This is an automatically translated article.
Optimal route selection is an important aspect of antibiotic therapy. Oral administration is the first choice for patients to treat infections. However, in practice, inpatients often apply intravenous injection. So how to switch antibiotics from parenteral to oral and vice versa?
1. How to choose antibiotic route?
Antibiotics are substances of microbial origin, prepared by synthetic or semi-synthetic chemical methods. Antibiotics are used to inhibit the growth or kill pathogenic bacteria. The two main dosage forms of antibiotics are oral and injectable. Depending on the specific condition of the patient, the doctor will consider deciding to use the appropriate antibiotic route. Oral antibiotics are usually preferred. However, in cases of severe infection or the patient cannot drink, the doctor will prescribe injectable antibiotics. During treatment, the doctor will flexibly switch parenteral antibiotics to oral and vice versa depending on the course of the disease.
MORE: Full awareness of antibiotics
2. When to switch from parenteral to oral antibiotics?
2.1. Conditions for transferring antibiotics from parenteral to oral route A patient was assigned to switch from parenteral to oral antibiotics when the patient's condition improved significantly. Specifically:
From day 3 onwards, the patient's body temperature is below 38 for at least 24 to 48 hours, breathing rate is less than 20 times/minute, heart rate is less than 90 times/minute, chest X-ray is progressing well. , blood count, white blood cell count decreased to normal. Patient can drink, no digestive problems such as: vomiting, severe diarrhea, swallowing disorder, gastrointestinal obstruction, intestinal obstruction, etc. The patient does not suffer from loss of consciousness such as fainting, comatose, unable to control himself. The patient does not have some serious, life-threatening infections such as endocarditis, meningitis, brain abscess, ocular cellulitis, deep abscess, etc.

Người bệnh được chuyển kháng sinh từ đường tiêm sang đường uống khi đáp ứng các yêu cầu của bác sĩ
In addition, to switch antibiotics from parenteral to oral route, the hospital must have suitable oral antibiotics on hand. The transfer of antibiotics from injection to oral route has many advantages such as: convenience for the patient, reduced treatment costs, and reduced risk of infection through the injection site. Reducing the use of intravenous antibiotics instead of taking oral antibiotics also helps limit the increase in resistance rates.
2.3. Thera different route of use. Switch therapy: Switching antibiotics in the same class, with the same antibacterial spectrum but different active ingredients and routes of administration. Taper therapy: Switching antibiotics can be of the same or different classes. The dose, frequency, and antibacterial spectrum of the previous parenteral antibiotic and the oral antibiotic of choice may not be the same. The choice of each therapy depends on the antibiotic and the available oral equivalent.
3. Switching antibiotics from oral to injectable
Patients are prescribed by the doctor to switch antibiotics from oral to parenteral route when the infection does not improve, the bacteria concentration in the blood is high, and it is difficult to control with oral antibiotics. Doctors also quickly switch antibiotics from oral to parenteral route if it is determined that the patient has severe, rapidly progressing, life-threatening infections such as endocarditis, meningitis, pericarditis, etc. In addition, the transfer of antibiotics from oral to parenteral route is also done if the patient has vomiting, intestinal obstruction, ... can not absorb the drug through the gastrointestinal tract.
Successful treatment of bacterial infections depends on many factors, including the choice of antibiotics and the appropriate route of antibiotic administration. Switching antibiotics from parenteral to oral and vice versa flexibly helps ensure safety, effectiveness in treatment and economy, and helps reduce antibiotic resistance in treatment.
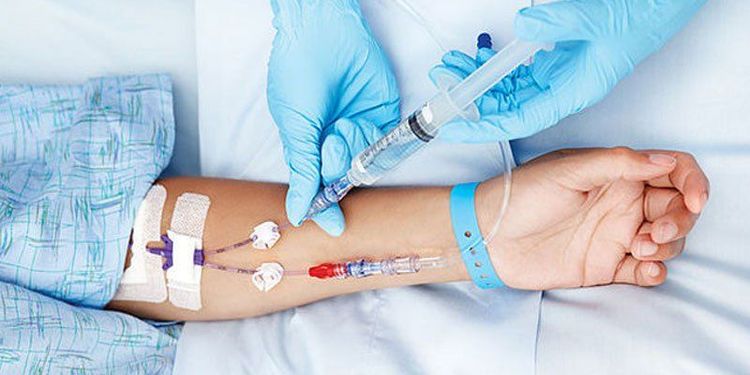
Một số trường hợp được bác sĩ chỉ định chuyển kháng sinh từ đường uống sang đường tiêm
Vinmec International General Hospital is the address for examination, treatment and prevention of diseases. When performing the examination process at Vinmec, customers will be welcomed and used the modern facilities and machinery system along with perfect medical services under the guidance and advice of the doctors. Good doctors, well-trained both at home and abroad.
In case it is necessary to use antibiotics to treat the disease, the doctors at Vinmec will provide a treatment plan, and advise and guide the patient to use the drug effectively, to avoid abuse and misuse. Indiscriminate antibiotics cause undesirable side effects such as antibiotic resistance.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: ncbi.nlm.nih.gov