This is an automatically translated article.
The stage of the cancer tells you the size and whether it has spread. Knowing the stage, type, and grade of the cancer can help doctors plan the right treatment for the patient.
1. What is lung cancer?
Lung cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the tissues of one or both lungs, lung tumors can also be caused by cancer that has spread from other parts of the body but they are not considered is lung cancer. There are two main types of primary lung cancer, Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) and Undifferentiated Large Cell Carcinoma.2. Stages of lung cancer
Stages of lung cancer i are classified by the TNM system, which stands for Tumour (T)- Nodes (N) - Metastasis (M)

Hệ thống TNM phân chia sự tiến triển của ung thư phổi thành 3 giai đoạn
Tumour
Tumour means tumor (T) - describes the size of the tumor and how far the cancer has spread into the lung tissue. Tumors can be classified from T1a (describe a tumor less than 1cm) to T4 (describe a tumor larger than 7cm).
TX means primary (primary) cancer could not be assessed. It does not show up on the scan, but there may be cancer cells present in the saliva or in the fluid taken from the lungs. T0 means no sign of cancer. T1 means the cancer is contained in the lung.
T1mi is a stage description for a type of non-small cell lung cancer called adenocarcinoma. It means minimally invasive adenocarcinoma. The widest part of the cancer is no more than 3cm. It grows no more than 0.5cm into deeper lung tissue. It is divided into T1a, T1b and T1c according to the diameter of the cancer. T1a means the cancer is 1cm or less at its widest part.T1b means the cancer is 1cm to 2cm across. T1c means the cancer is 2 to 3 centimeters across.
T2 can mean cancer is 3cm to 5cm across, or cancer has one or more features such as: It involves the main airway (main bronchus) but not near the area where the bronchi divide to enter each lung; It involves the inner lining of the chest cavity (visceral pleura) and part or all of the lung that collapses or becomes blocked due to inflammation. T2 is divided into T2a and T2b. T2a means the cancer is between 3cm and 4cm. T2b means cancer is between 4cm and 5cm.
T3 can mean the cancer is 5cm to 7cm long, or there is more than one tumor in the same lobe of the lung, or the cancer has grown into one or more structures such as: Chest wall (protective structure) around the lungs and other organs in the chest), the outer membrane of the chest cavity (parietal pleura), nerves near the lungs (phrenic nerves), the outer shell of the heart (pericardium).
T4 can mean the cancer is larger than 7cm, or it is located in more than one lobe of the lung, or it has spread into one or more structures such as the muscle under the lung (diaphragm), the area between the lungs in the middle of the chest (median) ventricles), the heart, the windpipe (trachea), the nerve that controls the voice box, the food pipe (esophagus), the bones of the spine, the area where the main airway divides to reach each lung
Tumour phân loại khối u theo 4 cấp độ tăng dần về kích thước
Nodes (N)
Nodes (N) - describes how far the tumor has spread to nearby lymph nodes. Nodes can be classified from N0 where there is no spread, to N3 where the cancer has spread to other areas of the body, such as the other side of the chest or collarbone.
Nodes- Nodes (N) describe whether cancer has spread to the lymph nodes. NX means lymph nodes cannot be assessed. N0 means the lymph nodes do not contain cancer cells. N1 means there are cancer cells in the lymph nodes inside the lung or in the lymph nodes in the area where the lungs join the airways. N2 means that there is cancer in the lymph nodes in the center of the chest (mediastinum) on the same side as the affected lung or just below where the windpipe branches to each lung. N3 means there is cancer in the lymph nodes on the opposite side of the chest from the affected lung or on the collarbone or at the top of the lung.
Metastasis
Metastasis means metastasis (M) – answers the question of whether the cancer has spread to other areas of the body outside of the lungs. Metastasis can be classified from M0, i.e. where there is no spread to M1c i.e. where the cancer has spread to other organs of the body and created additional tumors.
Lung cancer can be described by stages depending on how early or advanced the cancer is: early stage (stages I and II), locally advanced (stage III) and lung cancer metastasis (stage IV).
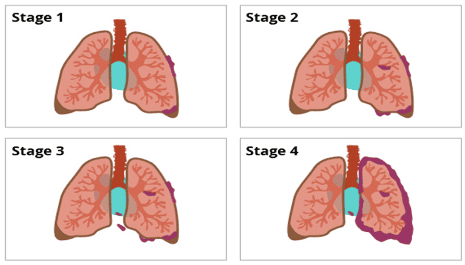
Bốn giai đoạn tiến triển của ung thư phổi
Metastasis (M) describes whether the cancer has spread to another part of the body. There are two stages of metastasis, M0 and M1. M0 means the cancer has not spread to another lobe of the lung or any other part of the body. M1 means the cancer has spread to other areas of the body. It is divided into M1a, M1b and M1c. M1a means there has been cancer in both lungs or there have been areas of cancer in the lining around the lungs or the lining around the heart with fluid around the lungs or heart containing cancer cells, this is called malignant pleural effusion or malignant pericardial effusion. M1b means there is an area of cancer outside the chest in an organ (such as the liver or brain) or a lymph node. M1c means there is more than one area of cancer in one or more organs.
Lung cancer screening is the most effective measure for you to detect and promptly treat lung cancer, protect your health and life. Currently, at Vinmec international general hospitals, there is a lung cancer screening package with many outstanding advantages such as: A team of highly qualified and experienced doctors; Having a full range of specialized facilities to diagnose the disease and stage it before treatment: Endoscopy, CT scan, PET-CT scan, MRI, histopathological diagnosis, gene-cell testing... There is a full range of main cancer treatment methods: surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, stem cell transplant....
If there is a need for consultation and examination at Vinmec Hospitals of the Medical system nationwide, please book an appointment on the website to be served.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: cancerresearchuk.org, iconcancercentre.sg