This is an automatically translated article.
Surgical site infection is considered a very common hospital-acquired infection today, occurring after a patient undergoes surgery to treat a certain medical condition. Infection of the surgical site causes adverse effects on the patient's health as well as making the treatment time take longer than usual. Therefore, the use of antibiotics to prevent surgical site infections is essential to prevent this from happening.1. Incisional infection
Among the types of hospital-acquired infections, surgical site infections are the most common, making the disease worse and taking longer to treat. It is extremely important that surgical site infections increase antibiotic resistance when antibiotics are used to treat this condition. The situation of surgical site infections in countries around the world is estimated to be about 5% of patients will have surgical site infections in patients who have undergone surgery, and surgical site infections account for 20% of these diseases. nosocomial infection. Infection of the surgical site will often make the disease worse and take longer than usual for about 7-10 days.
Infection of the surgical site is often affected by a number of factors such as the amount of bacteria that the patient is infected with, the virulence of the bacteria as well as the patient's immune system is strong enough or not. The cause of surgical site infection can be from inside the patient's body or from the external environment such as the operating room, medical staff, and external sources of infection such as devices implanted in the patient's body. or medical devices for the treatment of that patient. For surgical site infections in the gastrointestinal tract and genitourinary system, the most common pathogenic bacteria are gram (-) bacilli and anaerobic bacteria. In addition, there are also cases of surgical site infections caused by gram (+) bacteria.
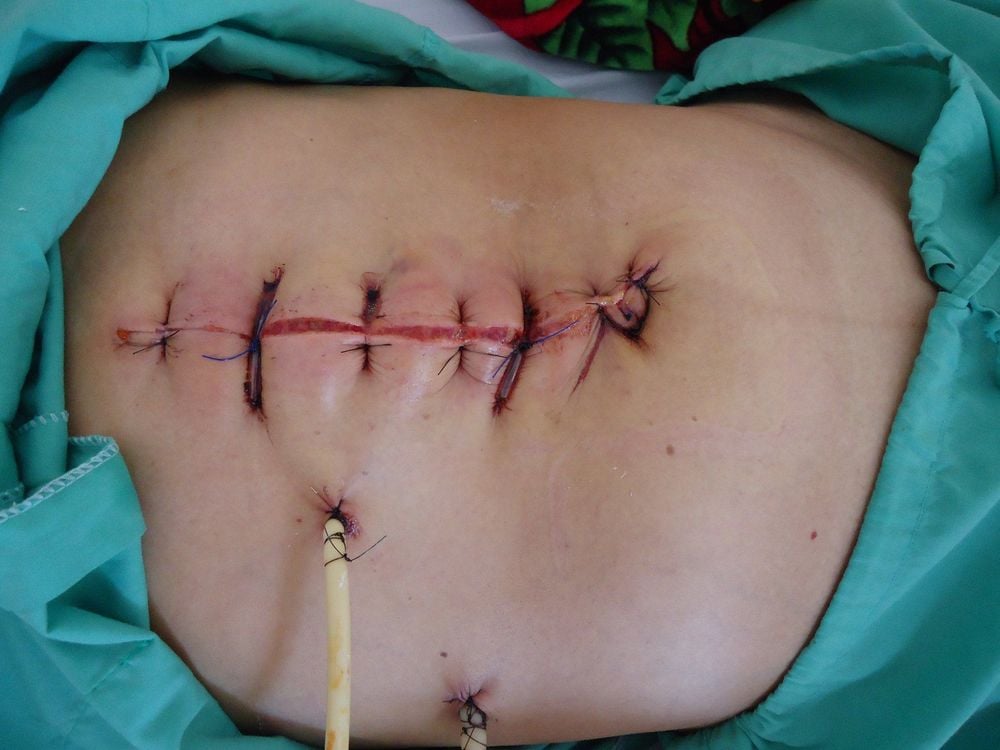
Nhiễm khuẩn vết mổ có thể do nhiều nguyên nhân
2. Antibiotics to prevent surgical site infections
The question that is asked a lot in the cases of patients facing surgical site infections is "how to guide to prevent surgical site infection" as well as "what medicine to take for wound infection? ". In addition to measures such as preparing the patient before surgery according to the correct procedure as well as the necessary requirements in surgery, from the operating room, the air filtration system, ensuring sterility, the correct surgical technique... The use of antibiotics to prevent surgical site infections plays a very important role in preventing surgical site infections in patients.
Antibiotics to prevent surgical site infections need to be specifically indicated by the treating doctor as well as depending on the cause of the wound infection, the purpose when using prophylactic antibiotics will be different. There are selections of appropriate antibiotics to use. A very important note when using antibiotics to prevent surgical site infections is to only use antibiotics for the purpose of preventing surgical site infections with cases diagnosed as clean surgery, clean surgery. - infection. As for the surgery that is classified in the group of infectious surgery and dirty surgery, now the purpose when using antibiotics is no longer prophylactic but to really treat that patient.
Some basic principles when using antibiotics to prevent surgical site infections are:
Use prophylactic antibiotics based on researched and published recommendations, there is evidence that the type of antibiotic used is effective. ability to reduce infection. Select antibiotics that are safe, economically appropriate for the patient, and have bactericidal functions. Specify the time to inject the first dose of antibiotic in order to achieve the most optimal bactericidal concentration. Continue to maintain antibiotic concentrations in serum and in tissues during surgery and until after surgery, suturing the skin for several hours. Some notes in the process of using antibiotics to prevent surgical site infections are:
Prophylactic antibiotics are used on patients before surgical incisions are made, to prevent surgical site infections right from the start. when bacteria come into contact with the surgical site. It is necessary to set the time to use antibiotics to prevent surgical site infections so that the concentration of antibiotics can reach the maximum level when surgery occurs. The most effective time is about 30 minutes before the first skin incision and for 2 hours after. Attention should be paid to the indications for the use of prophylactic antibiotics in surgical pathologies related to hollow organs. Surgery in the clean-contaminated group, such as non-urgent colon surgery, may require oral antibiotics and preoperative management of necessary techniques such as lavage and bowel preparation. old. In other cases, intravenous antibiotics will be used mainly. The types of surgery with skin incisions that do not involve the hollow viscera, do not involve the infected area, such as surgery to place a prosthetic joint, also require the use of antibiotics to prevent infection of the surgical site. Among the antibiotics, the Cephalosporin group of drugs is used quite a lot to prevent surgical site infections because it can be effective against gram (-) and gram (+) bacteria. In case the patient's body has an adverse reaction to Beta Lactam drugs, clindamycin and vancomycin can be used. In cases of gastrointestinal surgery, priority should be given to using Cefoxitin or second-generation Cephalosporin antibiotics to prevent infections caused by anaerobic bacteria. If the patient is diagnosed with the possibility of infection with methicillin-resistant staphylococci MRSA, vancomycin should be used in this case. An important note when using antibiotics to prevent surgical site infections is that in the process of taking the drug, it is necessary to go along with the inspection of hospital infections to minimize the risk of hospital-acquired infections. turned out to be one of the predisposing factors for surgical site infection.
Khi thực hiện kháng sinh dự phòng nhiễm khuẩn vết mổ, người bệnh cần lựa chọn những bệnh viên lớn và uy tín
Surgical site infection is a type of hospital-acquired infection that is complicated and caused by many different causes. In order to prevent this situation, it is necessary to diagnose the possibility of infection with any type of bacteria, then take appropriate preventive measures, in which antibiotics to prevent surgical site infection play an extremely important role to prevent infection. prevent this situation from happening a.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.