239 mg/dl: borderline The world should pay attention to coronary heart disease > 240 mg/dl: patients have hypercholesterolemia and have a risk of coronary artery disease 2 times higher than normal For HDL - cholesterol:
> 60 mg/dl: good significance when HDL- cholesterol increases help protect the body against cardiovascular risks HDL- low cholesterol when less than 40 mg/dl (for men) or less than 50 mg/dl (for women) is a major risk of heart disease For LDL-cholesterol :
< 100 mg/dl: very good 100-129 mg/dl: Within normal range 130-159 mg/dl: limit increase 160-189 mg/dl: elevated index (risk) high risk) > 190 mg/dl: very elevated number equates to very high risk

< 150 mg/dl: normal 150-199 mg/dl: slight increase 200-499 mg/dl: increase > 500 mg/dl: very high
3. Is dyslipidemia dangerous?
High cholesterol is a major risk factor for cardiovascular diseases such as coronary artery disease, myocardial infarction and cerebrovascular accident. When there is too much LDL cholesterol circulating in the blood, it will cause them to gradually settle into the blood vessel walls, causing the formation of atherosclerotic plaques that narrow the artery or even cause a complete blockage.Atherosclerosis is thought to be the infiltration of cholesterol and other atherosclerotic components into blood vessels resulting from damage to the vascular endothelium. Atherosclerosis may increase with age, familial factors, and risk factors other than dyslipidemia such as diabetes, hypertension, obesity, and smoking.
4. How to prevent dyslipidemia?
Through blood lipid tests, it is possible to assess the status of dyslipidemia in the body, one of the leading risks of cardiovascular disease. To prevent dyslipidemia, you can do the following things:Build a healthy lifestyle: Eat a healthy, reasonable diet, exercise regularly and eliminate habits such as smoking, drinking too much. lots of alcohol. Make appropriate adjustments when eating foods that raise LDL-cholesterol such as: saturated fat from animal or vegetable fats such as coconut, margarine, unsaturated fats such as pork, beef, full-fat butter, instant food, fast food, fried food, offal of animals,... Should eat foods such as: vegetables, fruits, cereals and processed raw (black bread, raw rice), fat-free milk , lean meat, skinless poultry, fatty fish, beans, nuts, unsaturated vegetable oils. Smoking is a factor that affects the formation of atherosclerosis and causes lipid disorders, so it should be eliminated immediately. Lose weight and keep your body mass index at an ideal level (BMI: 19-23).

Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.