This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by an Anesthesiologist - General Surgery Department - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.Anesthesia in patients with traumatic brain injury is an intensive method that needs to be performed quickly, promptly and accurately to be able to coordinate with neurosurgeons to save the patient's life. Traumatic anesthesia can be performed in an emergency setting or in a planned surgical procedure.
1. Evaluation of patients with traumatic brain injury before surgery
Traumatic brain surgery and anesthesia in traumatic brain injury patients have specific indications and contraindications. In order to prepare for a safe and effective surgery, the patient should be evaluated according to the following criteria:Assessment of consciousness using the Glasgow scale. irregularity, light reflection or not. Monitor vital signs including pulse, temperature, blood pressure, urine. Look for signs of increased intracranial pressure such as decreased heart rate, increased blood pressure, vomiting, papilledema. Evaluation of basic hemostatic function through paraclinical tests. Observe the injured areas on the CT scan of the brain, determine the location and extent of the damage. Evaluation of other accompanying injuries such as: spinal cord injury, lung injury, airway obstruction due to blood, fluid, foreign body, vomit and damage to other organs in the abdomen, thorax...
Phẫu thuật chấn thương sọ não cần được chỉ định cụ thể để đảm bảo an toàn cho bệnh nhân
2. Prepare resuscitation equipment before anesthesia for traumatic brain injury
Set up the patient two peripheral intravenous lines.If facilities are available and the anesthesiologist is experienced, a central venous catheter or a direct invasive arterial catheter can be placed for monitoring.
Measure intracranial pressure. Measure central venous oxygen saturation.
3. Anesthesia procedure in patients with traumatic brain injury
Anesthesia for traumatic brain injury needs to be performed quickly and according to the procedure to fulfill its purpose, including assisting in the conduct of neurosurgery, protecting the brain parenchyma and cells from other secondary injuries. , limiting complications of cerebral edema, widespread brain damage and lack of blood supply to the brain.3.1 Safe position for the patient Have the patient lie on his or her back. Do not put pressure on the jugular vein to limit cerebral edema due to the inability of blood to return to the heart. The head can be raised 30 degrees depending on the specific case. However, during the first 24 hours after a traumatic brain injury, the patient's head should not be elevated.
3.2 Induction Anesthesia with rapid endotracheal intubation is the anesthetic of choice for patients with traumatic brain injury requiring emergency surgery. Because at this time, all patients are not prepared and are considered to have a full stomach, the endotracheal tube is a device to help control the airway, prevent complications of aspiration of digestive juices and food. into the airway. In contrast, traumatic brain injury patients scheduled for elective surgery would not need to undergo rapid intubation (RSI).
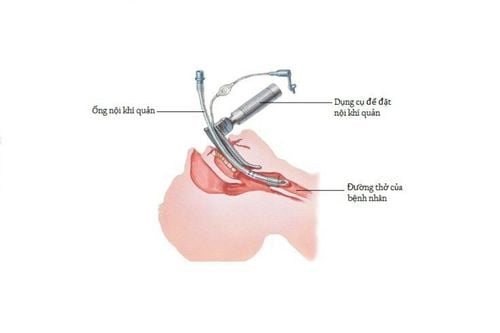
Đặt nội khí quản khi dẫn mê là lựa chọn phổ biến khi phẫu thuật cấp cứu
3.3 Maintenance of anesthesia The patient's anesthetic status will be maintained with intravenous anesthetics or inhaled volatile anesthetics. The choice of specific drug depends on the individual patient and local conditions available. In parallel with maintaining anesthesia, the patient needs to be assured of other issues such as:
Respiration: artificial ventilation should be increased to achieve PaCO2 maintained at 35 mmHg. When a traumatic brain injury patient presents with cerebral edema, the PaCO2 should be lowered by about 25-30 mmHg.
Ensure hemodynamics: 0.9% NaCl physiological saline is the solution of choice to ensure circulating volume in cases of blood loss. If it is not effective, the doctor may prescribe the use of other solutions for the patient such as macromolecular solutions, blood products, even sometimes needing to use vasopressors.
Treatment of cerebral edema: 20% Mannitol solution is the first choice to combat cerebral edema.
Some complications that can occur during the maintenance phase of anesthesia are bleeding, gas embolism and increased cerebral edema. Anesthesiologists need to closely monitor the patient to promptly detect and treat, and ensure the safety of the patient during surgery.
Trong quá trình phẫu thuật cần điều trị phù não cho bệnh nhân
Patients with traumatic brain injury before surgery who are awake, after surgery, need to restore consciousness and be able to breathe on their own. If the surgery results are good and the bleeding stops, the patient can be extubated.
On the contrary, if a traumatic brain injury patient falls into a coma before surgery or encounters complications during surgery such as excessive bleeding, cerebral edema, it is necessary to continue to maintain sedation, reduce pain, ventilatory support at least until the patient is conscious and vital signs are within normal limits.
Anesthesia in traumatic brain injury surgery is an important step not to be subjective when conducting, usually the doctor will apply anesthesia for intubation for brain surgery. Anesthesia ensures a smooth operation, avoids secondary injuries and maintains good resuscitation in the face of abnormal situations during surgery such as heavy blood loss, severe cerebral edema...
National General Hospital Vinmec Hospital is one of the hospitals that strictly apply safe surgical anesthesia practice standards according to international guidelines. With a team of experienced anesthesiologists and nurses, along with modern equipment such as nerve detectors, ultrasound machines, Karl Storz difficult airway control system, anesthesia monitoring system GE's comprehensive AoA (Adequate of Anesthesia) including monitoring of anesthesia, pain and muscle relaxation will deliver high quality and safety, helping patients to have adequate anesthesia, not awake, no residual relaxant muscle after surgery. Vinmec Health System is also proud to be the first hospital in Vietnam to sign with the World Anesthesiology Association (WFSA) towards the goal of becoming the safest hospital for surgical anesthesia in Southeast Asia.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.