This is an automatically translated article.
This article is professionally consulted by resident Doctor Le Thanh Tuan - Gastroenterologist - General Surgery Department - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.Surgical site infection is a major concern for patients who have just undergone surgery. They cause many impacts on patients in terms of both health and finance, especially severe surgical site infections are the leading cause of death for patients.
1. What is an infected surgical wound?
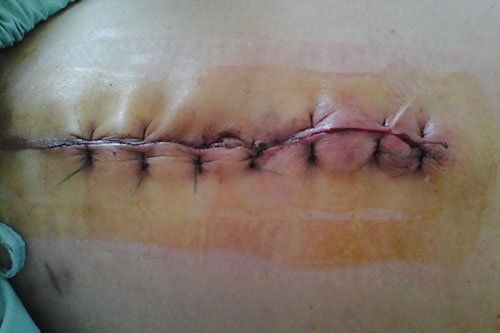
Infection of the surgical site is the most common problem after surgery, it is the most common undesirable consequence and an important cause of death in patients after surgery. Depending on the type of surgery, the infection rate ranges from 2% to 15% and occurs in 24% of patients after surgery, in which up to 90% of surgical incisions are infected with superficial and deep infections. The rate of surgical site infection varies from country to country, in advanced countries the figure is only 5-7% while in developing countries it is 15-20%Infected surgical incisions are understood are infections at the surgical site within 30 days of non-implantation surgery and within 1 year of prosthetic surgery.
Infections of the surgical site are divided into three types: superficial infections occurring in the subepidermal skin or skin tissues, deep infections occurring in muscles and connective tissues, and infections of organs and connective spaces. .
2. Consequences of an infected surgical wound
Infected surgical wounds cause many consequences for the patient including:Longer hospital stay means higher costs. According to studies, in Vietnam, patients with surgical site infections can spend twice as long in hospital as well as direct treatment costs compared to uninfected patients. Mortality rate increased higher, 89% of patients died due to severe surgical site infection. If the surgical site is infected with an implant, the treatment for surgical site infection has the highest cost compared with the treatment of dangerous surgical complications and the patient's hospital stay can be up to 30 days. Surgical site infection will increase the overuse of antibiotics for treatment, leading to an increased rate of antibiotic resistance, which is a major problem of worldwide medical concern.
3. What is the cause of surgical site infection?
3.1 Factors leading to surgical site infection The two main agents leading to surgical site infection are bacteria and fungi, in which bacteria play a major role. Currently, there are no exact studies that indicate viruses and parasites are the causes of surgical site infection.There are many types of bacteria that cause surgical site infections and vary depending on the clinic and the surgical site:
Prosthetic transplantation, cardiac surgery, neurosurgery, orthopedic surgery: S. aureus , S. epidermidis Eye surgery: S. aureus, S. epidermidis, Streptococcus, Bacillus Lung, vascular, appendix, biliary, colorectal, gastroduodenal surgery: Bacillus anaerobes, Bacillus, B. enterococci Surgery head and neck surgery: S. aureus, Streptococcus, Anaerobes, E. coli, Enterococci Obstetrics and gynecological surgery: Streptococci, Anaerobes Urological surgery, laparotomy, abdominal wounds: E. coli, Klebsiella sp, Pseudomonas spp, B. fragilis and other anaerobic bacteria. Currently, the bacteria that cause the surgical site to become infected is increasing, especially the group of multi-drug resistant bacteria, making it difficult for the patient's treatment and recovery process. Because the treatment of surgical site infections mainly uses antibiotics, leading to the overuse of antibiotics will create conditions for many strains of fungi causing surgical site infections to be born.
3.2 Two causes of surgical site infection Two main sources of surgical site infection include:
Endogenous causes: The bacteria are available on the patient, this is the main source of infection causing surgical site infection, They are often available in hospitals and are quite resistant to drugs. These bacteria already reside on the patient's body, they are present in skin cells, mucosa, hollow visceral cavity such as oral cavity, gastrointestinal tract, genital tract, urinary tract ... In addition, the bacteria in Infected sites are far from the incision but follow the blood or lymphatic routes to penetrate and cause surgical site infection. Exogenous causes: Due to bacteria entering the incision during surgery by direct invasion mechanism and after the surgical process takes place during incision care. They can originate from the environment where the surgery takes place, such as the air in the operating room, the tools used for the surgical process such as mechanical equipment, hemostatic materials, surgical preparation cloths, surgical hand hygiene ... or from the staff, the doctor in the surgical team such as from the hands, skin or respiratory tract.

Infection of the surgical site is a dangerous condition, so patients cannot self-treat at home, but need to go to medical facilities to be checked by a doctor and have timely intervention. In particular, it is necessary to seek medical attention immediately if the wound is large, deep or does not stop bleeding or shows signs of infection.
Vinmec International General Hospital is currently a high-quality healthcare center with a team of highly qualified and professional staff, technicians, and doctors in all specialties. In order to best serve the process of diagnosis and treatment, the hospital also has modern equipment and machinery of international standards, contributing to more effective treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.