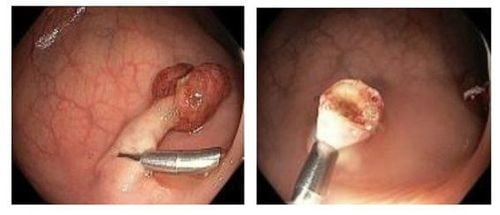
This is an automatically translated article.
Rectal prolapse is a dangerous disease that can cause many unpredictable complications such as rectal ulceration, bowel obstruction, rectal rupture,... Therefore, it is necessary to detect and treat rectal prolapse early. Surgical resection of the sigmoid colon is an effective treatment for rectal prolapse that is being widely used today.
1. Learn about sigmoid colon, rectal prolapse
1.1 What is sigmoid colon?
Anatomically, the colon is divided into 4 segments: ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon, and sigmoid colon. The sigmoid colon is a short section, located at the end of the colon that connects to the rectum, similar in shape to the Greek word sigma (ς). The sigmoid colon is located closest to the rectum and anus, ring-shaped, about 35-40cm long and about 2.5cm in diameter when contracted. The size of this part may vary from person to person. This organ is usually located in the pelvis, but because of its mobility, the sigmoid colon can be misplaced in the abdomen.The inner surface of the sigmoid colon is similar to the rest of the colon. This organ is responsible for storing waste in the stool until it is passed out.
1.2 What is rectal prolapse?
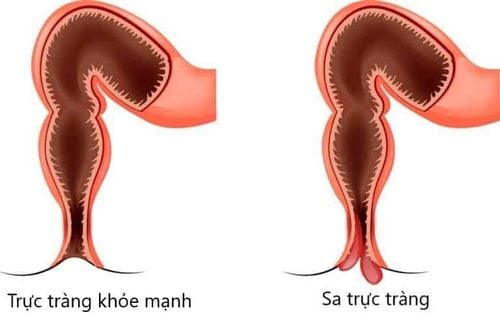
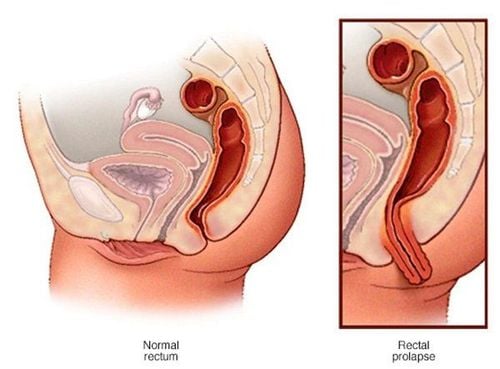
Rectal prolapse is a phenomenon where part or all of the rectal wall is inverted, coming out through the anal opening. Rectal prolapse is common in children 1-3 years old (mucosal prolapse) and people over 50 years old (mucosal prolapse and total prolapse). Although there are no dangerous complications, rectal prolapse causes many impacts on patients' activities and work.
Common causes of rectal prolapse include:
Congenital causes: Rectal failure to adhere to the posterior abdominal wall, lack of sacral curvature, low Douglas pouch, defective perineum, rectal ball flexion - insufficient anal canal, underdeveloped rectal valve; Causes of living: Malnutrition and vitamin B deficiency, underweight due to inadequate diet, episodes of diarrhea, chronic constipation, sitting on the potty to defecate at the wrong time; Cause of trauma: After gynecological surgery, history of trauma to the perineum. Symptoms of rectal prolapse include:
Feeling that the anal area is prolapsed; There is a prolapsed mass in the anus: Long and round, first appearing when defecating, later appearing when squatting; Blood in the stool: There is fresh blood on the stool or toilet paper; Uncontrolled bowel movements, possibly with mucus discharge. Rectal prolapse can lead to serious complications such as bleeding from mucosal ulcers, rectal ulceration, bowel obstruction, rectal rupture, female genital prolapse, and perineal hernia. Therefore, it is necessary to prevent the disease by limiting the risk of disease such as: Avoiding constipation and diarrhea for a long time, adding fiber to the diet, limiting eating spicy, hot and greasy foods, drinking 2-3 liters of water per day and sit in the correct posture when going to the toilet, do not push too long or too much.
In terms of treatment, in the early stages, rectal prolapse can be treated using stool softeners, suppositories or other medications. However, most patients require surgery to completely treat rectal prolapse. The type of surgery chosen will depend on the extent of the rectal prolapse and other health problems. There are 2 commonly used surgical methods:
Anal perineal resection: Removal of the prolapsed rectum. This method can be performed with spinal anesthesia to reduce the risk of complications, help patients recover faster; Sigmoidectomy and rectal immobilization: Removal of the sigmoid colon, then immobilize the rectum to bony structures in the lower spinal cord and pelvis. In many cases, patients are indicated for laparoscopic surgery with the advantage of smaller incision and shorter hospital stay compared to traditional open surgery.
Gây tê tủy sống được thực hiện cùng phẫu thuật cắt bỏ hậu môn đáy chậu
2. Learn the surgical method of sigmoidectomy to treat rectal prolapse
Sigmoidectomy is a surgical method to remove the sigmoid colon and a part of the upper rectum and the corresponding mesentery, which helps to restore the gastrointestinal tract by connecting the colon to the rectum with an instrument. machine stitching.
2.1 Indications/contraindications
Indications: Cases of rectal prolapse with abnormally long sigmoid colon; Contraindications: Elderly and frail patients with severe co-morbidities such as heart failure, respiratory failure,... can't perform laparoscopic surgery.
2.2 Preparation
Implementation personnel: Gastrointestinal surgeon, anesthesiologist and resuscitation; Technical facilities: Seamless laparoscopic surgery machine with specialized means, set of open surgery tools for digestive surgery, sutures, tools for suturing machines,...; Patients: Perform basic diagnostic tests, colonoscopy, biopsy, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging of the abdomen and pelvis, gastroduodenal endoscopy if polyps are present. diffuse in the colon, verify if there is suspicion of infiltration or fistula into other organs, prepare the colon as prescribed and improve the patient's condition before surgery by parenteral nutrition; Medical records: Complete all procedures as prescribed such as detailed medical records, minutes of consultation, minutes of pre-anesthesia examination, written consent for surgery of the patient or family.
2.3 Performing surgery
Check the complete records according to the regulations of the Ministry of Health; Checking the right patient with the right patient; The patient lies in the obstetric position, the bladder catheter is placed, and the surgical staff stands in a suitable position; Anesthesia: Endotracheal anesthesia; Place trocar: Usually 5 trocars are placed in the following positions: Below the navel, right iliac fossa, right flank, left iliac fossa and left flank; Exploration and assessment of injuries and visceral organs in the abdomen, bring the patient to the position of maximum low head, tilted to the right. Then move the colon up and to the right to clearly expose the pelvis and left half of the abdomen; Releasing the colon and rectum at the same time as cutting the rectum: Dissecting the inferior mesenteric vessels, releasing the right border of the sigmoid colon; Anatomy to release the posterior mesentery. Attention should be done gently to avoid tearing the anterior sacral vein because it is difficult to stop bleeding; Dissection of the left colon; Anatomy of the left margin of the sigmoid colon - rectum; Anatomy of the two sides of the rectum. Resection of the rectum, ending the dissection by laparoscopy; Laparotomy to cut the rectum: Small opening of the abdomen in the left iliac fossa, skin incision to cut the sigmoid colon, closing the abdominal wall; Re-establish gastrointestinal circulation: Insert the device through the anus to the apex of the rectum, open the machine to push the sharp nail through the rectal wall. The joint is located between the sigmoid colon and the rectum, check that the colon is in the correct direction, not stretched, and the mesentery is not twisted. After that, press the machine, remove the machine according to the technical requirements, check the 2 cutting heads on the machine; Check the anastomosis and perform suturing of the mesentery - peritoneum; Place endoscopic pelvic drainage, withdraw, close the trocar holes. Note: During the operation, it is necessary to push the entire prolapsed rectum out and bring the anal canal in. The colorectal anastomosis should be performed just enough, not too tight because it will be dangerous for the anastomosis and not too long because it increases the risk of recurrent rectal prolapse.

Nên thực hiện cắt nối đại - trực tràng vừa đủ để tránh sa trực tràng tái phát
2.4 Follow-up after surgery
Monitor the patient's overall condition including vital indicators such as pulse, blood pressure, respiration, temperature,...; Monitoring at the incision includes conditions such as bleeding, discharge, pain; After surgery, use 2 antibiotics in combination for 5-7 days, take pain relievers if necessary, make adequate hydration - electrolytes, daily energy, make up for albumin and blood protein; Give the patient a light meal and early exercise; Incision care: Perform daily dressing changes, when there are abnormal phenomena such as fluid infiltration, bleeding, the incision should be examined.
Sau phẫu thuật cần theo dõi kĩ vết mổ để tránh chảy dịch
2.5 Management of surgical complications
Complications in surgery:
Bleeding: If the bleeding cannot be stopped by endoscopic surgery, switch to open surgery; The connection mouth is not closed: It is recommended to switch to open surgery to check and handle according to each specific situation. Complications after surgery:
Bleeding: In case of intra-abdominal bleeding, close monitoring is required, if necessary, surgery will be performed immediately by laparoscopic or open surgery. In case of bleeding at the anastomosis, it is necessary to check the oesophagoscopy and usually just put a compress on the anastomosis to stop the bleeding. In case of bleeding into a beam, it is necessary to intervene to stop bleeding; Postoperative Intestinal Obstruction: Treat by examining whether the cause of the bowel obstruction is functional dilatation or mechanical obstruction. If the cause is mechanical intestinal obstruction, it is necessary to surgically examine and treat the cause. Anastomosis podium: Perform surgery to close the lower end, bring the upper intestine out and can keep the anastomosis, making the stoma to drain the entire upper part; Abdominal residual abscess: In case of localized abscess, drainage under ultrasound is performed. In case the abscess is located between the bowel loops, surgery is required to clean and drain the abdomen. Sigmoidectomy is an effective treatment for rectal prolapse. When surgery is indicated, patients need to strictly follow the doctor's instructions to improve the chances of successful treatment and minimize the risk of complications.
Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in examination and treatment, patients can rest assured to visit. and hospital treatment.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.
SEE MORE
Laparoscopic procedure for right extension colectomy with lymph node dissection Advantages of gastroscopy and colonoscopy with anesthesia Laparoscopic right and left colectomy in the treatment of rectal cancer