This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by resident Doctor Le Thanh Tuan - Department of General Surgery - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.
The technique of nasogastric tube placement can be indicated for many subjects of all ages, the process of taking care of patients with nasogastric tube plays an important role in limiting inflammation or unfortunate complications. can happen.
1. What is a nasogastric tube?
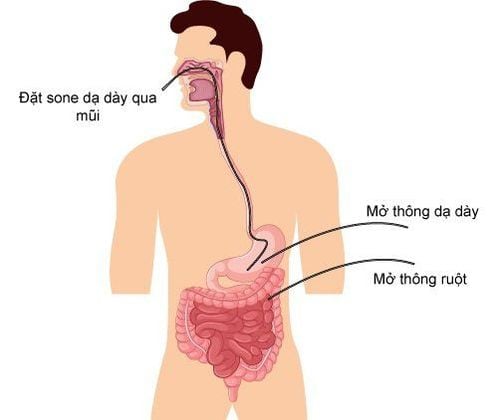
A nasogastric tube is a method of using a tube into the stomach to nourish food directly from the patient's body, aspirate gastric juice and monitor the condition of the stomach.The nasogastric tube technique will be applied when the patient loses the ability to eat normally, there are 2 common ways:
Route from the mouth to the stomach The route from the nose to the stomach
2. Indications for nasogastric tube placement
The technique of nasogastric tube placement is indicated for the following cases:People with tongue cancer, esophageal cancer People in a coma People with difficulty swallowing due to facial paralysis People who refuse to eat or eat too little to maintain their strength healthy People with acute gastritis and chronic gastritis or stomach cancer Suspected when diagnosing pneumonia, pulmonary tuberculosis in children In case patients after surgery experience abdominal distension Appear deformities in the tract Digestion Respiratory failure, suffocation when the patient has difficulty in eating and drinking. The patient washes the stomach due to food poisoning.
3. Gastric catheterization procedure
Place the patient in the semi-reclining position (the patient is awake) or the head is low, the face is tilted to the left (the patient is comatose). Measure the length of the cannula (measured from the tip of the nose to the earlobe, round to the sternum, about 45-50 cm across the bottom of the stomach or from the tooth to the navel). Lubricate the tip of the catheter (approximately 5cm, do not allow oil in the tube to cause the patient to choke) Ask the patient to open their mouth or, using a mouth opener or canun Guedel (the patient is not conscious), insert the tube through the mouth. If it is difficult, you can thread it through the nose along the way of the nostrils. Gently insert the tube into the mouth, close to the cheek, avoiding the nasopharynx and uvula, encouraging the patient to swallow despite the discomfort, while the nurse slowly pushes the tube and stops when the marker reaches the dental arch. again. If the patient has choking, severe cough, pale face, purple lips, pull out and bring back. Check if the catheter has entered the stomach correctly by 3 ways: pump about 30 ml of air and listen to the epigastrium and see the sound of gas flowing through the water or use a syringe to aspirate gastric juice or dip the outer end of the catheter into a cup of clean water. no bubbles seen. Secure the nasogastric tube with adhesive tape. Insert the drainage bag into the tip of the nasogastric tube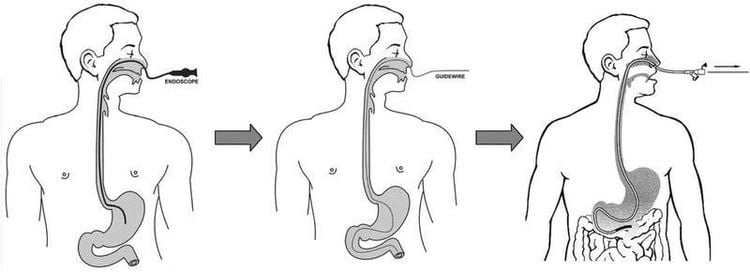
4. How to take care of a patient with a nasogastric tube
When taking care of a patient with a nasogastric tube, the patient's head should be placed at a height of about 30-45 degrees. If it is too low or too high, it is not good for the process of feeding the patient. At the same time, prepare some necessary tools such as towels and cleaning tools to help the food transmission process be cleaner and more thoughtful.4.1. Formulate menu For patients undergoing nasogastric tube placement, you should only give the patient soft, liquid, easy-to-swallow foods. Based on the patient's condition to build a suitable menu, providing reasonable nutrition to help the patient quickly recover health. Foods that need to be pureed or pressed to get water such as: nutritious porridge, soup, powdered milk, fresh milk, pureed food. In addition, it is necessary to rely on the medical condition of each person to provide a reasonable source of nutrition, such as hepatic coma, cerebrovascular accident, etc. Each disease is different and needs different food. together. Divide the daily meals into many small meals a day, an average of 5-6 times, each meal adults usually eat about 300ml - 400ml, while children should give about 20ml/one meal. 4.2 Some care notes When feeding, it is necessary to ensure that the food is pure and soft so that it can be easily pumped through the catheter. vomiting patient. Rinse the tube before feeding the patient and make sure the feed tube is clean, free of bacteria or fermentation. After feeding, the catheter should be cleaned thoroughly. The nasogastric tube should be replaced when it feels dirty, blocked or periodically changed. Oral hygiene should be given to the patient by rinsing the mouth with physiological saline daily. Determining the correct position of the catheter into the stomach, when replacing the catheter, the nostrils should be changed. Dr. Le Thanh Tuan has experience in examination, treatment and surgery of abdominal pathologies (both open surgery and laparoscopic surgery). In particular, the doctor has strengths in pediatric surgery to treat diseases such as: intussusception, appendicitis, inguinal hernia, postpartum malformations (fetal peritonitis, megacolon, no anus).
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.