This is an automatically translated article.
The article was consulted with Dr. Nguyen Luong Tan - Head of Cardiology Department - Cardiovascular Center - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Purulent pericarditis is inflammation caused by pyogenic bacteria in the pericardial cavity. The course of the disease starts from infectious pericarditis to pericarditis, if not treated promptly, it will turn into constrictive pericarditis.
1. Causes of pericarditis
The most common bacteria causing pyelonephritis are Staphylococcus aureus, then Hemophilus Influenza, streptococcus, pneumococcal, meningococcal...
Bacteria usually move through the bloodstream from primary infection sites. such as: Pneumonia , empyema pleura , osteomyelitis ... sometimes there are cases after endocarditis . The average age of common pericarditis is 6-7 years old. Purulent pericarditis occurs in 30-50% of pericarditis in children.
Viêm mủ màng tim ở trẻ em do vi khuẩn gây ra
2. Clinical diagnosis of pyelonephritis.
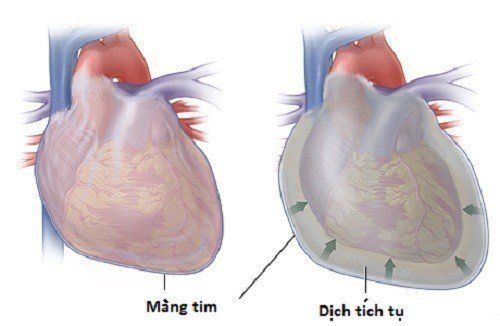
The classic symptoms of pyelonephritis include:Infectious and toxic syndrome: The patient is often in the context of blood infection, after a period of high fever, temperature does not decrease, the whole state collapses. Precardiac pain (for older children) occurs in 15 to 80% of cases, and is characterized by sudden onset of chest pain, when coughing, taking a deep breath, or changing position. Chest pain often radiates to the back because the lower third of the pericardium contains the phrenic nerve. Occurrence of evidence of fluid in the pericardial cavity: Pericardial rubbing sound, faint heart sound. Other signs such as: dyspnoea, edema, hepatomegaly, branch vessels, distended neck veins and when there are signs of cardiac tamponade, the patient has signs of paradoxical pulse, when blood pressure is checked, the systolic blood pressure drops by ≥ 10 mmHg during the stroke. inhale versus exhale.
3. Surgical treatment of pericarditis.
When the patient has been identified as pericarditis, the treatment strategy must be set as follows:
Clean up the pus, clear the infection (sterile) of the pericardium: aspiration, drainage or excision heart. Combined with high-dose antibiotics. Cardiac support : Anti heart failure . Diuretic: Anti-heart failure. The technique to clean pericardial pus will use professional manipulations to aspirate the pericardium. This technique is usually indicated for cases of acute empyema pericarditis, severe dyspnea, severe heart failure, not allowing other procedures, threatening cardiac arrest due to cardiac tamponade.
Place of aspiration on the left side of the sternal sword or the V intercostal space next to the sternum. In case of difficulty because of the small amount of pus, ultrasound can be performed. Usually, the doctor has to poke several times or insert a catheter to save it in conjunction with the irrigation pump. The effectiveness of this technique is often not very good, leaving sequelae because the suction is not thoroughly, the infection still does not decrease.
The extracardiac pus drainage technique will be indicated for cases where aspiration is unsuccessful or the results are not good. The doctor administers local anesthesia with pre-anesthesia and resuscitation. Drainage according to the Marfan line, however, this route is not thorough, so it is possible to cut the fifth and left costal cartilage, open the pericardium with a wider hole and thereby aspirate pus. Although this technique gives better results, the treatment time is still prolonged.
During the treatment, wait for the patient to get out of the dangerous phase. After that, when the health improves, there will be indications to remove the pericardium.

Khi điều trị viêm mủ màng tim cần kết hợp với kháng sinh liều cao
NOTE:
If the pericardium has pus, do not choose the thoracotomy along the middle of the sternum, because it is easy to cause infection of the sternum. Due to the limitation of the left thoracotomy, it cannot cut the right pericardium, but the main requirement at this time is to drain the pericardial pus through the pleural space and suck it out, reducing the pressure on the heart. Drainage of the pleural cavity after a pericardectomy. Check the drainage tube to ensure the standard of drainage of the pleural cavity, to drain thoroughly, to avoid empyema due to stagnation of purulent fluid.
Patients with purulent pericarditis should be examined immediately because the disease is potentially life-threatening. The stasis of pus deep in the body, especially in the pericardial cavity, makes the patient exhausted quickly and can affect the functioning of the heart.
Vinmec Hospital has enough human resources and equipment to treat this disease.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.