This is an automatically translated article.
Infection of the chest incision is one of the most common complications in surgery. Although this condition is common, if medical facilities, along with patients and family members, strictly follow preventive measures, the rate of surgical site infection can be significantly reduced.
1. What is a chest wound infection?
Incisional infection is infection at the surgical site from the time of surgery to 30 days postoperatively for non-implantation surgery and up to 1 year postoperatively for organ transplant surgery. .
Infection of the chest incision including the incision on the chest wall and also the infection of the sternum incision. Incisional infection can be divided into 3 types, including:
Superficial wound infection: Infection in the skin or under the skin at the incision site. Deep wound infection: Originating from superficial wound infection and progressing deep into the inner tendon layer. Infection spreads to organs or body cavities.
2. Treatment of chest incision infection
Sử dụng thuốc kháng sinh toàn thân để điều trị nhiễm trùng vết mổ ở ngực
Medical cooperation, use of systemic antibiotics, anti-edema, improve resistance, change surgical wound sanitary napkins daily. Chest surgery, debridement surgery, incision cleaning (apply when the above measures fail). Chest incision infections in particular and surgical site infections in general greatly affect the patient's health status and financial ability. It both prolongs the length of stay and increases the cost of treatment. In addition, surgical site infections increase the risk of antibiotic misuse, which can even lead to higher mortality.
Treatment of chest incision infection has no contraindications, but treatment of chest incision infection needs attention for severe systemic cases, exhaustion, severe heart failure...
3. Preparation for surgery
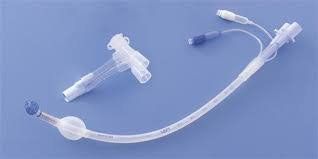
Ống nội khí quản hai nòng (Carlens)
The composition of the surgical team consists of 7-8 people including:
Surgical team: 1 surgeon, 2 surgical assistants, 1 nurse serving surgical instruments, 1 running outside the specialty Anesthesiology team : Anesthesiologist and 2 assistants Technical operation team (in case there is a problem with the endoscope) Surgical tools include:
Major surgery kit for common thoracotomy (preparation) ). A set of tools to help open and close the chest (ribs, rib only...) or close and open the sternum. Anesthesia equipment: Anesthesia kit for thoracic surgery, anesthetic and cardiovascular resuscitation drugs, double-bore endotracheal tube (Carlens)... Before performing thoracotomy, the patient is clinically examined. Careful, hygienic, prophylactic antibiotics, anesthetic examination and resuscitation. Patients and families are explained and guided about the surgical procedure as prescribed, and legal documents are completed.
4. Surgical procedure to treat chest wound infection
4.1 Patient position At the beginning of surgery, the patient is placed in supine position, tilted 90 degrees or 45 degrees to the opposite side depending on the location of the surgical wound infection on the chest wall.
4.2 Endotracheal Anesthesia The anesthesiologist conducts double-lumen endotracheal anesthesia.
4.3 Procedure Step 1: Monitor ECG and capillary oxygen saturation (SpO2) continuously. Place two central and peripheral intravenous lines, put the patient on mechanical ventilation with 100% oxygen support, and place a urinary catheter.
Step 2: Disinfect and define the surgical area as in the initial surgery. Collect fluid and necrotic tissues in the incision at different sites, culture bacteria and make antibiogram.
Hình ảnh gây mê nội khí quản cho bệnh nhân
Step 3: Locate the lesion and evaluate the entire lesion and related places (fissures with other areas, extensive necrosis...).
Step 4: Perform debridement to remove necrotic tissue, clean the bottom of the incision. (For infection of the sternum, use bone gnawing pliers to remove the maximum amount of dead bone tissue caused by inflammation in combination with controlling and cleaning the pericardium)
Step 5: Set up the incision guide system (to help drain the incision fluid) outside). For infection of the sternum, cleaning and drainage of the pericardium and retrosternal is required.
Step 6: Carefully disinfect the incision and use monofilament to close the incision in a single layer.
5. Follow-up and treatment after surgery
5.1 Postoperative follow-up Monitor and assess the overall condition: Pulse, blood pressure, temperature, drainage system... Blood count test, Hematocrit index right after the patient returns to the room. For patients to use antibiotics for intravenous infections, pain relief, blood transfusion and blood replacement solutions... depending on hemodynamic status and test results. Perform respiratory therapy from the first day after surgery. Educate patients and families on how to take care of the correct position of the chest incision, recognize the signs of surgical site infection, and report them early if these symptoms are identified. 5.2 Management of complications Post-operative atelectasis: This complication can occur when the patient is not breathing well and has extensive sputum obstruction after surgery. Recognizing signs are that the patient has difficulty breathing, fever, alveolar murmurs, X-ray images show atelectasis. To handle it, it is necessary to help the patient relieve pain, use systemic antibiotics, help the patient sit up and shake, cough and sputum, bronchoscopy (if necessary). Chronic fistula: Treated by thoroughly treating systemic diseases (if any), improving the patient's health, stimulating immunity, changing antibacterial dressings...
6. Prevention of wound infection

Sử dụng thuốc lá sẽ có nguy cơ nhiễm trùng vết mổ cao
To prevent infection of the surgical site, families and patients need to pay attention:
Inform the doctor about allergies, drug treatment, diabetes ... because this may affect the possibility of infection. postoperative wound. Do not use stimulants (tobacco, alcohol, alcohol...) to avoid reducing the body's resistance. Do not shave the area near the incision because the razor can irritate the skin, scratch and increase the risk of infection. Follow the instructions of the medical staff before breast surgery such as: bathing, personal hygiene, changing clothes, removing jewelry... After surgery, do not arbitrarily remove the bandage, touch the incision or optionally bandage the incision. The incision should be closed with a sterile dressing for 24-48 hours after surgery. Do not take it out for bathing or to wet the bandage. When changing a wound dressing, aseptic technique and aseptic dressing must be used. Wash your hands before and after changing the dressing or when there is any contact with the surgical site. Notify the nurse immediately when the patient has unusual signs such as: fever, increased pain at the incision site, swelling, redness or pus in the incision, drainage, loosening of the incision, the skin around the wound surgery for edema, swelling, pain... Surgery to treat infection in the chest incision is a widely indicated method for patients who unfortunately have post-operative infections. Patients should also follow all of their doctor's instructions during treatment to improve their chances of cure and reduce the risk of complications.
Any questions that need to be answered by a specialist doctor as well as customers wishing to be examined and treated at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide or register online HERE.