This is an automatically translated article.
Among hospital infections, surgical site infection is one of the most common types of infection today. In our country, about 10% of millions of surgical procedures are infected with surgical site infections.
1. What is surgical site infection?
Surgical site infection, also known as surgical site infection, is a common nosocomial infection after surgery. Surgical site infection increases the cost of treatment, prolongs the duration of the disease, and the pathogenesis of surgical site infection is related to the number of micro-organisms and the patient's resistance. There are 3 types of surgical site infections:
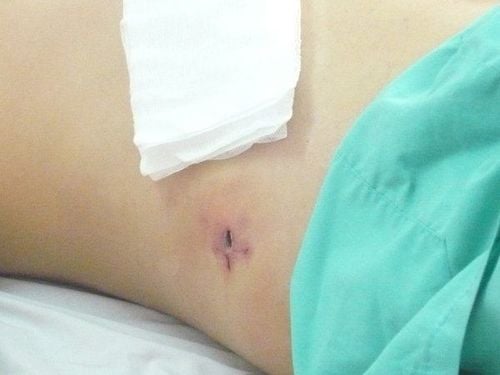
Deep incision infection originates from a superficial wound infection and goes deep into the inner tendon layer. Superficial wound infection is an infection in the skin or under the skin at the site. skin incision Infection in organs or body cavities. Signs of wound infection:
Wound is oozing with pus The wound is swollen, edematous, hot Feeling pain when touching the wound Causes of surgical site infection are:
The patient may have an infection of the surgical site Depends on the type of surgery, the location of the surgery, the time of surgery, the skill of the surgeon and how well the patient's immune system is able to fight the infection. In addition, the main cause of infection is bacteria, they have many different types. In particular, the bacteria causing surgical site infections are increasingly resistant to the antibiotics being used, making it difficult to treat; especially multi-drug resistant bacteria. In case of surgical site infection, the treatment of surgical site infection is mainly antibiotic therapy and depends on the level of the causative agent to use. In addition, in case the patient has a severe infection, it needs to be treated with surgery to drain the pus out.
Vi khuẩn gây ra nhiễm trùng vết mổ làm gia tăng tình trạng kháng kháng sinh
2. Surgical wound infection
2.1. Indications and contraindications
Indication for surgical wound infection when the patient is indicated to treat infection. Infected wounds spread widely and deeply, causing burns in many nooks and crannies. Contraindicated when the patient only has small, light, shallow wounds.
2.2 Surgical treatment of surgical site infections
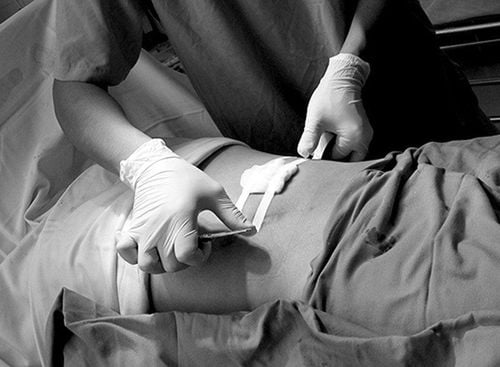
Step 1: Prepare the team to perform the surgery, medical instruments and equipment used in the case. Take the patient for basic tests, especially the patient must fast from the previous day. Step 2: Re-open the old incision, it is necessary to make a wider incision as appropriate. Step 3: Assess the damage to the extent and decide to treat depending on the extent of the injury Step 3: Dredging inflammation, with mild, superficial inflammation. Then remove the necrotic tissue, remove the fistulas, nooks and crannies, completely remove the pus, the necrotic tissue, remove the foreign body and inject a lot of antiseptic water, hydrogen peroxide. Step 4: Close the incision of excess skin, drain widely, not leave open for brain and joint surgery.
2.3 Follow-up after surgery
After surgery, infection should be monitored:
Whether the incision is bleeding, pus-filled or not Change the patient's antiseptic dressings daily for the patient's necrotic wound, continue surgery. again

Sau khi mổ. cần vệ sinh vết mổ sạch sẽ và thay băng gạc
3. Lifestyle and living habits to avoid surgical site infection
Follow your doctor's instructions, especially about wound care after surgery. Washing hands is the best way to prevent infection. Full use of prescribed antibiotics Remind family and friends wash their hands with soap before visiting friends Visit your doctor as scheduled to monitor your progress and symptoms and health Don't smoke. In addition, patients also need to focus on nutrition, especially foods that help strengthen resistance to restore health. Limit the use of foods that affect the incision. After surgery, it is necessary to follow the following regimen:
About 3-5 days after surgery, the patient should eat soft, easy-to-digest foods divided into 4-6 meals/day, pay attention to supplement vitamins, minerals and limit fiber processing. During the recovery period, the patient should eat enough energy and protein such as meat, fish, eggs, milk, yogurt, cheese, beans and fruits such as oranges, grapefruits, lemons, strawberries, kiwis. ... to prevent constipation , heal wounds quickly and limit the risk of infection . To ensure adequate nutrients for rapid recovery, patients should use high-energy nutritional products with a balanced protein:sugar:fat ratio, and supplement with essential vitamins and minerals. . In particular, it is possible to choose products with added immune-boosting substances. To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.