This is an automatically translated article.
Esophageal atrophy is a birth defect present in children from birth. Esophageal atrophy in neonates can be treated by transpleural thoracotomy, pleural effusion or thoracoscopic surgery to minimize possible complications during surgery.
1. Congenital esophageal atrophy
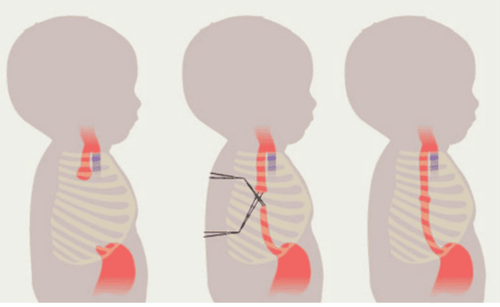
Neonatal esophageal atrophy is a birth defect of the gastrointestinal tract that appears very early, right from the time of birth. Esophageal atrophy is a phenomenon in which the esophagus is disrupted in its flow, which can lead to a loss of communication between the esophagus and the child's trachea. More than 50% of cases of congenital esophageal atrophy are often accompanied by other malformations such as vertebral malformations, anal aplasia, cardiovascular malformations...
Congenital esophageal atrophy can be diagnosed immediately from the time the fetus is still in the mother's womb, around 24 weeks of gestation thanks to modern paraclinical techniques including fetal ultrasound. To treat esophageal stricture in the fetus, the method used today is surgery. When detected early and in the period without dangerous complications, atrophy of the esophagus can still be treated safely and does not cause complications such as gastroesophageal reflux, disordered suckling reflex. swallowing or softening the tracheal cartilage.
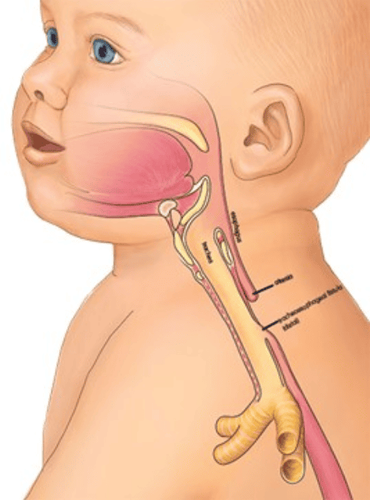
Teo thực quản bẩm sinh ở trẻ nhỏ
2. Causes of esophageal atrophy
The cause of esophageal atrophy has been shown to be due to an abnormality in embryogenesis between the 4th and 6th weeks of pregnancy. This is also the cause of a series of birth defects associated with esophageal stricture in infants. In addition, some other causes of congenital esophageal atresia have not been fully and accurately studied.
3. How are babies with congenital esophageal atresia handled?
For infants with esophageal atrophy, the most optimal treatment option is currently surgery, including endoscopic thoracoscopic surgery. This method is indicated for children with esophageal atresia with a distance of no more than 4 vertebrae and is usually considered for subjects weighing less than 2000 grams or children with abnormal heart defects. In particular, thoracic surgery to treat esophageal atrophy is absolutely not applied to children with complex cardiovascular malformations and pneumonia in the body, in addition, if the child has a state of blood gas as well as Hemodynamically unstable and should not undergo surgery.
To prepare for a safe and effective thoracoscopy surgery, it is necessary to prepare according to the following steps:
Prepare full equipment including: laparoscopic surgery machine with pump system Auto CO2 and gas heating, 5mm 30° rigid endoscope, trocar, 3mm laparoscopic surgery kit, 5-6/0 PDS thread, 5-6/0 Vicryl thread, cage surgery kit Conventional baby breasts. Complete patient assessment prior to surgery including necessary routine testing. Place patient on mechanical ventilation if respiratory failure or oxygen saturation lower than 90% Adjust patient status if acid-base disturbance occurs.
Phòng mổ cần được chuẩn bị đầy đủ thiết bị
Steps to conduct thoracoscopic surgery for esophageal atrophy in neonates include:
Intubation anesthesia for the child, establishment of airway control for the child during surgery, Place left lung ventilation in the child. Place the patient on the stomach so that the baby's head is towards the monitor, the feet are towards the surgeon, place a high pillow in the right chest position for the child, and at the same time let the leg lower. Place the first trocar in the IX intercostal space and 4cm from the spine. Place the second trocar in the X intercostal space and 2cm from the spine Place the third trocar in the VII intercostal space so that it is 2cm superiorly to the first trocar. During the first time inflating, let the inflation pressure be about 4mmHg, the flow rate is 1L/min, then increase to 6mmHg or 8mmHg depending on the case. Find the vein of Azygos then use an electric torch to burn and cut the vein in half. Find the lower end of the esophagus that communicates with the trachea to dissect them. The lower part of the esophagus was cut from the fistula into the trachea, and then sutured with PDS 5/0 separate stitches. The lower end of the esophagus 2cm was dissected so that it was enough to pull up with its upper end, opening along the lower part of the esophagus a segment about 1cm in size. Finding the upper esophageal tip, gently push the catheter into the sacrum of the upper esophagus. Dissection of the upper end of the esophagus from adjacent tissues. Separate the back of the sacrum from the trachea, cut off the top of the larynx, the mucosa to open the pouch and esophagus.
Trẻ được gây mê nội khí quản chuẩn bị phẫu thuật
Sew the two ends of the esophagus together with PDS 5/0 thread with the stitch at the 6 o'clock position, taking care that the knot is only in the heart of the restaurant. Continue to suture the back with 2 to 3 stitches with PDS 5/0 thread so that the tie is in the thoracic cavity and in the lumen of the esophagus. Push the tube through the mouth of the puppet into the child's stomach, sew the front, check the tightness of the stitches. Use water to aspirate the sites in the pleural cavity and then proceed to place a drainage of the pleural cavity. Withdrawal and suture of the trocar hole Transfer the patient to the ICU after completing the surgical steps, and inform the family of the patient's surgical status.
After finishing surgery, it is necessary to pay attention to monitor the following issues on the patient:
Resuscitate the patient, adjust acid-base balance and vital functions. Straight chest x-ray to examine the patient's lungs, fluid and air in the pleural space. Keep the patient on a ventilator for 12 to 24 hours after surgery. Monitor complications such as esophageal fistula, Azygos venous bleeding, tracheal tear, anastomosis after 5 days, anastomosis... Pumping milk through a nasogastric tube to provide nutrition to the patient after 48 hours . Esophagography 6 days after surgery Remove gastric tube in case there is no esophageal fistula. If there is stenosis of the anastomosis, it is necessary to periodically dilate the child and perform anastomosis. 2. Follow-up examination is performed at 1 month, 3 months, 6 months and every year to detect abnormalities in a timely manner.

Khi trẻ xuất hiện các biểu hiện bất thường về sức khỏe, phụ huynh nên đưa trẻ đến gặp bác sĩ
Laparoscopic surgery is the current safe, effective and low-complicated method in the treatment of esophageal atrophy in neonates. This is an intensive method, modern techniques and requires skill and experience, so patients need to choose reputable medical facilities for the most effective treatment of congenital esophageal atrophy.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.
Recommended video:
Periodic health check at Vinmec: Protect yourself before it's too late!
SEE MORE
7 methods of prenatal diagnosis to help detect fetal abnormalities 11 regular antenatal checkups pregnant mothers need to remember Periodic antenatal checkups - protect your baby from the very beginning