This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Doctor Tran Truong Giang - Intensive Care Unit - Vinmec Times City International HospitalThe procedure of super Doppler pulse technique in critically ill patients is a non-invasive exploratory technique that helps doctors quickly diagnose some vascular diseases in patients and take timely measures.
1. Outline
Bedside emergency vascular ultrasound is a necessary non-invasive exploratory technique in the emergency resuscitation of critically ill patients, helping clinicians quickly diagnose a number of vascular diseases, thereby provide positive and effective treatment for the patient.2. Indications for pulse Doppler technique in emergency resuscitation patients
Venous thromboembolismArterial thrombosis Carotid artery disease... Renal artery disease Aneurysm dissection
3. Contraindications of pulse Doppler technique in critically ill patients
There are no contraindications.4. Technical procedure of super Doppler pulse in patients in emergency resuscitation
4.1 Preparation Performers: 1 doctor and 2 nurses.The doctor has been trained in echocardiography, blood vessels:
Wear a hat, wear a mask, wash hands Sit on the right side of the patient Right hand holds the transducer, left hand adjusts the buttons of the ultrasound machine. Nursing: Wearing a hat, wearing a mask
01 The nurse monitors vital functions, ensures breathing and intravenous lines for the patient during the ultrasound. 01 Nursing assistant to the doctor during the procedure: Change the patient's position. Equipment: Ultrasound machine with vascular ultrasound function Life function monitor monitor: Heart rate, SpO2, breathing rate, blood pressure Ultrasound gel: 1 bottle Clean sterile gauze: 1 pack Examination gloves: 3 pairs of caps surgery: 3 pcs Surgical mask: 3 pcs Quick hand washing solution Electrocardiogram monitoring electrodes when doing ultrasound: 3 pcs Maintenance cost of the machine Depreciation expense Explain to the patient and the patient's family Know the benefits of bedside vascular ultrasound.
The patient lies on his back, depending on the position of the ultrasound, there are different positions.
Simultaneous electrocardiogram during ultrasound.
Patients with mechanical ventilation must pay attention to ensure the patient's respiratory status during the ultrasound.
Patients receiving vasopressor drugs must pay attention to ensure the intravenous line during the ultrasound.
Medical record:
Record the order of vascular ultrasound. Record the measured parameters on the ultrasound result sheet and paste it in the medical record 4.2 Steps to conduct Check the records: Recheck indications, contraindications and agreement to participate in the technique Re-check Patient: Vital functions see if the procedure can be performed. 4.3 Implementation of the technique Use a vascular probe (flat probe) placed in the position where blood vessels need to be probed.
Doppler ultrasound:
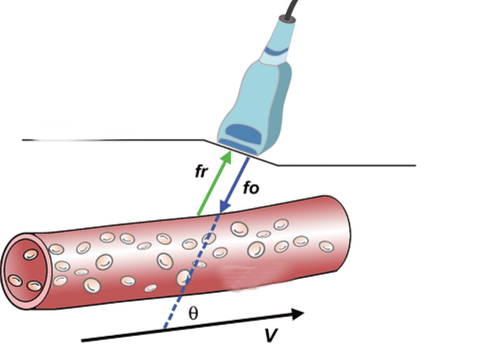
Principle: The doppler effect is generated when an ultrasonic wave with a given frequency fi encounters a moving structure, bounces back with frequency fr, the difference fi and fr is fd
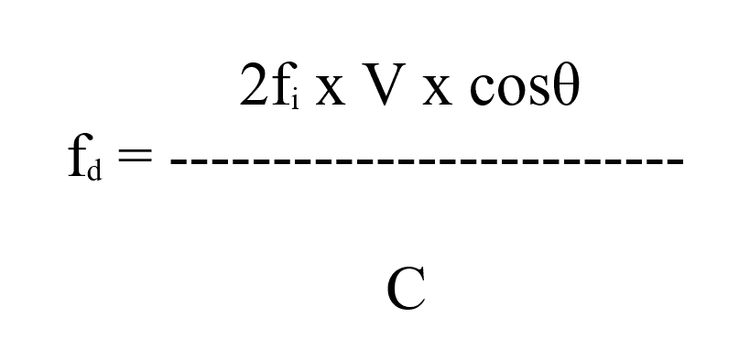
Công thức tính tần số sóng siêu âm
θ: angle formed by the incident ultrasound beam fi and the direction of movement of the structure. In cardiology the structure is blood flow, represented by red blood cells
C: velocity of ultrasound in biological tissues (1560 cm/sec). Purpose of doppler ultrasound: non-invasive hemodynamic investigation
Types of doppler ultrasound: Pulsed Doppler, continuous doppler, color doppler (a special form of pulsed doppler).
Pulsed Doppler: The emitted and received ultrasonic waves are made by a single crystal, so the ultrasound beam is emitted intermittently so that the transducer receives the echo after a time delay of which the length short depends on the depth to be probed. Continuous Doppler: The emitted and received ultrasound waves are performed by 2 different crystals of the transducer, so there is no restriction on blood speed. Color Doppler: Is a pulse doppler that the speed and direction of blood flow are shown in different colors with different intensity. By convention, when flow is directed toward the transducer, it is red, and blue when the flow is away from the transducer. Examination of the arterial system:
For the arteries of the lower extremities:
The patient lies in supine position. Investigate arterial blood flow in the thigh, popliteal, tibial... Next, the ultrasound probe is used to analyze the artery and internal blood flow. For the upper extremity artery: Examine the subclavian artery, then go up the brachial artery. For the arteries in the neck: First also the subclavian artery, then examine the arteries along the neck, the internal carotid artery and the external carotid artery. Some arteries in the brain can be examined with doppler ultrasound, the transducer is placed close to the temporal region. Intra-abdominal arteries: renal vessels, hepatic vessels, spleen... Through doppler ultrasound, arteries mainly look for the following factors:
Presence of atherosclerotic plaque inside the vessel lumen Measure blood flow inside the artery Find narrowing of the artery, associated with increased blood flow on the doppler Analyze the artery wall Look for blockages, corresponding to blood clots Examine the venous system
Same as the arterial system: Position the patient, use Using a vascular doppler probe (flat probe), probe placement.
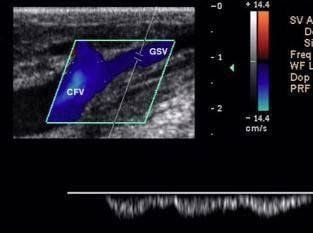
Chỗ nối tĩnh mạch hiển lớn và tĩnh mạch đùi chung bình thường
Venous circulation is blocked, which may be caused by the disease itself or by the surrounding tissue. Direct signs: There is no Doppler signal, the venous pressure is not collapsed or completely collapsed. Indirect signs: Decreased circulation rate above the occlusion site, increased velocity in the collateral veins (eg, saphenous veins of the lower extremities).
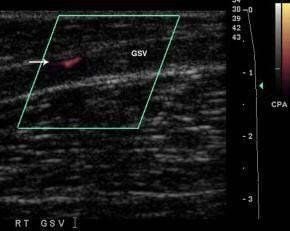
Doppler màu cắt dọc tĩnh mạch hiển lớn bị huyết khối chỉ thấy một dòng chảy nhỏ ở ngoại vi (mũi tên)
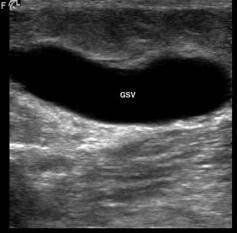
Tĩnh mạch hiển lớn giãn to ở Ngƣời bệnh suy tim xung huyết
The vein dilates even when the patient is lying down, the vein is round in cross section, and the vein is pressed without collapse under the transducer On 2D ultrasound, the morphology of the thrombus can be clearly seen, the thrombosis causing the blockage completely lumen (press without collapse). The thrombus usually adheres firmly to the venous wall, so this thrombosed venous area will not dilate during the Valsalva maneuver.
Thromboembolism causing incomplete occlusion of the lumen: Incomplete deflation of the vein, the Valsalva maneuver or squeezing below the transducer site can cause dilation of the vein wall. Sometimes the vein is partially blocked but the pressure still does not collapse, but when doing the Valsalva maneuver or squeezing hard enough at the bottom to position the transducer, it will increase the diameter of the vein.
Varicose veins due to compression from the outside:
The vein is continuously compressed:
At the site of compression: it collapses when the transducer is pressed but the vein does not dilate when the patient stands or squeezes below the affected area. pressed. Before and after the compression: The vein will dilate when the patient stands or squeezes below the compression. Temporarily compressed or standing veins:
Varicose veins of the lower extremities in pregnancy
The brachial veins are dilated due to compression by the pectoral fascia in a certain position in thoracic-brachial syndrome. Cockett's syndrome: Crossing of the left iliac vein with the right iliac artery → causes the right iliac vein to become compressed. Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in medical examination and treatment, patients can rest assured to visit. and hospital treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
MOREIs Vascular Ultrasound Painful? Can Doppler ultrasound of blood vessels detect arteriovenous fistula? Meaning of vascular ultrasound